Blockchain audit trails provide an immutable and transparent record of financial transactions, enhancing accuracy and reducing the risk of fraud compared to manual ledger entries prone to human error and manipulation. This decentralized technology ensures real-time verification, improving trust and efficiency in accounting processes. Discover how integrating blockchain can revolutionize your auditing practices and strengthen financial integrity.
Why it is important
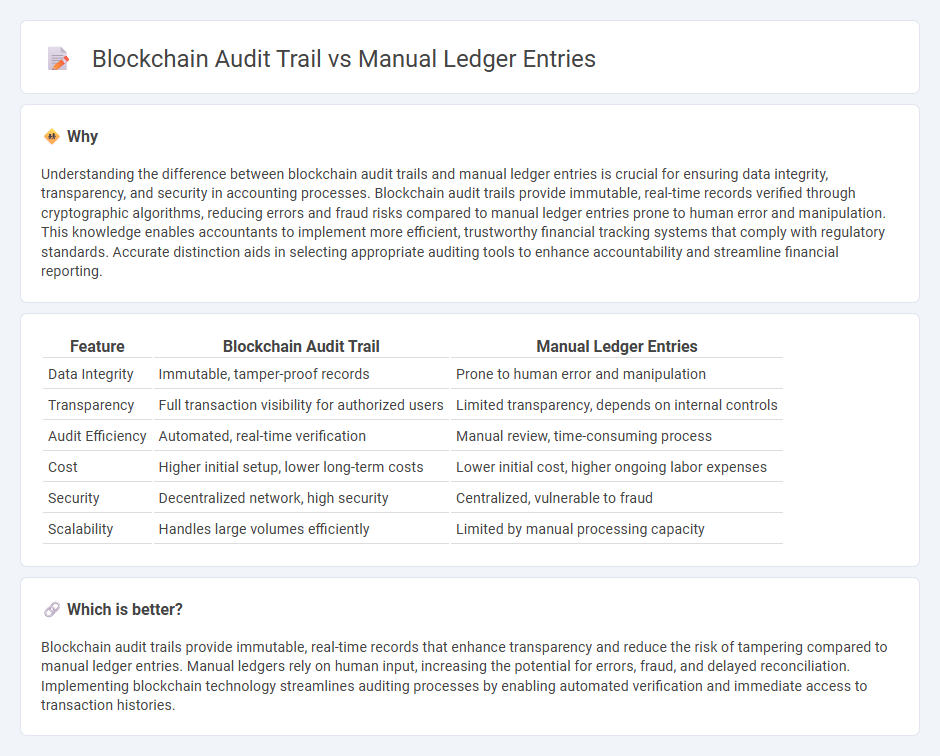
Understanding the difference between blockchain audit trails and manual ledger entries is crucial for ensuring data integrity, transparency, and security in accounting processes. Blockchain audit trails provide immutable, real-time records verified through cryptographic algorithms, reducing errors and fraud risks compared to manual ledger entries prone to human error and manipulation. This knowledge enables accountants to implement more efficient, trustworthy financial tracking systems that comply with regulatory standards. Accurate distinction aids in selecting appropriate auditing tools to enhance accountability and streamline financial reporting.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Blockchain Audit Trail | Manual Ledger Entries |
|---|---|---|
| Data Integrity | Immutable, tamper-proof records | Prone to human error and manipulation |
| Transparency | Full transaction visibility for authorized users | Limited transparency, depends on internal controls |
| Audit Efficiency | Automated, real-time verification | Manual review, time-consuming process |
| Cost | Higher initial setup, lower long-term costs | Lower initial cost, higher ongoing labor expenses |
| Security | Decentralized network, high security | Centralized, vulnerable to fraud |
| Scalability | Handles large volumes efficiently | Limited by manual processing capacity |
Which is better?
Blockchain audit trails provide immutable, real-time records that enhance transparency and reduce the risk of tampering compared to manual ledger entries. Manual ledgers rely on human input, increasing the potential for errors, fraud, and delayed reconciliation. Implementing blockchain technology streamlines auditing processes by enabling automated verification and immediate access to transaction histories.
Connection
Blockchain audit trails enhance traditional accounting by providing an immutable, transparent record of transactions, which complements manual ledger entries through increased data integrity and traceability. Manual ledger entries rely on human input and are prone to errors or fraud, while blockchain technology ensures real-time verification and secure documentation of financial activities. Integrating blockchain audit trails with manual ledgers streamlines reconciliation processes and strengthens overall financial reporting accuracy.
Key Terms
Double-entry bookkeeping
Manual ledger entries rely on traditional double-entry bookkeeping methods, where each transaction is recorded twice to maintain balance and accuracy, but are prone to human error and tampering. Blockchain audit trails provide a decentralized, immutable record of transactions, ensuring enhanced security, transparency, and real-time verification without the risk of alteration. Explore how integrating blockchain can revolutionize accuracy and trust in double-entry bookkeeping systems.
Immutable records
Manual ledger entries are prone to human error and tampering, compromising the integrity of financial records. Blockchain audit trails provide immutable records secured by cryptographic hashing, ensuring that data cannot be altered once recorded. Explore how blockchain technology enhances transparency and trust in audit processes.
Transparency
Manual ledger entries often lack real-time visibility and are prone to human errors or intentional manipulation, reducing transparency in financial records. Blockchain audit trails provide an immutable, decentralized record of transactions that enhances transparency by allowing continuous, verifiable access to data. Learn more about how blockchain technology revolutionizes transparency in financial auditing.
Source and External Links
GENERAL LEDGER: Visual Guide to Posting Journals - Manual journal entries in the general ledger involve recording transactions directly, such as debiting overhead expenses and crediting accrued expenses when an expense is incurred but not yet billed, updating account balances accordingly.
How to Post Journal Entries to the General Ledger - To post manual ledger entries, transfer each journal entry's debit and credit amounts directly to the corresponding general ledger accounts without altering the original entry details.
How to Create a Manual General Ledger with Excel? - Manual ledger entry setup in Excel includes columns for date, description, debit, credit, balance, and account code, with the balance calculated by adjusting the prior balance with each new debit or credit.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com