Tax equity financing is a strategic investment approach where investors receive tax benefits through credits and deductions by funding renewable energy projects, often used by corporations and financial institutions. Crowdfunding involves raising capital from a large number of individuals, usually via online platforms, allowing businesses or projects to access funds without traditional financial intermediaries. Explore how these financing methods impact capital formation and investor engagement.
Why it is important
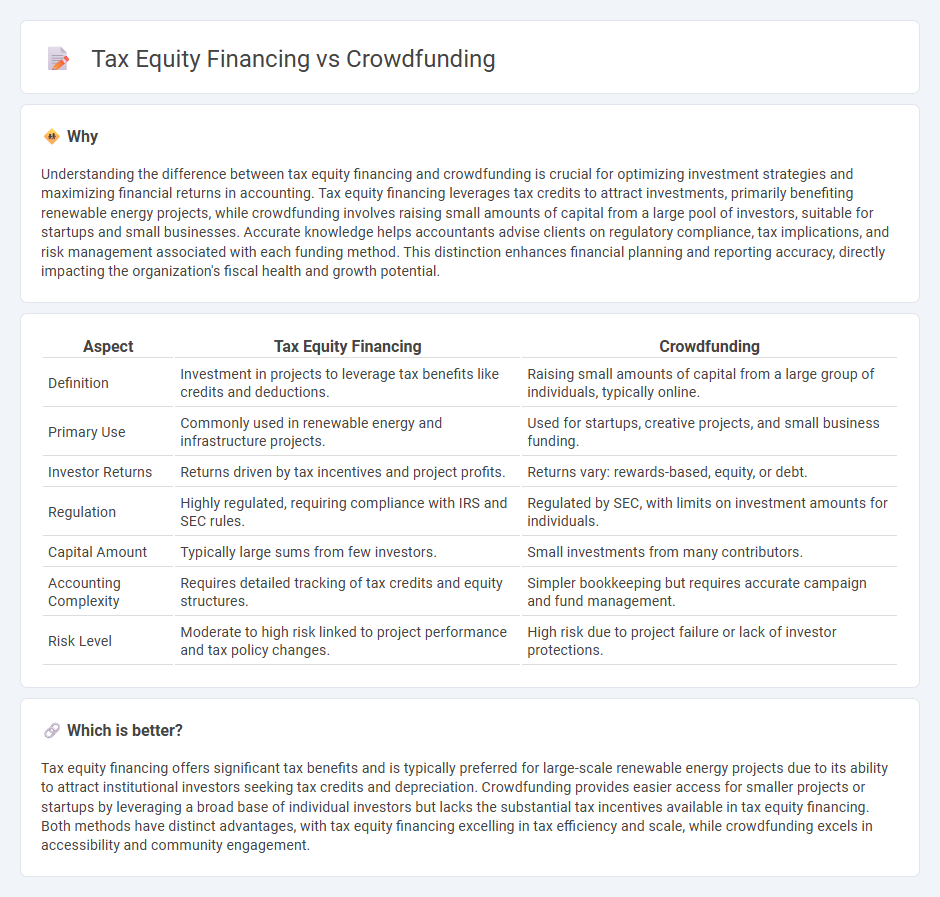
Understanding the difference between tax equity financing and crowdfunding is crucial for optimizing investment strategies and maximizing financial returns in accounting. Tax equity financing leverages tax credits to attract investments, primarily benefiting renewable energy projects, while crowdfunding involves raising small amounts of capital from a large pool of investors, suitable for startups and small businesses. Accurate knowledge helps accountants advise clients on regulatory compliance, tax implications, and risk management associated with each funding method. This distinction enhances financial planning and reporting accuracy, directly impacting the organization's fiscal health and growth potential.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Tax Equity Financing | Crowdfunding |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Investment in projects to leverage tax benefits like credits and deductions. | Raising small amounts of capital from a large group of individuals, typically online. |
| Primary Use | Commonly used in renewable energy and infrastructure projects. | Used for startups, creative projects, and small business funding. |
| Investor Returns | Returns driven by tax incentives and project profits. | Returns vary: rewards-based, equity, or debt. |
| Regulation | Highly regulated, requiring compliance with IRS and SEC rules. | Regulated by SEC, with limits on investment amounts for individuals. |
| Capital Amount | Typically large sums from few investors. | Small investments from many contributors. |
| Accounting Complexity | Requires detailed tracking of tax credits and equity structures. | Simpler bookkeeping but requires accurate campaign and fund management. |
| Risk Level | Moderate to high risk linked to project performance and tax policy changes. | High risk due to project failure or lack of investor protections. |
Which is better?
Tax equity financing offers significant tax benefits and is typically preferred for large-scale renewable energy projects due to its ability to attract institutional investors seeking tax credits and depreciation. Crowdfunding provides easier access for smaller projects or startups by leveraging a broad base of individual investors but lacks the substantial tax incentives available in tax equity financing. Both methods have distinct advantages, with tax equity financing excelling in tax efficiency and scale, while crowdfunding excels in accessibility and community engagement.
Connection
Tax equity financing and crowdfunding are connected through their roles in raising capital for projects, particularly in renewable energy sectors. Tax equity financing provides investors with tax benefits in exchange for funding, while crowdfunding leverages small contributions from a large number of individuals to finance projects. Both methods diversify funding sources, enhance project viability, and attract different types of investors to drive sustainable development.
Key Terms
Capital Structure
Crowdfunding offers startups and small businesses access to capital by pooling funds from numerous individual investors, diluting ownership but avoiding long-term debt liabilities. Tax equity financing leverages specific tax incentives, such as Investment Tax Credits (ITC) and Production Tax Credits (PTC), allowing capital providers to receive tax benefits in exchange for equity in renewable energy projects, fundamentally altering the capital structure by integrating tax-driven returns. Explore deeper insights on how capital structure decisions impact funding strategies and investor returns.
Investor Returns
Crowdfunding offers investors direct participation with potential high returns driven by project-specific success, often accompanied by higher risk and less regulatory oversight compared to tax equity financing. Tax equity financing provides investors with steady, lower-risk returns primarily through tax credits and predictable revenue streams generated by renewable energy projects. Explore further to understand which investment strategy best aligns with your financial goals and risk tolerance.
Tax Credits
Tax equity financing leverages specific tax credits such as the Investment Tax Credit (ITC) and Production Tax Credit (PTC), providing significant benefits to renewable energy projects by reducing tax liabilities for investors. Crowdfunding typically does not offer direct access to these tax incentives, making it less attractive for investors seeking tax-advantaged returns in clean energy sectors. Explore how tax equity financing can maximize the value of tax credits for your energy project.
Source and External Links
Crowdfunding - Wikipedia - Crowdfunding is the practice of raising money from a large number of people, typically via the internet, to fund projects or ventures without standard financial intermediaries, involving project initiators, supporters, and platforms.
What is crowdfunding? Here are four types for startups to know - Stripe - Crowdfunding enables startups to raise money through collective effort from individuals via the internet, as an alternative to traditional funding methods, allowing greater outreach and contributions of varied sizes.
Crowdfunding - Small Business Financing: A Resource Guide - Crowdfunding uses online platforms to collect small amounts of money from many people through donation, rewards, or equity models, helping businesses or causes raise required funds legally and publicly.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com