Integrated ESG reporting combines environmental, social, and governance metrics into a comprehensive framework, offering a holistic view of corporate sustainability and ethical impact. Environmental reporting, on the other hand, focuses solely on ecological factors such as carbon emissions, resource usage, and environmental compliance. Explore the advantages and applications of integrated ESG reporting to understand its growing importance in accounting and corporate transparency.
Why it is important
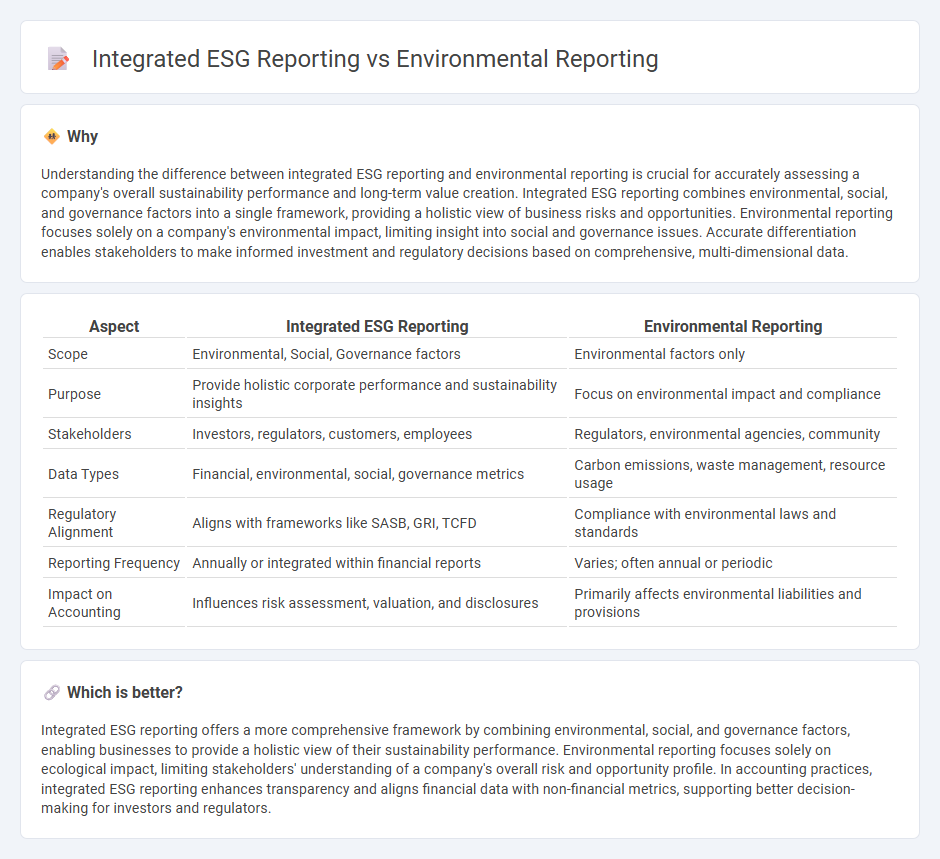
Understanding the difference between integrated ESG reporting and environmental reporting is crucial for accurately assessing a company's overall sustainability performance and long-term value creation. Integrated ESG reporting combines environmental, social, and governance factors into a single framework, providing a holistic view of business risks and opportunities. Environmental reporting focuses solely on a company's environmental impact, limiting insight into social and governance issues. Accurate differentiation enables stakeholders to make informed investment and regulatory decisions based on comprehensive, multi-dimensional data.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Integrated ESG Reporting | Environmental Reporting |
|---|---|---|
| Scope | Environmental, Social, Governance factors | Environmental factors only |
| Purpose | Provide holistic corporate performance and sustainability insights | Focus on environmental impact and compliance |
| Stakeholders | Investors, regulators, customers, employees | Regulators, environmental agencies, community |
| Data Types | Financial, environmental, social, governance metrics | Carbon emissions, waste management, resource usage |
| Regulatory Alignment | Aligns with frameworks like SASB, GRI, TCFD | Compliance with environmental laws and standards |
| Reporting Frequency | Annually or integrated within financial reports | Varies; often annual or periodic |
| Impact on Accounting | Influences risk assessment, valuation, and disclosures | Primarily affects environmental liabilities and provisions |
Which is better?
Integrated ESG reporting offers a more comprehensive framework by combining environmental, social, and governance factors, enabling businesses to provide a holistic view of their sustainability performance. Environmental reporting focuses solely on ecological impact, limiting stakeholders' understanding of a company's overall risk and opportunity profile. In accounting practices, integrated ESG reporting enhances transparency and aligns financial data with non-financial metrics, supporting better decision-making for investors and regulators.
Connection
Integrated ESG reporting and environmental reporting are closely connected through their shared focus on sustainability metrics that impact financial performance and stakeholder value. Both reporting frameworks use data on carbon emissions, energy consumption, and resource management to provide transparency on a company's environmental impact within the broader context of Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) factors. This connection enables accountants to deliver comprehensive assessments that align environmental risks and opportunities with financial disclosures and corporate strategy.
Key Terms
Sustainability Disclosure
Environmental reporting primarily details a company's impact on air, water, and waste management, focusing on regulatory compliance and environmental performance metrics. Integrated ESG reporting combines environmental, social, and governance factors into a comprehensive framework, highlighting sustainability disclosure that aligns with global standards such as the GRI, SASB, and TCFD. Explore how integrated ESG reporting enhances transparency and drives sustainable business strategies.
Triple Bottom Line
Environmental reporting centers on disclosing an organization's ecological impact, emphasizing resource use, emissions, and compliance with environmental regulations. Integrated ESG reporting expands this scope by incorporating environmental, social, and governance factors into a comprehensive framework aligned with the Triple Bottom Line, highlighting sustainability, social responsibility, and ethical management. Explore the nuances of integrated ESG reporting to enhance your understanding of sustainable business practices.
Materiality Assessment
Environmental reporting primarily captures data related to a company's environmental impact, such as carbon emissions, waste management, and resource usage, often based on regulatory compliance. Integrated ESG reporting extends beyond environmental metrics to include social and governance factors, emphasizing how these interconnected issues affect long-term business value through a rigorous Materiality Assessment. Explore the critical differences in Materiality Assessment approaches to enhance your understanding of ESG reporting frameworks.
Source and External Links
Sustainability 101: What is environmental reporting? - Cisco Blogs - Environmental reporting is how companies disclose their environmental impact and progress on sustainability to stakeholders, moving increasingly from voluntary to mandatory reporting to ensure transparency, accountability, and comparability of sustainability data.
What is Social and Environmental Reporting? - ESG | The Report - Environmental reporting involves assessing and communicating a company's impact on the environment, including carbon emissions, water usage, and waste management, setting measurable goals, and tracking progress to improve sustainability performance and build stakeholder trust.
ESG reporting and preparation of a Sustainability Report - PwC - Sustainability reports communicate a company's environmental, social, and governance impacts to help stakeholders understand risks and opportunities, with growing importance due to increasing regulatory requirements and investor demands.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com