Digital asset reporting involves tracking and disclosing transactions related to cryptocurrencies, NFTs, and blockchain-based assets, emphasizing transparency and accuracy in valuation. Securities reporting focuses on the regulation, compliance, and financial disclosure requirements of stocks, bonds, and other traditional investment instruments. Explore how evolving regulations impact digital and securities reporting to optimize your accounting practices.
Why it is important
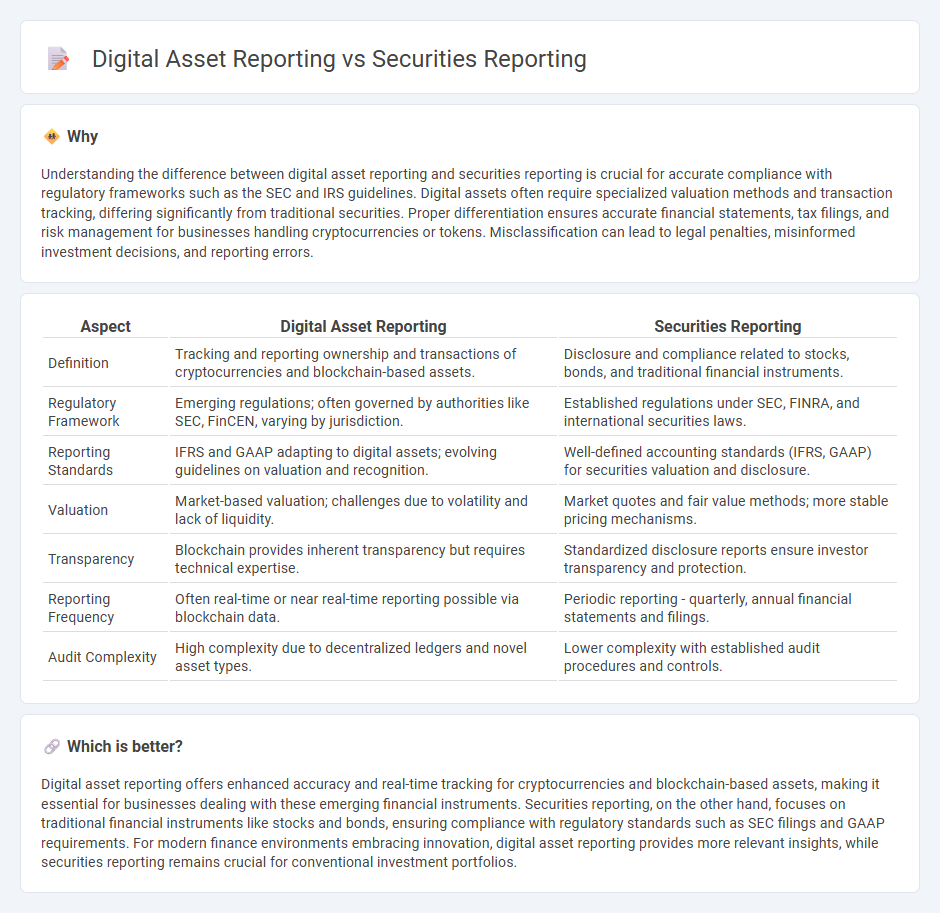
Understanding the difference between digital asset reporting and securities reporting is crucial for accurate compliance with regulatory frameworks such as the SEC and IRS guidelines. Digital assets often require specialized valuation methods and transaction tracking, differing significantly from traditional securities. Proper differentiation ensures accurate financial statements, tax filings, and risk management for businesses handling cryptocurrencies or tokens. Misclassification can lead to legal penalties, misinformed investment decisions, and reporting errors.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Digital Asset Reporting | Securities Reporting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Tracking and reporting ownership and transactions of cryptocurrencies and blockchain-based assets. | Disclosure and compliance related to stocks, bonds, and traditional financial instruments. |
| Regulatory Framework | Emerging regulations; often governed by authorities like SEC, FinCEN, varying by jurisdiction. | Established regulations under SEC, FINRA, and international securities laws. |
| Reporting Standards | IFRS and GAAP adapting to digital assets; evolving guidelines on valuation and recognition. | Well-defined accounting standards (IFRS, GAAP) for securities valuation and disclosure. |
| Valuation | Market-based valuation; challenges due to volatility and lack of liquidity. | Market quotes and fair value methods; more stable pricing mechanisms. |
| Transparency | Blockchain provides inherent transparency but requires technical expertise. | Standardized disclosure reports ensure investor transparency and protection. |
| Reporting Frequency | Often real-time or near real-time reporting possible via blockchain data. | Periodic reporting - quarterly, annual financial statements and filings. |
| Audit Complexity | High complexity due to decentralized ledgers and novel asset types. | Lower complexity with established audit procedures and controls. |
Which is better?
Digital asset reporting offers enhanced accuracy and real-time tracking for cryptocurrencies and blockchain-based assets, making it essential for businesses dealing with these emerging financial instruments. Securities reporting, on the other hand, focuses on traditional financial instruments like stocks and bonds, ensuring compliance with regulatory standards such as SEC filings and GAAP requirements. For modern finance environments embracing innovation, digital asset reporting provides more relevant insights, while securities reporting remains crucial for conventional investment portfolios.
Connection
Digital asset reporting and securities reporting intersect through regulatory frameworks that govern transparency, valuation, and transaction disclosures for both traditional and digital financial instruments. Blockchain technology enhances the accuracy and traceability of digital asset records, aligning with securities reporting requirements under agencies like the SEC and FINRA. Integrating these reporting standards ensures compliance, reduces fraud risks, and provides investors with consistent, reliable information across asset classes.
Key Terms
**Securities Reporting:**
Securities reporting involves the disclosure of financial information related to stocks, bonds, and other traditional investment instruments, ensuring compliance with regulations from bodies such as the SEC (Securities and Exchange Commission). This reporting mandates detailed forms like 10-Ks and 10-Qs to provide transparency on ownership, transactions, and financial health. Explore further to understand how securities reporting frameworks evolve alongside digital asset regulations.
Fair Value Measurement
Fair value measurement in securities reporting adheres to established accounting standards such as GAAP or IFRS, emphasizing reliable market data and observable inputs for valuation. In digital asset reporting, fair value determination faces challenges due to market volatility, limited liquidity, and evolving regulatory frameworks, often requiring specialized valuation models and frequent reassessments. Explore deeper insights on fair value measurement disparities and best practices in both securities and digital asset contexts.
Disclosure Requirements
Securities reporting mandates comprehensive disclosure of financial statements, risk factors, and insider transactions to ensure transparency and investor protection. Digital asset reporting emphasizes transparency in blockchain transactions, asset valuation, and custody solutions, reflecting the unique characteristics of decentralized finance. Explore the evolving regulatory landscape to understand the critical distinctions in disclosure requirements.
Source and External Links
Exchange Act Reporting and Registration - SEC.gov - SEC rules mandate companies file annual reports on Form 10-K and quarterly reports on Form 10-Q, along with current reports on Form 8-K for certain significant events, with all filings made electronically and publicly available through the SEC's EDGAR system.
The Laws That Govern the Securities Industry | Investor.gov - Securities reporting involves disclosure of essential financial and business information through registration to enable informed investor decisions, with few exemptions, under laws such as the Securities Act of 1933.
Public Company SEC Reporting Requirements | Anthony L.G., PLLC - Public companies with securities registered under the Exchange Act must regularly file reports including Forms 10-K, 10-Q, 8-K, and others to ensure transparency and keep shareholders and markets informed.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com