Triple entry accounting enhances transparency by incorporating blockchain technology to create a third, immutable ledger alongside traditional debit and credit entries. Financial accounting focuses on recording, summarizing, and reporting historical financial transactions to provide insights for stakeholders. Explore the differences to understand how triple entry accounting revolutionizes financial accuracy and trust.
Why it is important
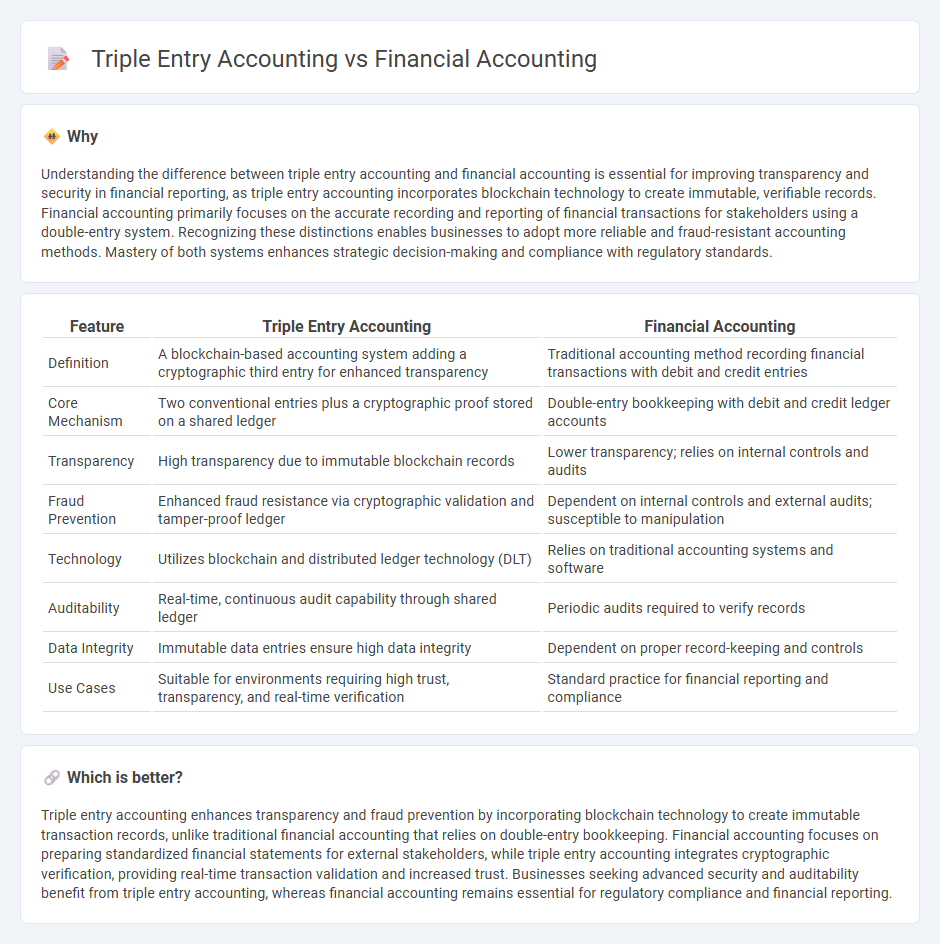
Understanding the difference between triple entry accounting and financial accounting is essential for improving transparency and security in financial reporting, as triple entry accounting incorporates blockchain technology to create immutable, verifiable records. Financial accounting primarily focuses on the accurate recording and reporting of financial transactions for stakeholders using a double-entry system. Recognizing these distinctions enables businesses to adopt more reliable and fraud-resistant accounting methods. Mastery of both systems enhances strategic decision-making and compliance with regulatory standards.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Triple Entry Accounting | Financial Accounting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A blockchain-based accounting system adding a cryptographic third entry for enhanced transparency | Traditional accounting method recording financial transactions with debit and credit entries |
| Core Mechanism | Two conventional entries plus a cryptographic proof stored on a shared ledger | Double-entry bookkeeping with debit and credit ledger accounts |
| Transparency | High transparency due to immutable blockchain records | Lower transparency; relies on internal controls and audits |
| Fraud Prevention | Enhanced fraud resistance via cryptographic validation and tamper-proof ledger | Dependent on internal controls and external audits; susceptible to manipulation |
| Technology | Utilizes blockchain and distributed ledger technology (DLT) | Relies on traditional accounting systems and software |
| Auditability | Real-time, continuous audit capability through shared ledger | Periodic audits required to verify records |
| Data Integrity | Immutable data entries ensure high data integrity | Dependent on proper record-keeping and controls |
| Use Cases | Suitable for environments requiring high trust, transparency, and real-time verification | Standard practice for financial reporting and compliance |
Which is better?
Triple entry accounting enhances transparency and fraud prevention by incorporating blockchain technology to create immutable transaction records, unlike traditional financial accounting that relies on double-entry bookkeeping. Financial accounting focuses on preparing standardized financial statements for external stakeholders, while triple entry accounting integrates cryptographic verification, providing real-time transaction validation and increased trust. Businesses seeking advanced security and auditability benefit from triple entry accounting, whereas financial accounting remains essential for regulatory compliance and financial reporting.
Connection
Triple entry accounting enhances financial accounting by incorporating blockchain technology to record transactions with immutable, cryptographic entries, increasing transparency and accuracy. This system links debits and credits to a third entry--a secure, verifiable record--strengthening audit trails and reducing fraud risks. The integration supports financial accounting by providing real-time verification and enhanced reliability in financial statements and reports.
Key Terms
Double-entry
Double-entry accounting records each transaction with equal debit and credit entries, ensuring accuracy and preventing errors in financial reporting. It forms the foundation of traditional financial accounting by maintaining balanced ledgers that reflect a company's financial position. Explore how triple-entry accounting enhances transparency by incorporating cryptographic verification and blockchain technology.
Triple-entry
Triple-entry accounting enhances traditional financial accounting by introducing a third component: a cryptographic receipt that records each transaction, increasing transparency and security. This innovative method ensures immutable and verifiable records on a distributed ledger, reducing fraud and errors common in double-entry systems. Explore how triple-entry accounting revolutionizes financial record-keeping with blockchain technology.
Blockchain
Financial accounting traditionally records transactions using a double-entry system, balancing debits and credits to reflect a company's financial state, while triple-entry accounting leverages blockchain technology by adding a cryptographic receipt as a third entry, enhancing transparency and security. This third entry creates an immutable, tamper-proof ledger accessible to all participants, reducing fraud and errors in financial reporting. Explore how blockchain-based triple-entry accounting revolutionizes audit trails and financial integrity for deeper insights.
Source and External Links
What Is Financial Accounting? Key Principles, Careers & More - Financial accounting records and summarizes business transactions to prepare standardized financial statements, providing an accurate picture of a company's financial health for investors, lenders, and regulators.
Financial accounting - Wikipedia - Financial accounting systematically records, classifies, and summarizes financial transactions to produce statements that reveal a business's profitability, financial position, and solvency for decision-making by management and stakeholders.
What Is Financial Accounting? - Financial accounting involves documenting, summarizing, and disclosing financial transactions to ensure regulatory compliance, transparency, and support for budgeting, forecasting, and strategic business decisions.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com