Decentralized ledger accounting distributes transaction records across multiple nodes, enhancing transparency and security while reducing the risk of data manipulation. Centralized ledger accounting consolidates all financial records within a single system controlled by a central authority, simplifying management but increasing vulnerability to errors and fraud. Explore the intricacies of both systems to understand their impact on financial accuracy and trust.
Why it is important
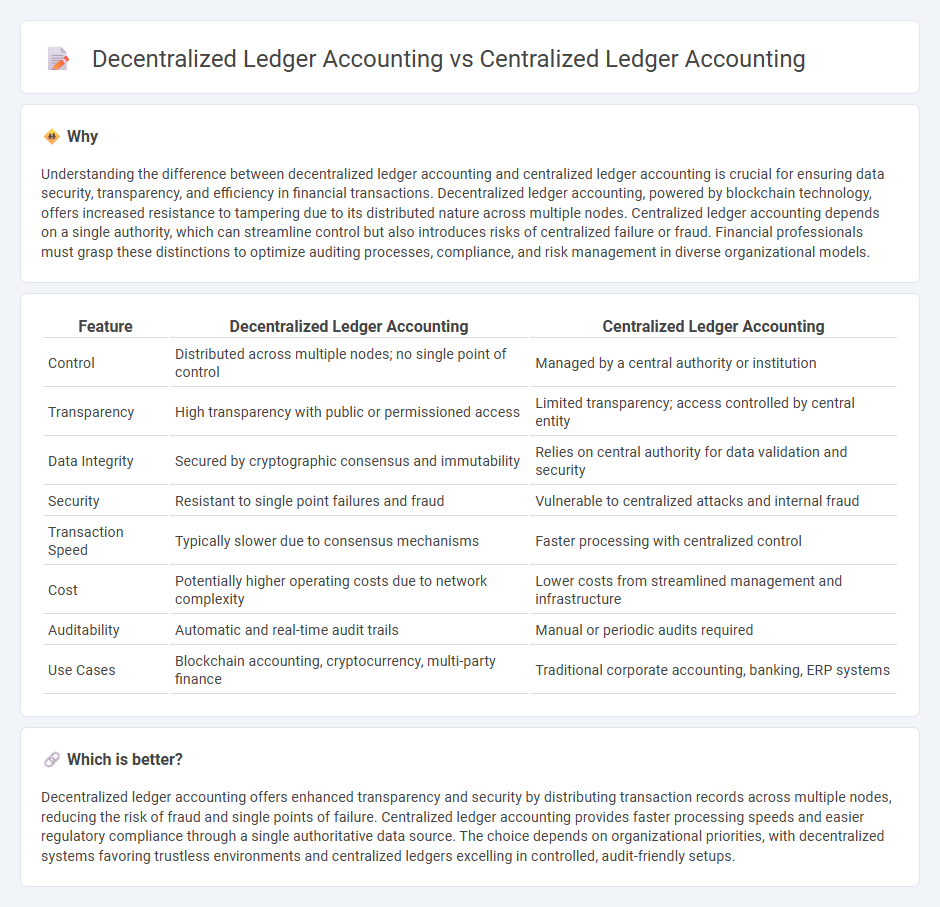
Understanding the difference between decentralized ledger accounting and centralized ledger accounting is crucial for ensuring data security, transparency, and efficiency in financial transactions. Decentralized ledger accounting, powered by blockchain technology, offers increased resistance to tampering due to its distributed nature across multiple nodes. Centralized ledger accounting depends on a single authority, which can streamline control but also introduces risks of centralized failure or fraud. Financial professionals must grasp these distinctions to optimize auditing processes, compliance, and risk management in diverse organizational models.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Decentralized Ledger Accounting | Centralized Ledger Accounting |
|---|---|---|
| Control | Distributed across multiple nodes; no single point of control | Managed by a central authority or institution |
| Transparency | High transparency with public or permissioned access | Limited transparency; access controlled by central entity |
| Data Integrity | Secured by cryptographic consensus and immutability | Relies on central authority for data validation and security |
| Security | Resistant to single point failures and fraud | Vulnerable to centralized attacks and internal fraud |
| Transaction Speed | Typically slower due to consensus mechanisms | Faster processing with centralized control |
| Cost | Potentially higher operating costs due to network complexity | Lower costs from streamlined management and infrastructure |
| Auditability | Automatic and real-time audit trails | Manual or periodic audits required |
| Use Cases | Blockchain accounting, cryptocurrency, multi-party finance | Traditional corporate accounting, banking, ERP systems |
Which is better?
Decentralized ledger accounting offers enhanced transparency and security by distributing transaction records across multiple nodes, reducing the risk of fraud and single points of failure. Centralized ledger accounting provides faster processing speeds and easier regulatory compliance through a single authoritative data source. The choice depends on organizational priorities, with decentralized systems favoring trustless environments and centralized ledgers excelling in controlled, audit-friendly setups.
Connection
Decentralized ledger accounting and centralized ledger accounting both serve as systems for recording financial transactions but differ in data control and transparency. Decentralized ledgers distribute transaction records across multiple nodes, enhancing security and reducing fraud risk, while centralized ledgers consolidate data management in a single entity, allowing faster reconciliation and streamlined oversight. The integration of blockchain technology bridges these models by enabling centralized institutions to adopt decentralized features for improved trust and auditability.
Key Terms
Data Ownership
Centralized ledger accounting consolidates data ownership within a single entity, ensuring streamlined control but creating potential risks related to data breaches and manipulation. Decentralized ledger accounting distributes data ownership across multiple participants, enhancing transparency, security, and resistance to tampering while enabling real-time validation of transactions. Explore the advantages and trade-offs in data ownership models to determine the best fit for your accounting needs.
Transaction Validation
Transaction validation in centralized ledger accounting relies on a trusted central authority to verify and record transactions, ensuring consistency and control over the ledger's integrity. In decentralized ledger accounting, multiple nodes independently validate transactions through consensus mechanisms, enhancing transparency and reducing the risk of single points of failure. Explore the nuances and impact of these validation methods to understand their advantages in different financial ecosystems.
Accessibility
Centralized ledger accounting relies on a single entity to maintain and control the financial records, which can limit accessibility to authorized personnel only and introduce risks associated with centralized failures. In contrast, decentralized ledger accounting uses distributed blockchain technology, enabling transparent and secure access for multiple parties without a central authority, enhancing real-time verification and reducing dependency on intermediaries. Explore the advantages and challenges of these accounting methods to understand which system best suits your business needs.
Source and External Links
Difference Between Centralized and Distributed Ledgers - Centralized ledger accounting is managed and controlled by a single entity, offering consistent, reliable data and easier integration with existing systems, but is vulnerable to cyber attacks and lacks transparency for external verification.
ledger | Wex | US Law | LII / Legal Information Institute - In centralized ledger accounting, both the general ledger and subledgers are typically accessible only to a limited number of authorized parties within an organization, with modifications subject to accounting laws and regulations.
Central Ledger Definition - CoinMarketCap - A central ledger is a physical or digital record managed by a business's accounting department to track all economic transactions in a centralized manner, improving accuracy but also introducing risks if the central authority makes errors.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com