Cryptocurrency auditing involves verifying blockchain transactions and digital asset holdings to ensure accuracy and compliance with emerging regulations. Tax auditing focuses on assessing financial records and declarations to confirm correct tax reporting and adherence to tax laws. Explore the key differences and best practices in both auditing types for comprehensive financial oversight.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between cryptocurrency auditing and tax auditing is crucial for accurate financial reporting and compliance, as cryptocurrency auditing focuses on verifying blockchain transactions and asset integrity, while tax auditing ensures correct tax liabilities and adherence to regulatory requirements. Cryptocurrency auditing involves evaluating the security, accuracy, and valuation of digital assets using blockchain technology, whereas tax auditing concentrates on assessing declared income, deductions, and tax payments according to tax laws. Distinguishing these audits helps businesses avoid legal penalties, optimize tax strategies, and maintain transparent accounting records. Precise knowledge of each audit's scope supports effective risk management and regulatory compliance in the evolving financial landscape.
Comparison Table
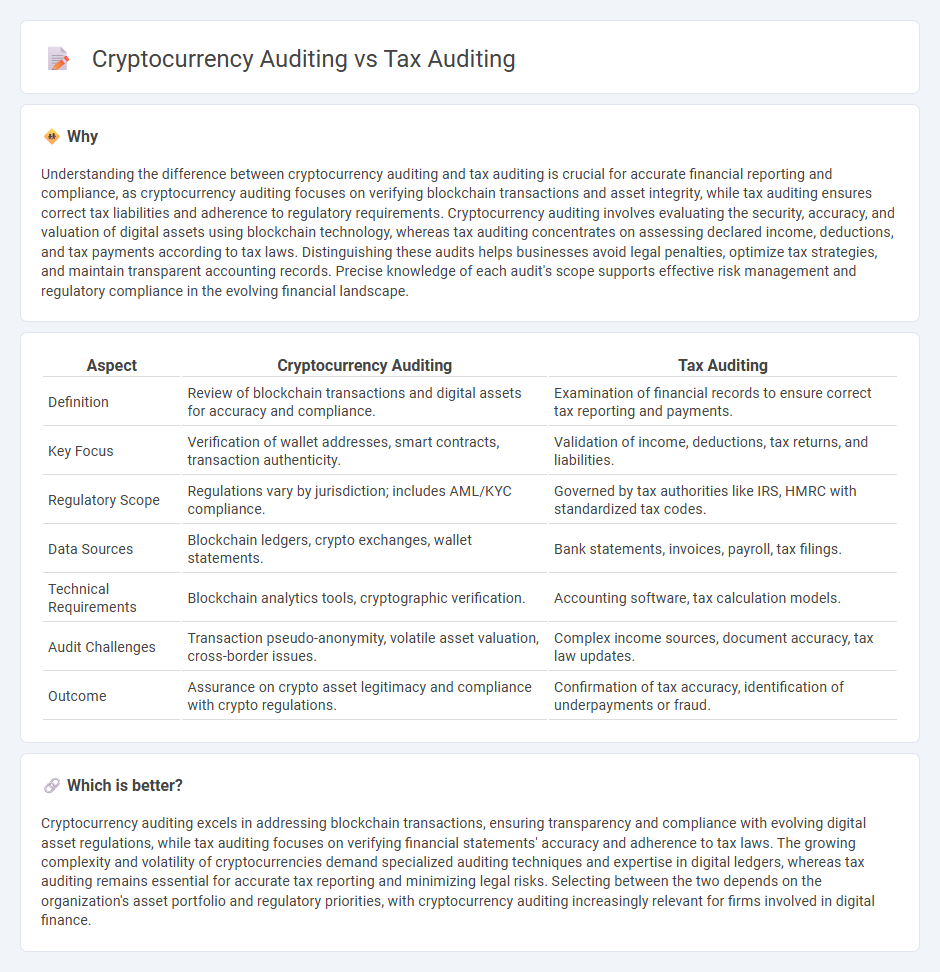
| Aspect | Cryptocurrency Auditing | Tax Auditing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Review of blockchain transactions and digital assets for accuracy and compliance. | Examination of financial records to ensure correct tax reporting and payments. |
| Key Focus | Verification of wallet addresses, smart contracts, transaction authenticity. | Validation of income, deductions, tax returns, and liabilities. |
| Regulatory Scope | Regulations vary by jurisdiction; includes AML/KYC compliance. | Governed by tax authorities like IRS, HMRC with standardized tax codes. |
| Data Sources | Blockchain ledgers, crypto exchanges, wallet statements. | Bank statements, invoices, payroll, tax filings. |
| Technical Requirements | Blockchain analytics tools, cryptographic verification. | Accounting software, tax calculation models. |
| Audit Challenges | Transaction pseudo-anonymity, volatile asset valuation, cross-border issues. | Complex income sources, document accuracy, tax law updates. |
| Outcome | Assurance on crypto asset legitimacy and compliance with crypto regulations. | Confirmation of tax accuracy, identification of underpayments or fraud. |
Which is better?
Cryptocurrency auditing excels in addressing blockchain transactions, ensuring transparency and compliance with evolving digital asset regulations, while tax auditing focuses on verifying financial statements' accuracy and adherence to tax laws. The growing complexity and volatility of cryptocurrencies demand specialized auditing techniques and expertise in digital ledgers, whereas tax auditing remains essential for accurate tax reporting and minimizing legal risks. Selecting between the two depends on the organization's asset portfolio and regulatory priorities, with cryptocurrency auditing increasingly relevant for firms involved in digital finance.
Connection
Cryptocurrency auditing and tax auditing intersect through the verification of digital asset transactions to ensure compliance with tax regulations. Accurate recording of cryptocurrency trades, valuations, and income recognition is essential to prevent tax evasion and regulatory penalties. Tax auditors rely on blockchain data and audit trails to reconcile reported taxable events with actual cryptocurrency holdings and transfers.
Key Terms
**Tax Auditing:**
Tax auditing involves the thorough examination of an individual or business's financial records to ensure compliance with tax laws and accurate reporting of income, deductions, and credits to tax authorities such as the IRS. It focuses on verifying tax returns, detecting discrepancies, preventing evasion, and ensuring the correct amount of tax is paid based on legislation and regulatory standards. Discover key strategies and tools used in tax auditing to protect against tax liabilities and penalties.
Compliance
Tax auditing ensures strict adherence to government tax laws by examining financial records for accuracy and compliance with tax regulations. Cryptocurrency auditing focuses on verifying blockchain transactions, wallet holdings, and smart contract integrity to meet emerging regulatory standards in digital asset management. Explore how these auditing practices intersect and differ in ensuring compliance within evolving financial ecosystems.
Deductible Expenses
Tax auditing rigorously examines deductible expenses to ensure compliance with tax laws, verifying documentation and legitimacy to prevent fraud. Cryptocurrency auditing focuses on tracing digital transactions and validating deductible expenses within blockchain records, addressing unique challenges like volatility and lack of traditional receipts. Explore detailed insights on how deductibles are treated differently in these audit types.
Source and External Links
What Are Tax Audits? - TurboTax Tax Tips & Videos - A tax audit is an examination by the IRS or state tax agency to verify the accuracy of your tax return and ensure the correct amount of tax has been paid, which can be triggered by discrepancies, unusual deductions, or random selection.
IRS audits | Internal Revenue Service - An IRS audit is a review of an individual's or organization's financial records to confirm that information reported on tax returns complies with tax laws and that the correct tax amount has been reported, with selection methods including random checks, computer screening, and related examinations.
Four Types of Tax Audits - RJS LAW - There are four main types of IRS audits: correspondence (by mail), office (in-person at an IRS office), field (at the taxpayer's location), and the Taxpayer Compliance Measurement Program (TCMP), each varying in complexity and scope based on the issues identified in the return.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com