Deep learning forecasting leverages complex neural networks to identify intricate patterns and nonlinear relationships in large financial datasets, outperforming traditional regression analysis in predictive accuracy. Regression analysis, a foundational statistical method, estimates relationships between variables using defined linear models, making it simpler but sometimes less adaptive to complex accounting trends. Explore deeper insights into how these methodologies revolutionize financial forecasting accuracy and decision-making.
Why it is important
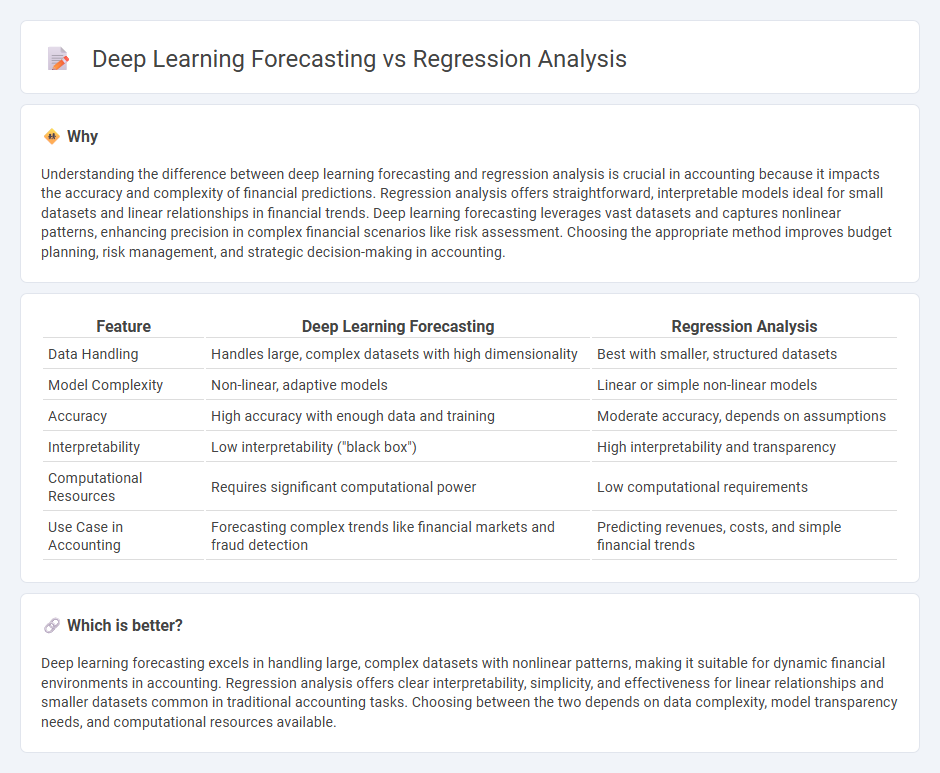
Understanding the difference between deep learning forecasting and regression analysis is crucial in accounting because it impacts the accuracy and complexity of financial predictions. Regression analysis offers straightforward, interpretable models ideal for small datasets and linear relationships in financial trends. Deep learning forecasting leverages vast datasets and captures nonlinear patterns, enhancing precision in complex financial scenarios like risk assessment. Choosing the appropriate method improves budget planning, risk management, and strategic decision-making in accounting.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Deep Learning Forecasting | Regression Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| Data Handling | Handles large, complex datasets with high dimensionality | Best with smaller, structured datasets |
| Model Complexity | Non-linear, adaptive models | Linear or simple non-linear models |
| Accuracy | High accuracy with enough data and training | Moderate accuracy, depends on assumptions |
| Interpretability | Low interpretability ("black box") | High interpretability and transparency |
| Computational Resources | Requires significant computational power | Low computational requirements |
| Use Case in Accounting | Forecasting complex trends like financial markets and fraud detection | Predicting revenues, costs, and simple financial trends |
Which is better?
Deep learning forecasting excels in handling large, complex datasets with nonlinear patterns, making it suitable for dynamic financial environments in accounting. Regression analysis offers clear interpretability, simplicity, and effectiveness for linear relationships and smaller datasets common in traditional accounting tasks. Choosing between the two depends on data complexity, model transparency needs, and computational resources available.
Connection
Deep learning forecasting leverages complex neural networks to identify patterns in large financial datasets, enhancing predictive accuracy in accounting tasks such as revenue estimation and risk assessment. Regression analysis serves as a foundational statistical method within this context, enabling the modeling of relationships between financial variables and serving as a benchmark for evaluating deep learning models. Integrating regression frameworks into deep learning architectures improves interpretability and performance in accounting forecasts.
Key Terms
Predictors (Independent Variables)
Regression analysis typically relies on a limited number of well-defined predictors or independent variables that have a clear relationship with the dependent variable, making it ideal for interpretability and hypothesis testing. Deep learning forecasting utilizes large datasets with numerous predictors, including complex and nonlinear relationships among variables, to capture intricate patterns and improve prediction accuracy. Explore the strengths and applications of both methods to determine the best fit for your forecasting needs.
Overfitting
Regression analysis offers a straightforward approach to forecasting with clear assumptions and less risk of overfitting when dealing with smaller datasets. Deep learning forecasting can capture complex patterns but is more prone to overfitting, especially without sufficient data or proper regularization techniques. Explore further to understand the best practices in managing overfitting for each method.
Model Interpretability
Regression analysis offers high model interpretability by providing clear coefficients that explain relationships between variables, making it ideal for understanding underlying data patterns. Deep learning forecasting delivers superior predictive accuracy in complex datasets but suffers from low interpretability due to its intricate neural network structures. Explore further to understand which approach best suits your forecasting needs based on transparency and performance.
Source and External Links
What Is Regression Analysis in Business Analytics? - Regression analysis is a statistical method used to determine the structure of the relationship between variables and to forecast one variable based on others, commonly visualized as a best-fit line in a scatter plot.
Regression Analysis - Corporate Finance Institute - Regression analysis includes methods such as linear and nonlinear regression to estimate relationships between dependent and independent variables, used extensively in finance and other fields to model and predict outcomes.
Regression Analysis: The Complete Guide - Qualtrics - This method analyzes factors influencing an outcome and identifies key variables, helping businesses forecast performance by modeling relationships through regression lines and statistical software.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com