Continuous assurance delivers real-time monitoring and analysis of financial transactions using automated controls and data analytics, enhancing accuracy and early fraud detection. Periodic audit involves scheduled examinations of financial statements at specific intervals, providing a comprehensive review of past performance and compliance. Explore how these approaches shape modern accounting practices for improved financial integrity.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between continuous assurance and periodic audit is crucial for maintaining accurate and timely financial reporting. Continuous assurance provides real-time monitoring and risk management, enhancing data reliability throughout the fiscal year. Periodic audits, conducted at specific intervals, offer comprehensive evaluations of financial statements to ensure compliance with accounting standards. Recognizing these distinctions helps organizations optimize internal controls and improve decision-making processes.
Comparison Table
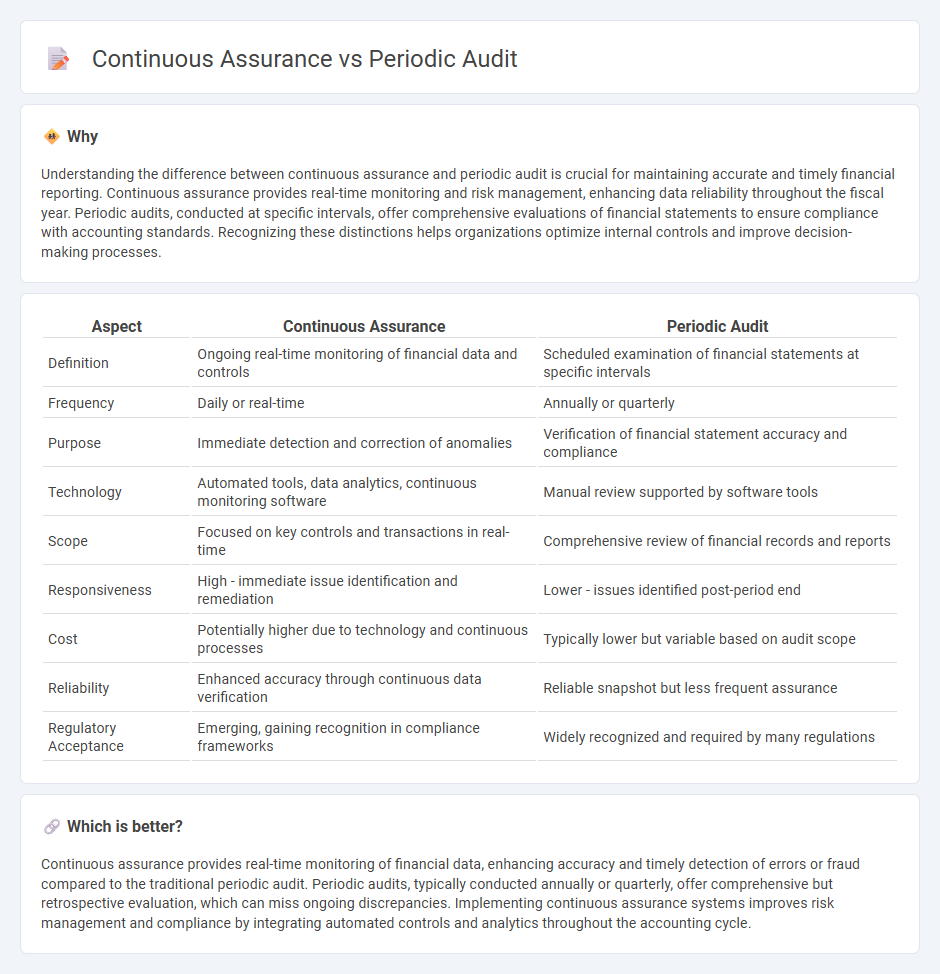
| Aspect | Continuous Assurance | Periodic Audit |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ongoing real-time monitoring of financial data and controls | Scheduled examination of financial statements at specific intervals |
| Frequency | Daily or real-time | Annually or quarterly |
| Purpose | Immediate detection and correction of anomalies | Verification of financial statement accuracy and compliance |
| Technology | Automated tools, data analytics, continuous monitoring software | Manual review supported by software tools |
| Scope | Focused on key controls and transactions in real-time | Comprehensive review of financial records and reports |
| Responsiveness | High - immediate issue identification and remediation | Lower - issues identified post-period end |
| Cost | Potentially higher due to technology and continuous processes | Typically lower but variable based on audit scope |
| Reliability | Enhanced accuracy through continuous data verification | Reliable snapshot but less frequent assurance |
| Regulatory Acceptance | Emerging, gaining recognition in compliance frameworks | Widely recognized and required by many regulations |
Which is better?
Continuous assurance provides real-time monitoring of financial data, enhancing accuracy and timely detection of errors or fraud compared to the traditional periodic audit. Periodic audits, typically conducted annually or quarterly, offer comprehensive but retrospective evaluation, which can miss ongoing discrepancies. Implementing continuous assurance systems improves risk management and compliance by integrating automated controls and analytics throughout the accounting cycle.
Connection
Continuous assurance and periodic audit are interconnected processes that enhance financial accuracy and compliance by providing ongoing monitoring and comprehensive evaluation at specific intervals. Continuous assurance employs real-time data analytics and automated controls to detect anomalies promptly, supporting the periodic audit's in-depth review of financial statements and internal controls. Integrating continuous assurance with periodic audits improves risk management, reduces fraud, and ensures regulatory adherence in accounting practices.
Key Terms
Audit frequency
Periodic audits occur at fixed intervals, typically annually or semi-annually, providing a comprehensive review of financial statements and compliance within a specific timeframe. Continuous assurance involves real-time or near-real-time monitoring of transactions and controls using automated systems, enabling ongoing risk identification and quicker issue resolution. Explore how integrating both approaches can enhance organizational transparency and risk management.
Real-time monitoring
Periodic audits provide snapshots of financial health at specific intervals, while continuous assurance ensures ongoing, real-time monitoring of data integrity and compliance. Real-time monitoring leverages advanced analytics and automated systems to detect discrepancies immediately, reducing risks and enabling proactive decision-making. Explore how integrating continuous assurance can transform your organization's risk management and operational efficiency.
Reporting interval
Periodic audits are typically conducted at fixed intervals, such as annually or quarterly, providing a snapshot of financial or operational compliance during that specific period. Continuous assurance employs real-time data monitoring and automated controls to offer ongoing validation of processes and transactions, significantly reducing the lag between occurrence and reporting. Explore how these differing reporting intervals impact risk management and organizational decision-making.
Source and External Links
Periodic Audit: A Comprehensive Guide to Its Legal Definition and Role - A periodic audit is an evaluation conducted at regular intervals to assess whether an organization is managing its federal awards in compliance with applicable terms and conditions, focusing on overall compliance rather than individual transactions.
What is periodic audit? Simple Definition & Meaning - LSD.Law - A periodic audit is a regular examination of an individual's or organization's financial records, compliance with regulations, and current condition, conducted at set intervals to identify issues and enable corrective action.
Connecting the Dots: Periodic Audit Requirement - Financial Data - Periodic audits are mandated by regulations such as those for managed care plans, requiring states to review and validate financial data to ensure program integrity and compliance with federal standards.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com