Carbon accounting focuses on measuring and reporting greenhouse gas emissions to help organizations manage their environmental impact and comply with regulations. Fund accounting, primarily used by nonprofits and government entities, tracks and reports financial resources by categorizing funds according to their intended purposes and restrictions. Explore more to understand how these accounting methods serve different organizational goals.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between carbon accounting and fund accounting is crucial for accurately measuring environmental impact versus financial management. Carbon accounting tracks greenhouse gas emissions to support sustainability goals and regulatory compliance. Fund accounting focuses on managing and reporting financial resources within non-profit or governmental organizations. Knowing each ensures precise reporting and decision-making tailored to environmental or fiscal responsibilities.
Comparison Table
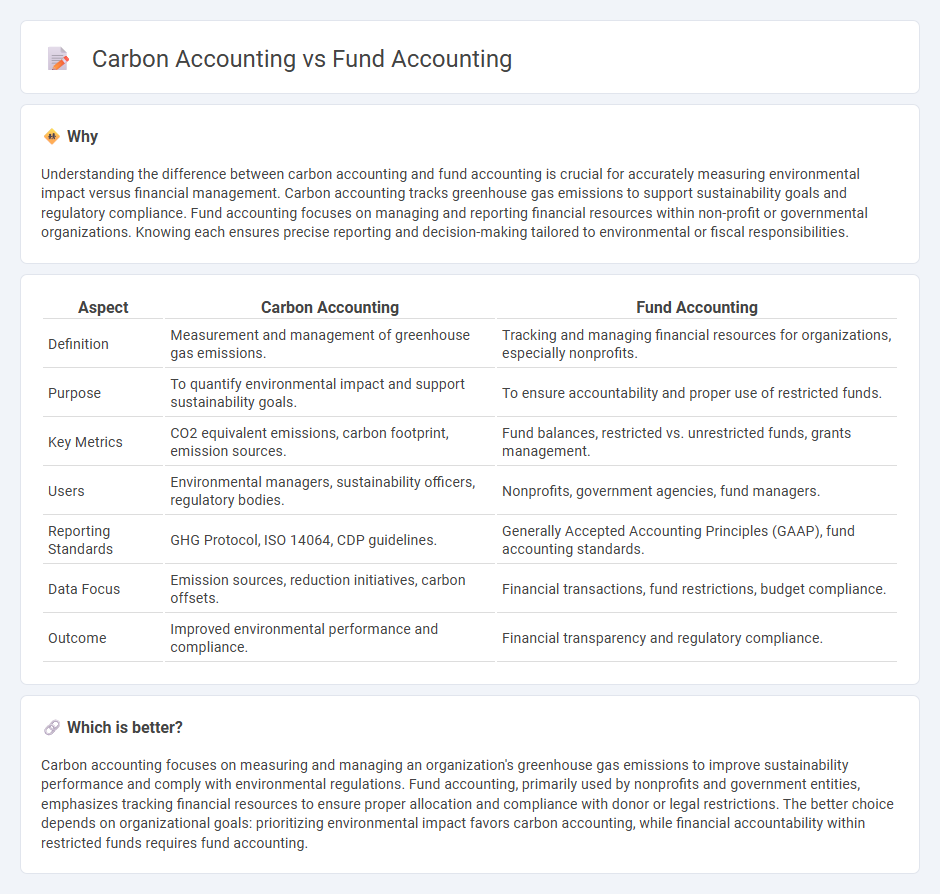
| Aspect | Carbon Accounting | Fund Accounting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Measurement and management of greenhouse gas emissions. | Tracking and managing financial resources for organizations, especially nonprofits. |
| Purpose | To quantify environmental impact and support sustainability goals. | To ensure accountability and proper use of restricted funds. |
| Key Metrics | CO2 equivalent emissions, carbon footprint, emission sources. | Fund balances, restricted vs. unrestricted funds, grants management. |
| Users | Environmental managers, sustainability officers, regulatory bodies. | Nonprofits, government agencies, fund managers. |
| Reporting Standards | GHG Protocol, ISO 14064, CDP guidelines. | Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP), fund accounting standards. |
| Data Focus | Emission sources, reduction initiatives, carbon offsets. | Financial transactions, fund restrictions, budget compliance. |
| Outcome | Improved environmental performance and compliance. | Financial transparency and regulatory compliance. |
Which is better?
Carbon accounting focuses on measuring and managing an organization's greenhouse gas emissions to improve sustainability performance and comply with environmental regulations. Fund accounting, primarily used by nonprofits and government entities, emphasizes tracking financial resources to ensure proper allocation and compliance with donor or legal restrictions. The better choice depends on organizational goals: prioritizing environmental impact favors carbon accounting, while financial accountability within restricted funds requires fund accounting.
Connection
Carbon accounting and fund accounting intersect in organizations focused on environmental sustainability and financial transparency. Carbon accounting tracks greenhouse gas emissions to quantify environmental impact, while fund accounting manages restricted financial resources dedicated to sustainability projects. Integrating these systems ensures precise allocation of funds toward carbon reduction initiatives, enhancing accountability and reporting accuracy for stakeholders.
Key Terms
**Fund Accounting:**
Fund accounting is a specialized accounting system used primarily by non-profit organizations and government entities to track and manage financial resources based on specific purposes or restrictions. It emphasizes accountability and compliance with donor-imposed restrictions, categorizing resources into distinct funds such as general, restricted, and capital project funds. Explore more about fund accounting to understand its principles and applications in managing public and organizational finances effectively.
Fund Balance
Fund accounting emphasizes tracking fund balances to ensure financial resources are allocated and restricted according to specific purposes, promoting transparency and compliance with regulations. Carbon accounting focuses on quantifying greenhouse gas emissions and offsets, integrating environmental data to support sustainability goals and carbon neutrality efforts. Explore the distinctions and synergies between fund balance management and carbon footprint accounting for a comprehensive understanding.
Restricted Funds
Restricted funds in fund accounting require precise tracking to ensure compliance with donor-imposed limitations, emphasizing accountability in financial reporting. Carbon accounting, by contrast, quantifies greenhouse gas emissions associated with specific projects or operations, often aligning emissions data with funding sources to measure environmental impact. Explore the distinctions and applications of these accounting methods to optimize resource management and sustainability reporting.
Source and External Links
What Is Fund Accounting? - Fund accounting is used primarily by nonprofit organizations to track money based on its designated purpose, focusing on accountability rather than profitability by maintaining separate fund accounts for different revenue sources such as grants and donations.
Fund accounting - Wikipedia - Fund accounting is an accounting system designed for recording resources restricted by donors or laws, emphasizing accountability and used by nonprofits and governments, organizing funds as self-balancing accounts classified by restrictions imposed on them.
Fund Accounting 101 : Office of Budgeting - Texas State - Fund accounting classifies all financial resources into self-balancing funds with their own revenues, expenditures, assets, and liabilities, reflecting specific limitations on fund usage and showing how fund balances change based on additions and deductions.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com