Cryptocurrency taxation involves unique challenges due to its decentralized nature, requiring precise tracking of digital asset transactions and valuation at fair market value during exchanges or sales. Foreign currency taxation follows established rules based on gains or losses from currency fluctuations during international transactions, typically governed by specific IRS guidelines. Explore detailed differences and compliance strategies to master accounting for both asset types effectively.
Why it is important
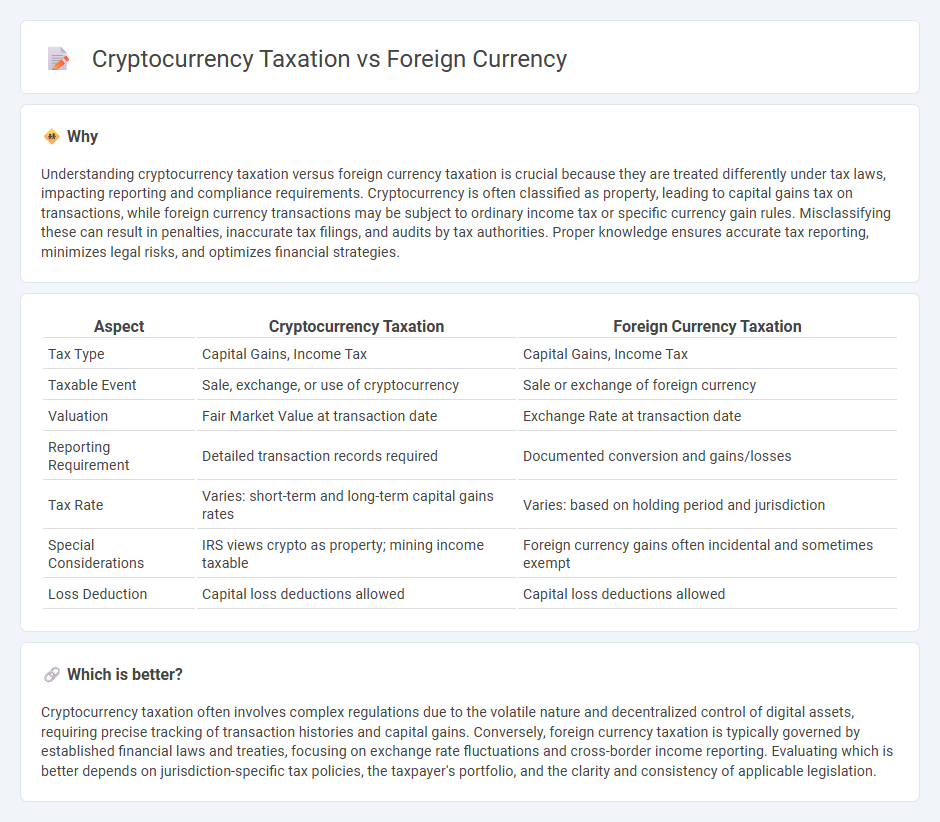
Understanding cryptocurrency taxation versus foreign currency taxation is crucial because they are treated differently under tax laws, impacting reporting and compliance requirements. Cryptocurrency is often classified as property, leading to capital gains tax on transactions, while foreign currency transactions may be subject to ordinary income tax or specific currency gain rules. Misclassifying these can result in penalties, inaccurate tax filings, and audits by tax authorities. Proper knowledge ensures accurate tax reporting, minimizes legal risks, and optimizes financial strategies.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Cryptocurrency Taxation | Foreign Currency Taxation |
|---|---|---|
| Tax Type | Capital Gains, Income Tax | Capital Gains, Income Tax |
| Taxable Event | Sale, exchange, or use of cryptocurrency | Sale or exchange of foreign currency |
| Valuation | Fair Market Value at transaction date | Exchange Rate at transaction date |
| Reporting Requirement | Detailed transaction records required | Documented conversion and gains/losses |
| Tax Rate | Varies: short-term and long-term capital gains rates | Varies: based on holding period and jurisdiction |
| Special Considerations | IRS views crypto as property; mining income taxable | Foreign currency gains often incidental and sometimes exempt |
| Loss Deduction | Capital loss deductions allowed | Capital loss deductions allowed |
Which is better?
Cryptocurrency taxation often involves complex regulations due to the volatile nature and decentralized control of digital assets, requiring precise tracking of transaction histories and capital gains. Conversely, foreign currency taxation is typically governed by established financial laws and treaties, focusing on exchange rate fluctuations and cross-border income reporting. Evaluating which is better depends on jurisdiction-specific tax policies, the taxpayer's portfolio, and the clarity and consistency of applicable legislation.
Connection
Cryptocurrency taxation intersects with foreign currency regulations due to the classification of digital assets as property or foreign currency by many tax authorities, affecting how gains and losses are reported. Transactions involving cryptocurrencies often require conversion to local fiat currency at the time of each exchange, creating complex tax implications similar to foreign currency exchange gains or losses. Understanding these overlaps ensures accurate compliance with tax laws related to both cryptocurrency holdings and foreign currency transactions.
Key Terms
Exchange Rate
Taxation of foreign currency involves calculating gains or losses based on official exchange rates at the time of each transaction, while cryptocurrency taxation often requires tracking market rates from specific exchanges due to high volatility. The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) treats cryptocurrencies as property, necessitating precise record-keeping of exchange rates for each trade to determine taxable events accurately. Explore detailed regulations and best practices to ensure compliance with both foreign currency and cryptocurrency tax laws.
Taxable Event
Foreign currency taxation considers taxable events such as currency exchange, receipt of income in foreign money, and gains realized upon conversion to local currency, often treated as ordinary income or capital gains depending on holding period and purpose. Cryptocurrency taxation classifies taxable events by transactions including trading, spending, mining, and exchanging crypto assets, treated as property with capital gains tax implications. Explore detailed guidelines and jurisdiction-specific rules to understand your obligations fully.
Fair Market Value
Taxation of foreign currency and cryptocurrency hinges on the determination of Fair Market Value (FMV) at the time of each transaction, which influences capital gains and income reporting. While foreign currency transactions often rely on exchange rates from official financial institutions, cryptocurrency FMV depends on market prices from recognized crypto exchanges, adding complexity due to price volatility. Explore the nuances of FMV application and regulatory guidelines in both domains to optimize tax compliance and reporting.
Source and External Links
Currency Converter | Foreign Exchange Rates - Convert between 140 currencies at mid-market rates, track historical performance, and view top currency pairings for USD conversions.
Xe Currency Converter - Live Exchange Rates Today - Get live exchange rates for all major global currencies, use the mid-market rate for conversions, and access data for 170+ currencies.
Currency Converter | Foreign Exchange Rates - Convert all major world currencies, check average bid/ask rates, and access over 31 years of historical FX data for 38,000+ currency pairs.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com