ESG assurance evaluates the accuracy and reliability of environmental, social, and governance disclosures to enhance corporate transparency and stakeholder trust. Forensic audits focus on investigating financial records to detect fraud, embezzlement, and regulatory non-compliance within organizations. Explore the distinct roles and methodologies of ESG assurance and forensic audits to strengthen your accounting expertise.
Why it is important
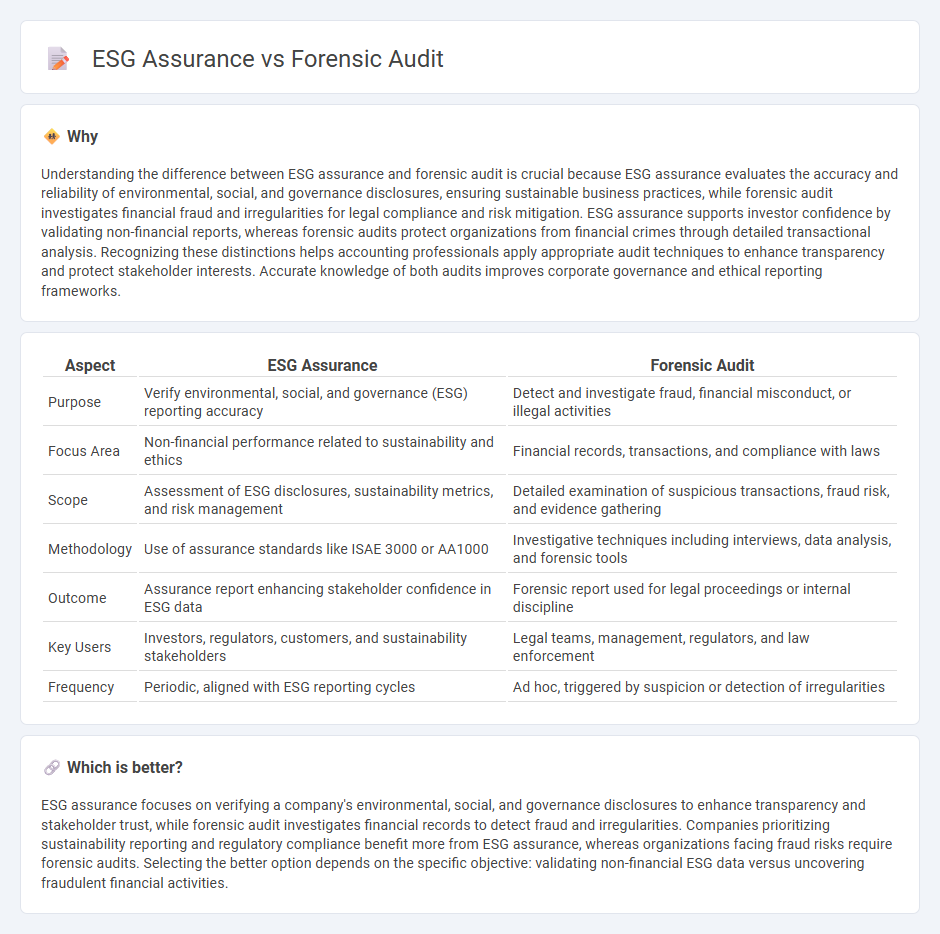
Understanding the difference between ESG assurance and forensic audit is crucial because ESG assurance evaluates the accuracy and reliability of environmental, social, and governance disclosures, ensuring sustainable business practices, while forensic audit investigates financial fraud and irregularities for legal compliance and risk mitigation. ESG assurance supports investor confidence by validating non-financial reports, whereas forensic audits protect organizations from financial crimes through detailed transactional analysis. Recognizing these distinctions helps accounting professionals apply appropriate audit techniques to enhance transparency and protect stakeholder interests. Accurate knowledge of both audits improves corporate governance and ethical reporting frameworks.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | ESG Assurance | Forensic Audit |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Verify environmental, social, and governance (ESG) reporting accuracy | Detect and investigate fraud, financial misconduct, or illegal activities |
| Focus Area | Non-financial performance related to sustainability and ethics | Financial records, transactions, and compliance with laws |
| Scope | Assessment of ESG disclosures, sustainability metrics, and risk management | Detailed examination of suspicious transactions, fraud risk, and evidence gathering |
| Methodology | Use of assurance standards like ISAE 3000 or AA1000 | Investigative techniques including interviews, data analysis, and forensic tools |
| Outcome | Assurance report enhancing stakeholder confidence in ESG data | Forensic report used for legal proceedings or internal discipline |
| Key Users | Investors, regulators, customers, and sustainability stakeholders | Legal teams, management, regulators, and law enforcement |
| Frequency | Periodic, aligned with ESG reporting cycles | Ad hoc, triggered by suspicion or detection of irregularities |
Which is better?
ESG assurance focuses on verifying a company's environmental, social, and governance disclosures to enhance transparency and stakeholder trust, while forensic audit investigates financial records to detect fraud and irregularities. Companies prioritizing sustainability reporting and regulatory compliance benefit more from ESG assurance, whereas organizations facing fraud risks require forensic audits. Selecting the better option depends on the specific objective: validating non-financial ESG data versus uncovering fraudulent financial activities.
Connection
ESG assurance and forensic audit intersect by enhancing financial transparency and mitigating risks related to environmental, social, and governance factors. Forensic audits investigate potential fraud or misstatements within ESG reports, ensuring accuracy and compliance with regulatory standards. This connection supports investors and stakeholders in making informed decisions based on reliable, ethically verified accounting information.
Key Terms
Forensic audit:
Forensic audit involves a detailed examination of financial records to detect fraud, embezzlement, or other financial misconduct, utilizing techniques such as data analytics, interviews, and document verification. It plays a critical role in legal proceedings and regulatory compliance by providing credible evidence for dispute resolution and risk mitigation. Learn more about how forensic audits enhance transparency and corporate accountability.
Fraud detection
Forensic audits utilize detailed financial analysis and investigative techniques to detect and prevent fraud, focusing on uncovering manipulations, misappropriations, and financial discrepancies. ESG assurance emphasizes validation of environmental, social, and governance data, ensuring transparency and accuracy but does not primarily target fraudulent financial activities. Discover how integrating forensic audit processes enhances fraud detection within ESG frameworks.
Evidence collection
Forensic audit centers on systematic evidence collection to detect fraud, financial misstatements, and legal breaches, employing detailed transaction analysis and interview techniques. ESG assurance emphasizes gathering evidence on environmental, social, and governance data to validate sustainability claims, often relying on third-party verification and standardized reporting criteria. Explore our comprehensive insights to understand the nuanced methodologies behind forensic audits and ESG assurance processes.
Source and External Links
What is a Forensic Audit and Do I Need One? - DHJJ - This webpage provides an overview of forensic audits, including their purpose and the steps involved in conducting them.
Forensic Audit Guide - Definition, Steps, Reasons - This guide defines forensic audits and outlines the reasons and steps involved in these specialized investigations, often used to gather evidence for legal proceedings.
Forensic accounting - Wikipedia - This article discusses forensic accounting as a specialty area of accounting focused on investigating financial crimes and translating complex financial data into understandable terms.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com