Dark data auditing uncovers hidden or unstructured data within an organization to identify risks and compliance issues often overlooked in traditional audits. Forensic accounting involves detailed analysis of financial records to detect fraud, embezzlement, and legal disputes. Explore how these specialized accounting practices enhance financial transparency and security.
Why it is important
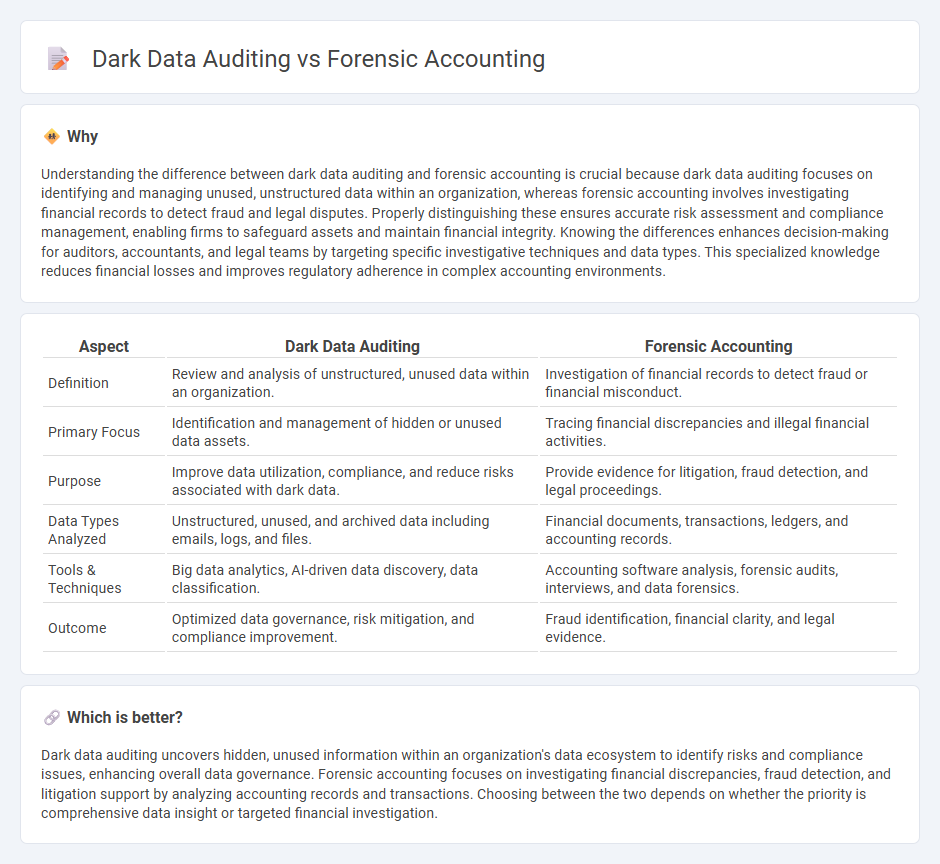
Understanding the difference between dark data auditing and forensic accounting is crucial because dark data auditing focuses on identifying and managing unused, unstructured data within an organization, whereas forensic accounting involves investigating financial records to detect fraud and legal disputes. Properly distinguishing these ensures accurate risk assessment and compliance management, enabling firms to safeguard assets and maintain financial integrity. Knowing the differences enhances decision-making for auditors, accountants, and legal teams by targeting specific investigative techniques and data types. This specialized knowledge reduces financial losses and improves regulatory adherence in complex accounting environments.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Dark Data Auditing | Forensic Accounting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Review and analysis of unstructured, unused data within an organization. | Investigation of financial records to detect fraud or financial misconduct. |
| Primary Focus | Identification and management of hidden or unused data assets. | Tracing financial discrepancies and illegal financial activities. |
| Purpose | Improve data utilization, compliance, and reduce risks associated with dark data. | Provide evidence for litigation, fraud detection, and legal proceedings. |
| Data Types Analyzed | Unstructured, unused, and archived data including emails, logs, and files. | Financial documents, transactions, ledgers, and accounting records. |
| Tools & Techniques | Big data analytics, AI-driven data discovery, data classification. | Accounting software analysis, forensic audits, interviews, and data forensics. |
| Outcome | Optimized data governance, risk mitigation, and compliance improvement. | Fraud identification, financial clarity, and legal evidence. |
Which is better?
Dark data auditing uncovers hidden, unused information within an organization's data ecosystem to identify risks and compliance issues, enhancing overall data governance. Forensic accounting focuses on investigating financial discrepancies, fraud detection, and litigation support by analyzing accounting records and transactions. Choosing between the two depends on whether the priority is comprehensive data insight or targeted financial investigation.
Connection
Dark data auditing uncovers hidden or unstructured data within organizations, providing forensic accountants with critical evidence for fraud detection and financial discrepancy analysis. Forensic accounting utilizes these insights from dark data audits to reconstruct accurate financial records and support legal investigations. The integration of dark data auditing enhances forensic accounting's ability to identify concealed financial manipulations and improve audit accuracy.
Key Terms
Forensic accounting:
Forensic accounting involves the use of accounting, auditing, and investigative skills to examine financial records for fraud, embezzlement, or other financial crimes, often providing crucial evidence in legal disputes. Its core function is to detect, analyze, and prevent financial misconduct by meticulously reviewing transactions and identifying irregularities within accounting systems. Explore more to understand how forensic accounting drives financial transparency and supports legal integrity.
Fraud detection
Forensic accounting systematically examines financial records to uncover fraudulent transactions and anomalies, using techniques such as data analytics and tracing asset flow. Dark data auditing targets unstructured, hidden information within an organization's IT environment that often escapes traditional audits, revealing covert fraud activities through advanced data discovery tools. Explore how integrating forensic accounting with dark data auditing enhances fraud detection accuracy and strengthens organizational security.
Litigation support
Forensic accounting and dark data auditing both play crucial roles in litigation support by uncovering hidden financial evidence and analyzing unstructured or concealed data respectively. Forensic accountants specialize in tracing fraudulent transactions, quantifying damages, and preparing reports for legal proceedings, while dark data auditors focus on extracting and interpreting underlying data sources that traditional audits might overlook. Explore these fields further to understand how they enhance accuracy and integrity in legal disputes.
Source and External Links
Forensic Accounting Career Overview - Forensic accounting involves using accounting and auditing skills to investigate financial crimes such as fraud and embezzlement, support legal proceedings, assess financial risks, and provide expert testimony in court.
What is Forensic Accounting? - NICE Actimize - Forensic accounting is the process of investigating and analyzing financial records to detect and prevent fraud and financial misconduct, often employed by law enforcement to uncover illegal financial activities.
What Is Forensic Accounting? - MVNU - Forensic accountants apply accounting skills to investigate financial crimes, assess damages, and trace illicit funds, often preparing expert reports and assisting in court cases.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com