Forensic analytics involves the use of advanced data analysis techniques to detect fraud, financial misconduct, and irregularities within an organization's financial records. External audits focus on providing an independent evaluation of a company's financial statements to ensure accuracy and compliance with accounting standards. Discover how forensic analytics and external audits differ in objectives, methodologies, and impact on financial assurance.
Why it is important
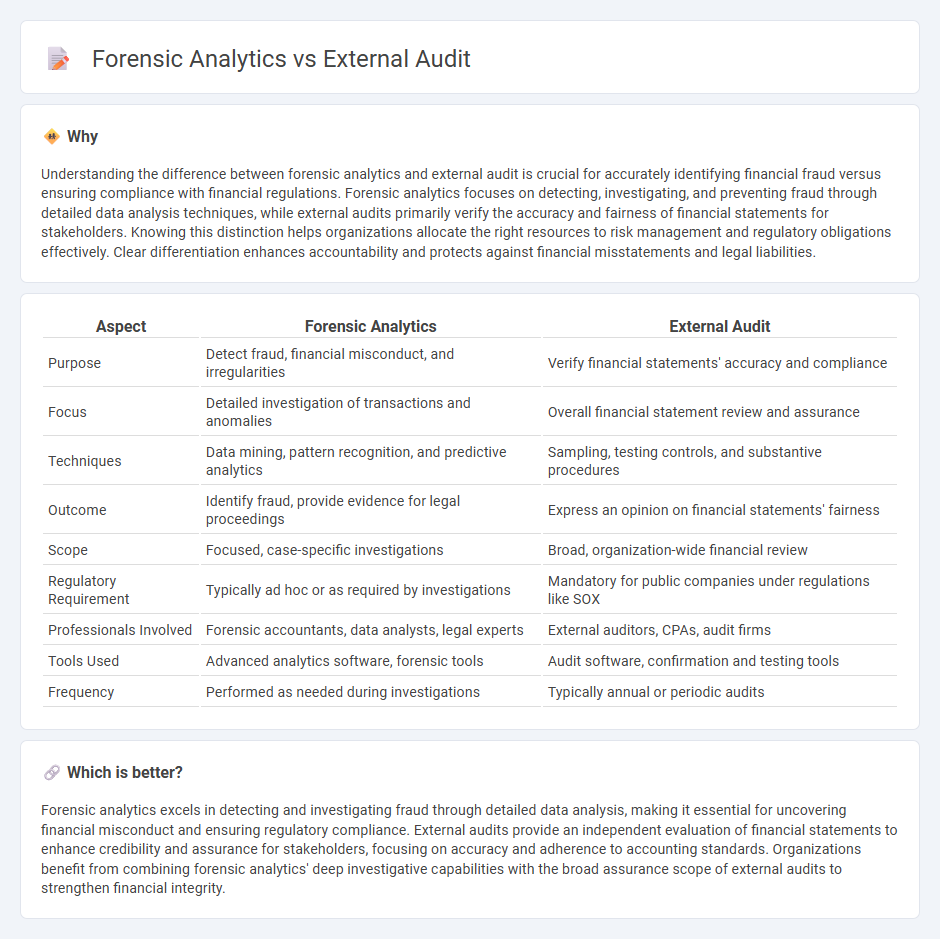
Understanding the difference between forensic analytics and external audit is crucial for accurately identifying financial fraud versus ensuring compliance with financial regulations. Forensic analytics focuses on detecting, investigating, and preventing fraud through detailed data analysis techniques, while external audits primarily verify the accuracy and fairness of financial statements for stakeholders. Knowing this distinction helps organizations allocate the right resources to risk management and regulatory obligations effectively. Clear differentiation enhances accountability and protects against financial misstatements and legal liabilities.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Forensic Analytics | External Audit |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Detect fraud, financial misconduct, and irregularities | Verify financial statements' accuracy and compliance |
| Focus | Detailed investigation of transactions and anomalies | Overall financial statement review and assurance |
| Techniques | Data mining, pattern recognition, and predictive analytics | Sampling, testing controls, and substantive procedures |
| Outcome | Identify fraud, provide evidence for legal proceedings | Express an opinion on financial statements' fairness |
| Scope | Focused, case-specific investigations | Broad, organization-wide financial review |
| Regulatory Requirement | Typically ad hoc or as required by investigations | Mandatory for public companies under regulations like SOX |
| Professionals Involved | Forensic accountants, data analysts, legal experts | External auditors, CPAs, audit firms |
| Tools Used | Advanced analytics software, forensic tools | Audit software, confirmation and testing tools |
| Frequency | Performed as needed during investigations | Typically annual or periodic audits |
Which is better?
Forensic analytics excels in detecting and investigating fraud through detailed data analysis, making it essential for uncovering financial misconduct and ensuring regulatory compliance. External audits provide an independent evaluation of financial statements to enhance credibility and assurance for stakeholders, focusing on accuracy and adherence to accounting standards. Organizations benefit from combining forensic analytics' deep investigative capabilities with the broad assurance scope of external audits to strengthen financial integrity.
Connection
Forensic analytics enhances external audits by providing detailed examination of financial data to detect fraud, errors, and anomalies. External auditors use forensic analytics tools to improve the accuracy and reliability of their audit findings, ensuring compliance with regulatory standards. This integration strengthens the overall assurance process by identifying risks that traditional audit techniques might overlook.
Key Terms
**External audit**: Opinion, Financial statements, Independence
External audits provide an independent opinion on the fairness and accuracy of an organization's financial statements, ensuring compliance with accounting standards and regulatory requirements. The auditor's independence is crucial, maintaining objectivity and avoiding conflicts of interest to uphold the credibility of the audit report. Learn more about the role of external auditors and how their assessments safeguard financial transparency.
**Forensic analytics**: Fraud detection, Data mining, Evidence
Forensic analytics leverages advanced data mining techniques to detect and investigate fraudulent activities by analyzing large datasets for unusual patterns or anomalies. It provides critical evidence that supports legal proceedings and financial audits by uncovering hidden relationships and inconsistencies within transaction records. Explore how forensic analytics enhances fraud detection and strengthens audit accuracy.
Independence
External audits prioritize independence to provide objective assurance on financial statements, safeguarding stakeholders' trust by adhering to strict regulatory standards. Forensic analytics, while also valuing independence, focuses more on detecting fraud and irregularities through in-depth data examination and investigative techniques. Explore more about how independence shapes the effectiveness of these two crucial financial examination methods.
Source and External Links
Understanding the Purpose and Benefits of External Audits - Concur - An external audit involves an independent auditor evaluating a company's financial statements, internal controls, and processes to provide assurance on the accuracy of financial reporting and highlight areas for improvement.
What is an External Audit - GoCardless - An external audit is conducted by an independent, qualified firm to verify the financial statements of a business, ensuring they are free from material misstatement and comply with applicable laws, typically as a legal requirement.
External Audit vs. Internal Audit: What's the Difference? - The main goal of an external audit is to provide an unbiased, independent opinion on the fairness and reliability of a company's financial statements for stakeholders such as shareholders and regulators.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com