Supply chain finance optimizes working capital by enabling buyers to extend payment terms while suppliers receive early payments through third-party financing, improving cash flow across the supply chain. Invoice factoring involves selling outstanding invoices to a factoring company at a discount, providing immediate liquidity but potentially higher costs and loss of control over collections. Discover detailed comparisons to determine which financing solution best supports your business needs.
Why it is important
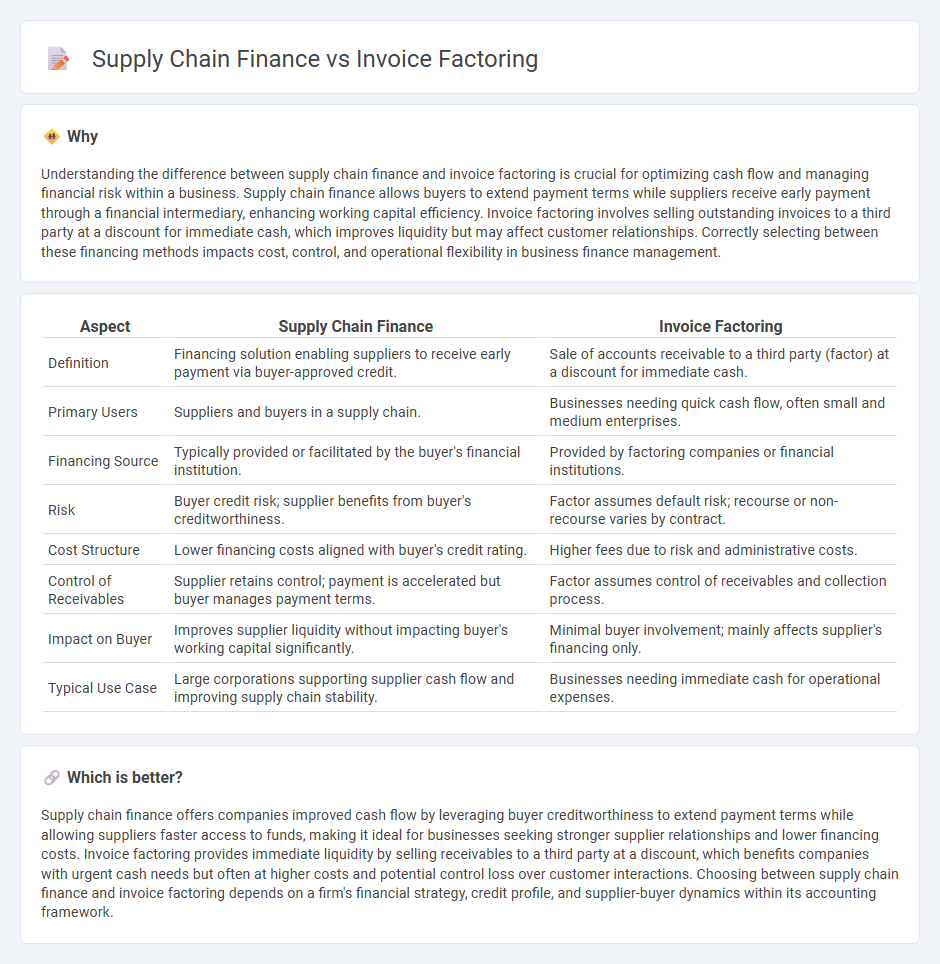
Understanding the difference between supply chain finance and invoice factoring is crucial for optimizing cash flow and managing financial risk within a business. Supply chain finance allows buyers to extend payment terms while suppliers receive early payment through a financial intermediary, enhancing working capital efficiency. Invoice factoring involves selling outstanding invoices to a third party at a discount for immediate cash, which improves liquidity but may affect customer relationships. Correctly selecting between these financing methods impacts cost, control, and operational flexibility in business finance management.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Supply Chain Finance | Invoice Factoring |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Financing solution enabling suppliers to receive early payment via buyer-approved credit. | Sale of accounts receivable to a third party (factor) at a discount for immediate cash. |
| Primary Users | Suppliers and buyers in a supply chain. | Businesses needing quick cash flow, often small and medium enterprises. |
| Financing Source | Typically provided or facilitated by the buyer's financial institution. | Provided by factoring companies or financial institutions. |
| Risk | Buyer credit risk; supplier benefits from buyer's creditworthiness. | Factor assumes default risk; recourse or non-recourse varies by contract. |
| Cost Structure | Lower financing costs aligned with buyer's credit rating. | Higher fees due to risk and administrative costs. |
| Control of Receivables | Supplier retains control; payment is accelerated but buyer manages payment terms. | Factor assumes control of receivables and collection process. |
| Impact on Buyer | Improves supplier liquidity without impacting buyer's working capital significantly. | Minimal buyer involvement; mainly affects supplier's financing only. |
| Typical Use Case | Large corporations supporting supplier cash flow and improving supply chain stability. | Businesses needing immediate cash for operational expenses. |
Which is better?
Supply chain finance offers companies improved cash flow by leveraging buyer creditworthiness to extend payment terms while allowing suppliers faster access to funds, making it ideal for businesses seeking stronger supplier relationships and lower financing costs. Invoice factoring provides immediate liquidity by selling receivables to a third party at a discount, which benefits companies with urgent cash needs but often at higher costs and potential control loss over customer interactions. Choosing between supply chain finance and invoice factoring depends on a firm's financial strategy, credit profile, and supplier-buyer dynamics within its accounting framework.
Connection
Supply chain finance optimizes working capital by allowing suppliers to receive early payment on invoices through financial intermediaries, closely linking it to invoice factoring, where businesses sell invoices at a discount for immediate cash flow. Both methods improve liquidity and reduce credit risk by converting accounts receivable into cash quickly. Integrating supply chain finance with invoice factoring streamlines transaction processes, enhances financial stability, and supports seamless operational efficiency in accounting.
Key Terms
Receivables
Invoice factoring accelerates cash flow by selling receivables to a third party at a discount, providing immediate liquidity without waiting for customer payments. Supply chain finance optimizes working capital by enabling buyers to extend payment terms while suppliers receive early payment, typically facilitated by a financial institution. Explore the advantages and suitability of each solution to enhance your receivables management.
Liquidity
Invoice factoring provides immediate cash flow by selling accounts receivable to a third party at a discount, accelerating liquidity for businesses with outstanding invoices. Supply chain finance, also known as reverse factoring, optimizes working capital by enabling buyers to extend payment terms while suppliers receive early payments through a financial intermediary. Explore more about how these financing solutions enhance liquidity and improve cash management.
Risk transfer
Invoice factoring transfers credit risk from the seller to the factoring company, which assumes the responsibility of collecting payments from customers and managing bad debts. Supply chain finance primarily mitigates risk by optimizing payment terms and enhancing liquidity for suppliers, but the buyer retains credit risk since they often guarantee payment. Explore how each financing method manages risk to determine the best fit for your business needs.
Source and External Links
Your Complete Guide to Invoice Factoring - This guide explains how invoice factoring works by selling outstanding invoices to a third-party company in exchange for cash to improve cash flow.
Invoice Factoring: What It Is and How It Works - It details the process of invoice factoring, including selling invoices at a discount and the fees involved in the transaction.
What is invoice factoring? - This definition outlines the process of selling unpaid invoices to a third party for immediate cash, typically receiving 70-90% of the invoice value upfront.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com