Algorithmic compliance in accounting involves automated systems that ensure transactions adhere strictly to predefined regulatory standards, reducing human error and enhancing accuracy. Exception reporting focuses on identifying and flagging transactions that deviate from normal patterns or compliance rules, enabling targeted reviews and risk management. Explore further to understand how these approaches optimize financial accuracy and regulatory adherence.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between Algorithmic Compliance and Exception Reporting in accounting is crucial for accurate financial monitoring and fraud detection. Algorithmic compliance ensures transactions follow predefined rules and standards, minimizing errors and regulatory risks. Exception reporting identifies anomalies or deviations from standard patterns, highlighting potential issues for further investigation. Mastery of both concepts enhances audit efficiency and ensures robust internal controls.
Comparison Table
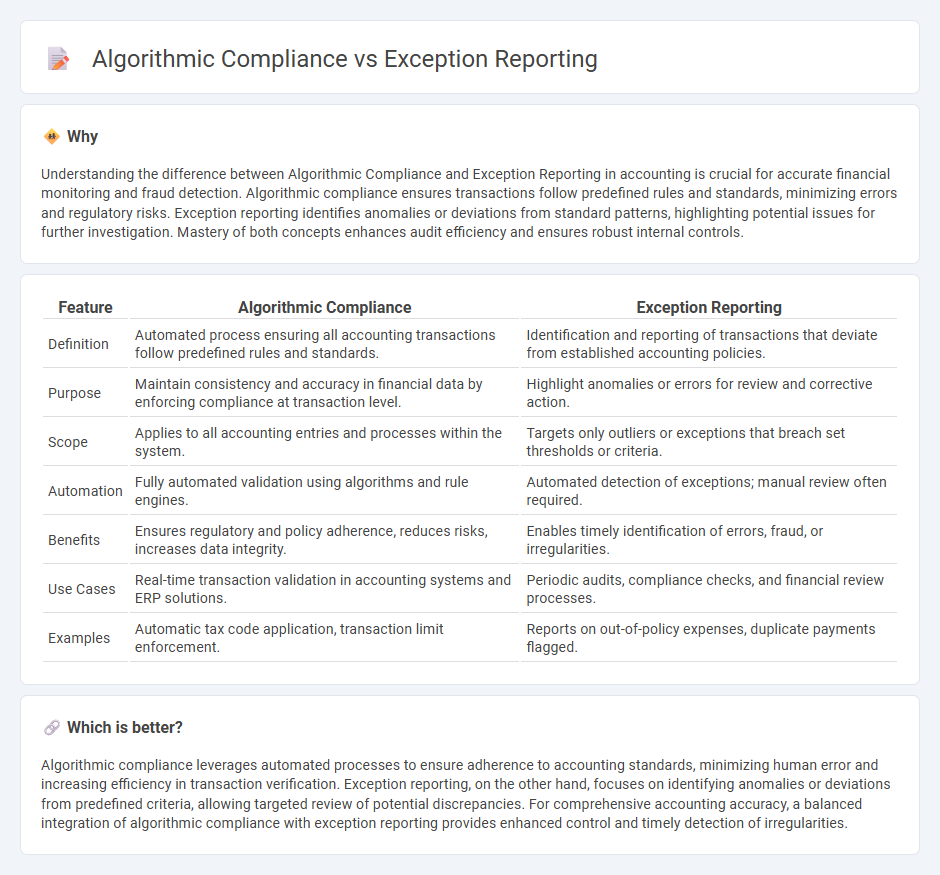
| Feature | Algorithmic Compliance | Exception Reporting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Automated process ensuring all accounting transactions follow predefined rules and standards. | Identification and reporting of transactions that deviate from established accounting policies. |
| Purpose | Maintain consistency and accuracy in financial data by enforcing compliance at transaction level. | Highlight anomalies or errors for review and corrective action. |
| Scope | Applies to all accounting entries and processes within the system. | Targets only outliers or exceptions that breach set thresholds or criteria. |
| Automation | Fully automated validation using algorithms and rule engines. | Automated detection of exceptions; manual review often required. |
| Benefits | Ensures regulatory and policy adherence, reduces risks, increases data integrity. | Enables timely identification of errors, fraud, or irregularities. |
| Use Cases | Real-time transaction validation in accounting systems and ERP solutions. | Periodic audits, compliance checks, and financial review processes. |
| Examples | Automatic tax code application, transaction limit enforcement. | Reports on out-of-policy expenses, duplicate payments flagged. |
Which is better?
Algorithmic compliance leverages automated processes to ensure adherence to accounting standards, minimizing human error and increasing efficiency in transaction verification. Exception reporting, on the other hand, focuses on identifying anomalies or deviations from predefined criteria, allowing targeted review of potential discrepancies. For comprehensive accounting accuracy, a balanced integration of algorithmic compliance with exception reporting provides enhanced control and timely detection of irregularities.
Connection
Algorithmic compliance automates the monitoring of financial transactions against regulatory standards, enabling real-time identification of discrepancies. Exception reporting highlights anomalies or deviations flagged by algorithmic checks, allowing accountants to focus on irregularities requiring manual review. Together, they streamline audit processes and enhance accuracy in financial reporting.
Key Terms
Variance Analysis
Exception reporting highlights deviations from expected outcomes by flagging instances that fall outside predetermined thresholds, enabling targeted investigations. Algorithmic compliance enforces adherence to rules through automated processes that minimize human error and maintain consistency in data handling. Explore deeper insights on how integrating exception reporting and algorithmic compliance enhances variance analysis effectiveness.
Audit Trail
Exception reporting highlights deviations from standard procedures by flagging anomalies, ensuring clear audit trail documentation of non-compliance incidents. Algorithmic compliance automates adherence to predefined rules, creating a detailed, immutable audit trail that supports transparent verification processes. Explore the nuances of audit trail management to optimize regulatory compliance and risk mitigation strategies.
Threshold Breach
Exception reporting highlights instances when transaction values exceed predefined limits, triggering alerts for manual review to prevent errors or fraud. Algorithmic compliance automates monitoring by continuously tracking threshold breaches across numerous parameters, ensuring real-time adherence to regulatory standards. Explore how integrating exception reporting with algorithmic compliance enhances risk management and operational efficiency.
Source and External Links
Exception report definition - AccountingTools - An exception report is a document that highlights instances where actual performance deviates significantly from expectations, usually negatively, focusing management attention on areas needing immediate action, such as budget overruns or inventory mismatches.
Exception Reports for Banks & Credit Unions - How Are They Used? - Exception reports in banks list missing or expired documents and can be tracked via spreadsheets, in-house databases, or automated software that flags critical issues and routes reports to staff for resolution.
Exception Reports - LeapFrogBI - Exception reports identify out-of-range or unexpected situations, often used in reconciliations to find data discrepancies requiring corrective actions to resolve underlying problems.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com