Green ledger emphasizes sustainability by tracking environmental impacts and eco-friendly financial activities, integrating carbon accounting and renewable resource investments. Brown ledger focuses on traditional financial transactions, often highlighting activities linked to fossil fuels and high carbon emissions without prioritizing ecological considerations. Explore how these two approaches transform financial reporting and decision-making.
Why it is important
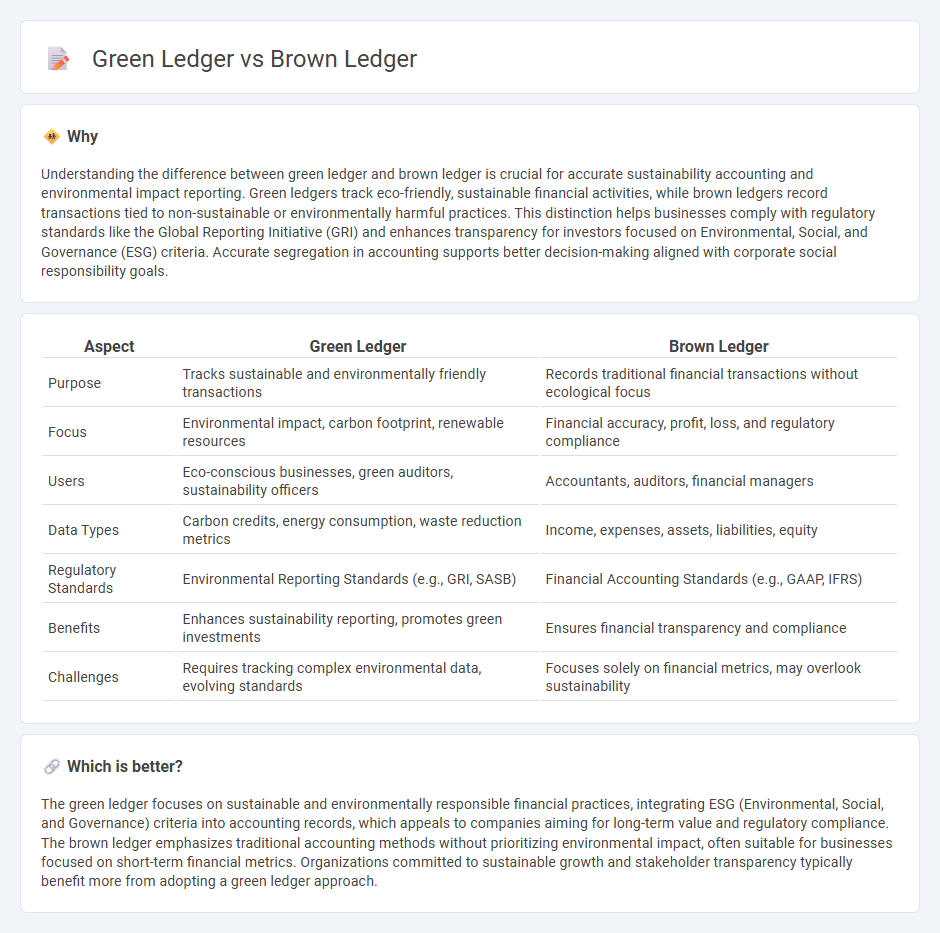
Understanding the difference between green ledger and brown ledger is crucial for accurate sustainability accounting and environmental impact reporting. Green ledgers track eco-friendly, sustainable financial activities, while brown ledgers record transactions tied to non-sustainable or environmentally harmful practices. This distinction helps businesses comply with regulatory standards like the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) and enhances transparency for investors focused on Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) criteria. Accurate segregation in accounting supports better decision-making aligned with corporate social responsibility goals.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Green Ledger | Brown Ledger |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Tracks sustainable and environmentally friendly transactions | Records traditional financial transactions without ecological focus |
| Focus | Environmental impact, carbon footprint, renewable resources | Financial accuracy, profit, loss, and regulatory compliance |
| Users | Eco-conscious businesses, green auditors, sustainability officers | Accountants, auditors, financial managers |
| Data Types | Carbon credits, energy consumption, waste reduction metrics | Income, expenses, assets, liabilities, equity |
| Regulatory Standards | Environmental Reporting Standards (e.g., GRI, SASB) | Financial Accounting Standards (e.g., GAAP, IFRS) |
| Benefits | Enhances sustainability reporting, promotes green investments | Ensures financial transparency and compliance |
| Challenges | Requires tracking complex environmental data, evolving standards | Focuses solely on financial metrics, may overlook sustainability |
Which is better?
The green ledger focuses on sustainable and environmentally responsible financial practices, integrating ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) criteria into accounting records, which appeals to companies aiming for long-term value and regulatory compliance. The brown ledger emphasizes traditional accounting methods without prioritizing environmental impact, often suitable for businesses focused on short-term financial metrics. Organizations committed to sustainable growth and stakeholder transparency typically benefit more from adopting a green ledger approach.
Connection
Green ledger tracks sustainable and environmentally friendly financial transactions, while brown ledger records traditional, non-sustainable activities. Both ledgers are interconnected through integrated accounting systems that categorize and report environmental impact data alongside standard financial metrics. This connection enables businesses to assess overall sustainability performance and regulatory compliance within their accounting framework.
Key Terms
Environmental Accounting
Brown ledger primarily tracks traditional financial transactions without integrating environmental costs or resource consumption, leading to limited visibility of ecological impact. Green ledger incorporates environmental accounting by quantifying ecological footprints, carbon emissions, and sustainability metrics, enabling organizations to measure and manage their environmental performance effectively. Explore how green ledger systems transform corporate accountability and promote sustainable business practices.
Sustainability Reporting
Brown ledger tracks traditional financial metrics, emphasizing capital flows and asset values, often neglecting environmental and social factors crucial for sustainability. Green ledger integrates ecological data and social impact metrics, enabling organizations to measure carbon footprints, resource usage, and community benefits alongside financial performance. Explore further to understand how green ledgers drive actionable insights for sustainable business strategies.
Carbon Footprint
Brown ledger systems primarily track traditional financial transactions with minimal consideration for environmental impact, providing limited data on carbon emissions. Green ledger technology integrates carbon footprint metrics directly into accounting records, enabling businesses to monitor and reduce their environmental impact effectively. Explore the distinct advantages of green ledger solutions for sustainable carbon management and enhanced environmental reporting.
Source and External Links
Terrado Brown Concrete Stacked Stone Ledger Corner - This product features rustic warm brown tones and varied natural shapes, with each piece made of concrete and available in nominal sizes of 4" x Random, thickness ranging from 0.5"-1.5".
Brown Ledger - Offers guidance and support for entrepreneurs and executives to achieve transformative success through planning and execution.
Florence Brown 3-D Stackstone Ledger Stone Sandstone - Features a honed finish, made from sandstone with primary colors of brown, available in different sizes and quoted per square foot basis.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com