Zero trust accounting rejects assumptions about transaction validity, continuously verifying every financial entry to prevent fraud and errors. Double-entry accounting maintains balanced records by recording equal debits and credits, ensuring accuracy and traceability in ledgers. Explore the key differences and benefits of zero trust versus double-entry accounting to optimize your financial security.
Why it is important
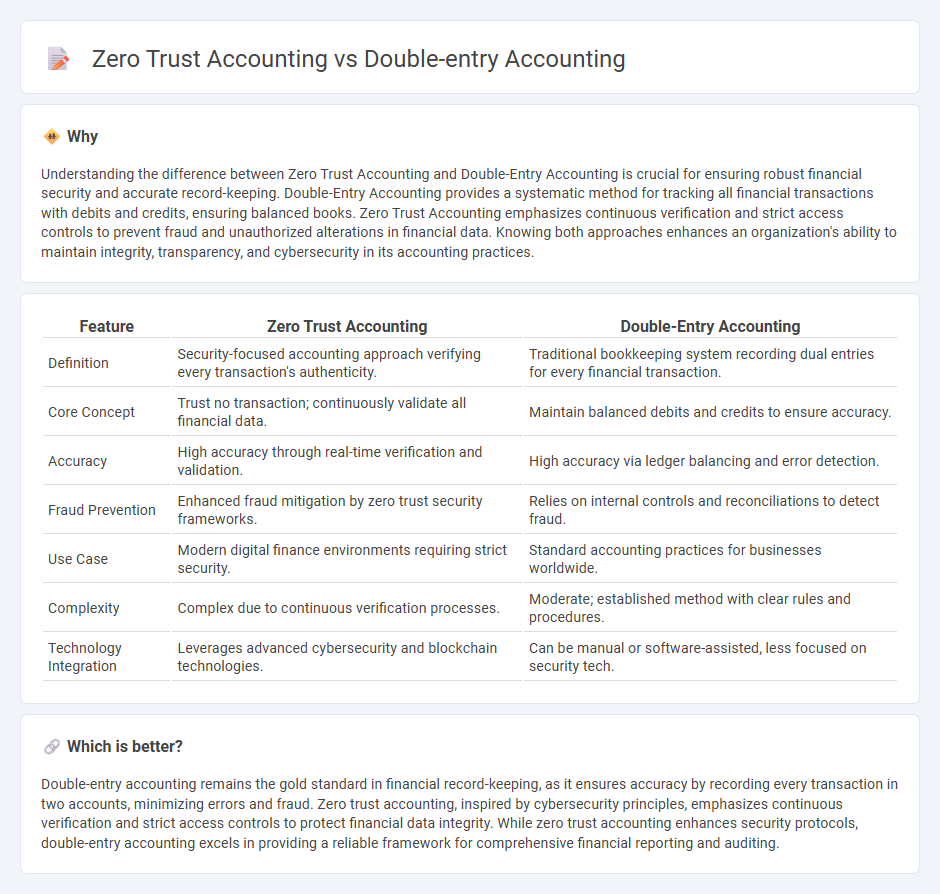
Understanding the difference between Zero Trust Accounting and Double-Entry Accounting is crucial for ensuring robust financial security and accurate record-keeping. Double-Entry Accounting provides a systematic method for tracking all financial transactions with debits and credits, ensuring balanced books. Zero Trust Accounting emphasizes continuous verification and strict access controls to prevent fraud and unauthorized alterations in financial data. Knowing both approaches enhances an organization's ability to maintain integrity, transparency, and cybersecurity in its accounting practices.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Zero Trust Accounting | Double-Entry Accounting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Security-focused accounting approach verifying every transaction's authenticity. | Traditional bookkeeping system recording dual entries for every financial transaction. |
| Core Concept | Trust no transaction; continuously validate all financial data. | Maintain balanced debits and credits to ensure accuracy. |
| Accuracy | High accuracy through real-time verification and validation. | High accuracy via ledger balancing and error detection. |
| Fraud Prevention | Enhanced fraud mitigation by zero trust security frameworks. | Relies on internal controls and reconciliations to detect fraud. |
| Use Case | Modern digital finance environments requiring strict security. | Standard accounting practices for businesses worldwide. |
| Complexity | Complex due to continuous verification processes. | Moderate; established method with clear rules and procedures. |
| Technology Integration | Leverages advanced cybersecurity and blockchain technologies. | Can be manual or software-assisted, less focused on security tech. |
Which is better?
Double-entry accounting remains the gold standard in financial record-keeping, as it ensures accuracy by recording every transaction in two accounts, minimizing errors and fraud. Zero trust accounting, inspired by cybersecurity principles, emphasizes continuous verification and strict access controls to protect financial data integrity. While zero trust accounting enhances security protocols, double-entry accounting excels in providing a reliable framework for comprehensive financial reporting and auditing.
Connection
Zero trust accounting enhances the security and accuracy of double-entry accounting by implementing strict verification protocols for every transaction, minimizing the risk of fraud and errors. Double-entry accounting relies on the principle of recording equal and opposite entries in two accounts, ensuring balanced financial statements, while zero trust frameworks enforce continuous validation of these entries. Integrating zero trust models with double-entry accounting strengthens internal controls and supports regulatory compliance through meticulous audit trails.
Key Terms
**Double-entry accounting:**
Double-entry accounting is a systematic method that records each financial transaction in two accounts, debits and credits, ensuring accuracy and balance in financial statements. This approach provides a clear audit trail, enhances fraud detection, and improves financial transparency for businesses. Discover more about how double-entry accounting strengthens financial management and compliance.
Debit and Credit
Double-entry accounting records each transaction as both a debit and a credit, ensuring balanced ledgers and accurate financial tracking. Zero trust accounting applies rigorous access controls to debit and credit entries, minimizing fraud risks by verifying every access attempt regardless of network location. Explore how integrating zero trust principles can enhance the reliability and security of traditional double-entry accounting systems.
Ledger
Double-entry accounting records transactions in two accounts, ensuring balanced ledgers and accurate financial statements. Zero trust accounting leverages blockchain technology to create decentralized, tamper-proof ledgers that enhance security and transparency. Explore how integrating zero trust principles with traditional ledger systems can revolutionize financial integrity.
Source and External Links
Double-Entry Accounting: What It Is and How It Works - Double-entry accounting records every financial transaction in at least two accounts, using debits and credits to keep the accounting equation balanced.
Double-Entry Accounting: What It Is and Why It Matters - This bookkeeping system requires one debit and one credit entry per transaction, tracking assets, liabilities, equity, revenue, and expenses for a complete picture of business finances.
Double Entry - Overview, History, How It Works, Example - Double-entry bookkeeping ensures every debit entry has a corresponding credit entry, maintaining balance using the equation Assets = Liabilities + Shareholders' Equity.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com