Environmental Social Governance (ESG) accounting focuses on measuring and reporting a company's sustainability practices, social impact, and governance structures to provide transparency for stakeholders. Integrated reporting combines financial and non-financial information, offering a holistic view of an organization's strategy, performance, and value creation over time. Explore how these frameworks enhance corporate accountability and stakeholder communication.
Why it is important
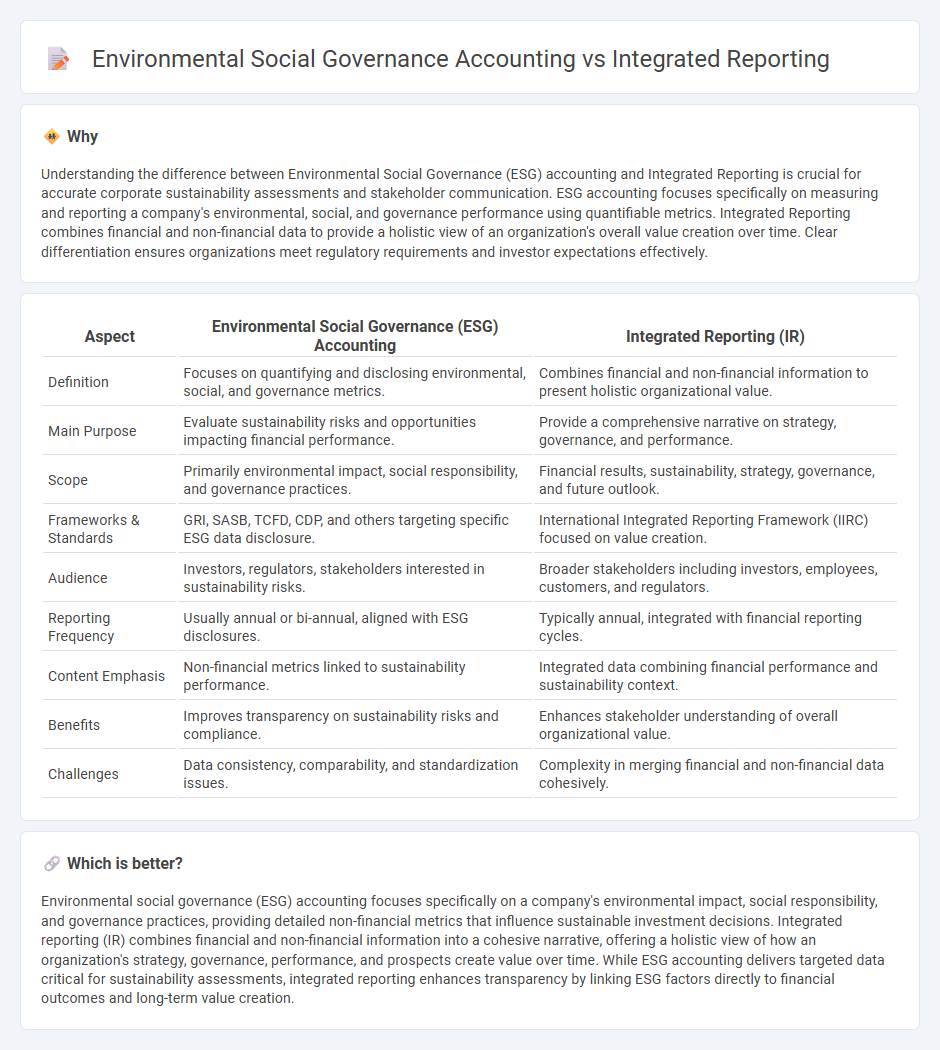
Understanding the difference between Environmental Social Governance (ESG) accounting and Integrated Reporting is crucial for accurate corporate sustainability assessments and stakeholder communication. ESG accounting focuses specifically on measuring and reporting a company's environmental, social, and governance performance using quantifiable metrics. Integrated Reporting combines financial and non-financial data to provide a holistic view of an organization's overall value creation over time. Clear differentiation ensures organizations meet regulatory requirements and investor expectations effectively.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Environmental Social Governance (ESG) Accounting | Integrated Reporting (IR) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Focuses on quantifying and disclosing environmental, social, and governance metrics. | Combines financial and non-financial information to present holistic organizational value. |
| Main Purpose | Evaluate sustainability risks and opportunities impacting financial performance. | Provide a comprehensive narrative on strategy, governance, and performance. |
| Scope | Primarily environmental impact, social responsibility, and governance practices. | Financial results, sustainability, strategy, governance, and future outlook. |
| Frameworks & Standards | GRI, SASB, TCFD, CDP, and others targeting specific ESG data disclosure. | International Integrated Reporting Framework (IIRC) focused on value creation. |
| Audience | Investors, regulators, stakeholders interested in sustainability risks. | Broader stakeholders including investors, employees, customers, and regulators. |
| Reporting Frequency | Usually annual or bi-annual, aligned with ESG disclosures. | Typically annual, integrated with financial reporting cycles. |
| Content Emphasis | Non-financial metrics linked to sustainability performance. | Integrated data combining financial performance and sustainability context. |
| Benefits | Improves transparency on sustainability risks and compliance. | Enhances stakeholder understanding of overall organizational value. |
| Challenges | Data consistency, comparability, and standardization issues. | Complexity in merging financial and non-financial data cohesively. |
Which is better?
Environmental social governance (ESG) accounting focuses specifically on a company's environmental impact, social responsibility, and governance practices, providing detailed non-financial metrics that influence sustainable investment decisions. Integrated reporting (IR) combines financial and non-financial information into a cohesive narrative, offering a holistic view of how an organization's strategy, governance, performance, and prospects create value over time. While ESG accounting delivers targeted data critical for sustainability assessments, integrated reporting enhances transparency by linking ESG factors directly to financial outcomes and long-term value creation.
Connection
Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) accounting integrates sustainability metrics into financial statements, providing stakeholders with comprehensive insights on corporate responsibility and risk management. Integrated reporting combines financial and ESG data to present a holistic view of organizational performance, enhancing transparency and long-term value creation. This connection facilitates informed decision-making by linking sustainability practices directly to financial outcomes and strategic objectives.
Key Terms
Value Creation
Integrated reporting combines financial and non-financial data to present a holistic view of an organization's value creation over time, emphasizing connectivity between strategy, governance, performance, and prospects. Environmental Social Governance (ESG) accounting specifically measures a company's impact and performance on environmental sustainability, social responsibility, and ethical governance, often used by investors to assess long-term risks and opportunities. Explore how integrating both approaches enhances transparent value creation and strategic decision-making in modern business frameworks.
Sustainability
Integrated reporting combines financial and non-financial data into a holistic view of organizational performance, emphasizing long-term value creation through environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors. Environmental Social Governance accounting specifically focuses on measuring and managing a company's ESG risks and impacts, providing a framework for sustainable business practices and stakeholder accountability. Explore our comprehensive resources to understand how these frameworks drive sustainability and corporate responsibility.
Stakeholder Engagement
Integrated reporting emphasizes comprehensive disclosure, combining financial, environmental, social, and governance factors to provide a holistic view of an organization's value creation, thereby enhancing stakeholder engagement through transparency and accountability. Environmental Social Governance (ESG) accounting specifically measures and reports environmental and social impacts alongside governance practices, targeting investors and stakeholders interested in sustainable and ethical business conduct. Explore how each framework uniquely facilitates impactful stakeholder communication and drives sustainability performance.
Source and External Links
Integrated Reporting: Building a Holistic Picture - Integrated reporting connects financial and non-financial data to provide a comprehensive view of an organization's performance, emphasizing integrated thinking and the interdependencies of different capitals to enhance transparency, decision-making, and stakeholder engagement.
Integrated reporting - Integrated reporting is a concise communication that explains how an organization's strategy, governance, performance, and prospects create value over time, combining financial and non-financial information primarily to benefit investors and support long-term capital allocation decisions.
What is Integrated Reporting? - Integrated reporting provides a streamlined view of a company's financial and ESG factors, demonstrating how these interact with business strategy and governance to create sustainable value, thereby fostering transparency, accountability, and trust among stakeholders.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com