Continuous audit provides real-time monitoring and analysis of financial transactions, enabling rapid detection of anomalies and enhancing the accuracy of financial reporting. Information systems audit focuses on evaluating the controls, security, and efficiency of IT infrastructure that supports financial systems, ensuring data integrity and compliance. Discover more about how these audit approaches improve organizational transparency and risk management.
Why it is important
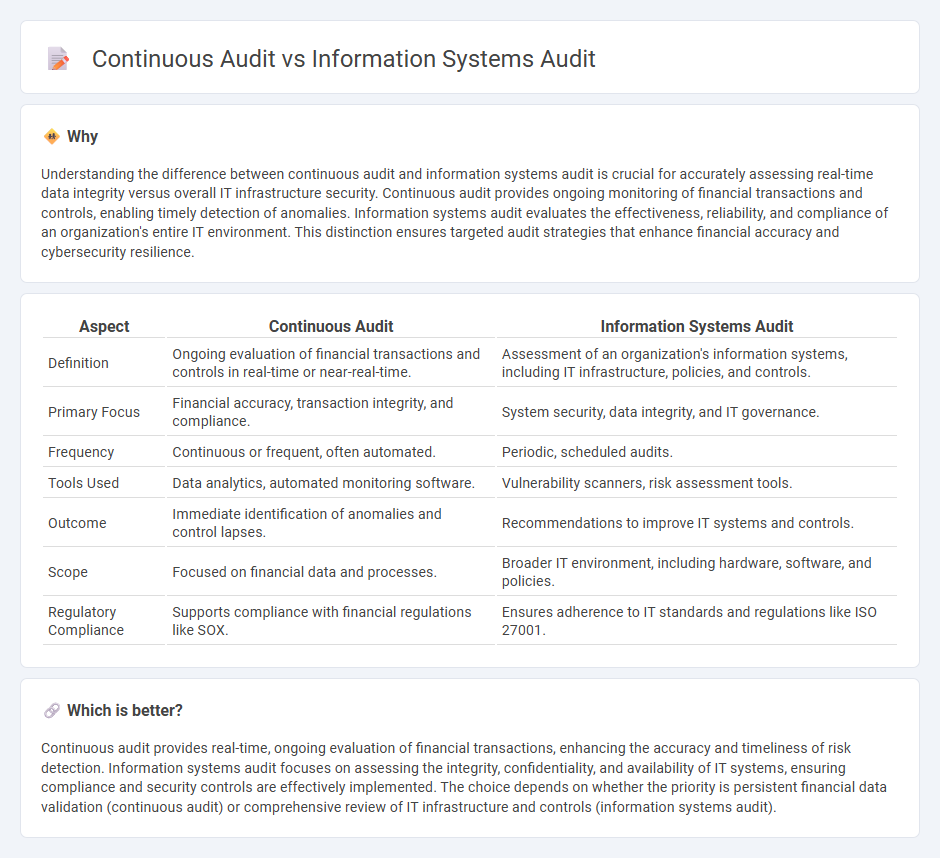
Understanding the difference between continuous audit and information systems audit is crucial for accurately assessing real-time data integrity versus overall IT infrastructure security. Continuous audit provides ongoing monitoring of financial transactions and controls, enabling timely detection of anomalies. Information systems audit evaluates the effectiveness, reliability, and compliance of an organization's entire IT environment. This distinction ensures targeted audit strategies that enhance financial accuracy and cybersecurity resilience.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Continuous Audit | Information Systems Audit |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ongoing evaluation of financial transactions and controls in real-time or near-real-time. | Assessment of an organization's information systems, including IT infrastructure, policies, and controls. |
| Primary Focus | Financial accuracy, transaction integrity, and compliance. | System security, data integrity, and IT governance. |
| Frequency | Continuous or frequent, often automated. | Periodic, scheduled audits. |
| Tools Used | Data analytics, automated monitoring software. | Vulnerability scanners, risk assessment tools. |
| Outcome | Immediate identification of anomalies and control lapses. | Recommendations to improve IT systems and controls. |
| Scope | Focused on financial data and processes. | Broader IT environment, including hardware, software, and policies. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Supports compliance with financial regulations like SOX. | Ensures adherence to IT standards and regulations like ISO 27001. |
Which is better?
Continuous audit provides real-time, ongoing evaluation of financial transactions, enhancing the accuracy and timeliness of risk detection. Information systems audit focuses on assessing the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of IT systems, ensuring compliance and security controls are effectively implemented. The choice depends on whether the priority is persistent financial data validation (continuous audit) or comprehensive review of IT infrastructure and controls (information systems audit).
Connection
Continuous audit leverages automated processes to provide real-time financial data analysis, enhancing the accuracy and timeliness of information systems audits. Information systems audits evaluate the integrity, security, and reliability of an organization's IT infrastructure, which supports continuous audit mechanisms. Both audits are interconnected through their focus on improving risk management, compliance, and operational efficiency via ongoing monitoring and data validation techniques.
Key Terms
**Information Systems Audit:**
Information systems audit evaluates the effectiveness, security, and compliance of an organization's IT infrastructure at specific points in time, ensuring data integrity and system reliability. It involves thorough examination of hardware, software, data management, and IT governance to detect risks and vulnerabilities. Explore comprehensive insights into information systems audit to enhance organizational security and compliance measures.
Control Objectives
Information systems audit primarily evaluates the effectiveness of control objectives through periodic assessments, ensuring compliance and reliability of IT systems at specific intervals. Continuous audit employs automated tools and real-time data analysis to monitor control objectives consistently, enabling prompt detection of anomalies and ongoing assurance over IT processes. Explore further to understand how these approaches impact IT governance and risk management.
IT General Controls (ITGC)
An information systems audit evaluates IT General Controls (ITGC) periodically to ensure the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of information systems, emphasizing compliance and risk mitigation at set intervals. Continuous audit employs automated tools and real-time monitoring to provide ongoing assurance over ITGC, enabling quicker detection and response to control deviations or vulnerabilities. Explore further to understand how integrating continuous audit enhances IT governance and security frameworks.
Source and External Links
Information Systems Auditing | EBSCO Research Starters - This webpage provides an overview of Information Systems (IS) auditing, highlighting its importance in evaluating management controls for security, integrity, and effective use of IT systems.
Information Technology Audit - Wikipedia - This article describes IT audits as examinations of management controls within IT infrastructures to safeguard assets, maintain data integrity, and ensure effective operations.
Information Systems Auditing: Tools and Techniques - This document outlines the audit process for information systems, emphasizing the importance of gathering evidence and preparing audit reports to ensure secure and reliable IT operations.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com