Taxonomy alignment in accounting organizes financial data consistently across different reporting standards, improving comparability and regulatory compliance. Currency translation involves converting financial statements of foreign subsidiaries into the parent company's reporting currency, reflecting exchange rate fluctuations and ensuring accurate consolidated financial reports. Explore the distinctions between these processes to enhance global financial reporting accuracy.
Why it is important
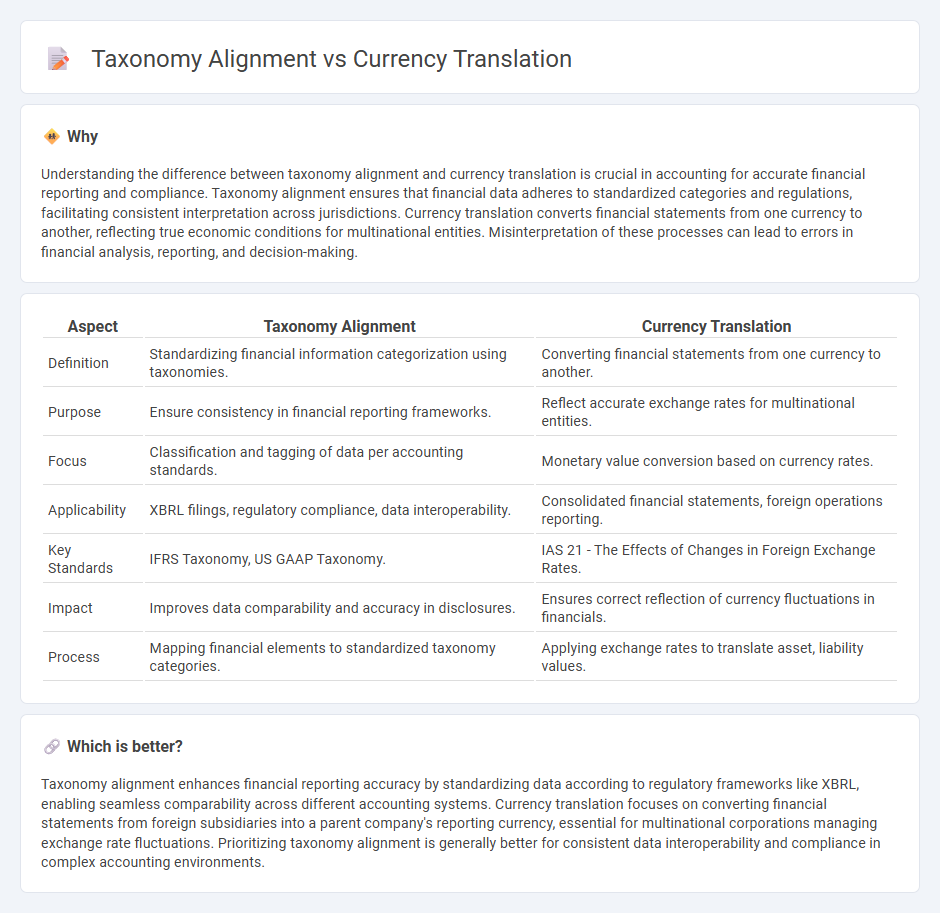
Understanding the difference between taxonomy alignment and currency translation is crucial in accounting for accurate financial reporting and compliance. Taxonomy alignment ensures that financial data adheres to standardized categories and regulations, facilitating consistent interpretation across jurisdictions. Currency translation converts financial statements from one currency to another, reflecting true economic conditions for multinational entities. Misinterpretation of these processes can lead to errors in financial analysis, reporting, and decision-making.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Taxonomy Alignment | Currency Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Standardizing financial information categorization using taxonomies. | Converting financial statements from one currency to another. |
| Purpose | Ensure consistency in financial reporting frameworks. | Reflect accurate exchange rates for multinational entities. |
| Focus | Classification and tagging of data per accounting standards. | Monetary value conversion based on currency rates. |
| Applicability | XBRL filings, regulatory compliance, data interoperability. | Consolidated financial statements, foreign operations reporting. |
| Key Standards | IFRS Taxonomy, US GAAP Taxonomy. | IAS 21 - The Effects of Changes in Foreign Exchange Rates. |
| Impact | Improves data comparability and accuracy in disclosures. | Ensures correct reflection of currency fluctuations in financials. |
| Process | Mapping financial elements to standardized taxonomy categories. | Applying exchange rates to translate asset, liability values. |
Which is better?
Taxonomy alignment enhances financial reporting accuracy by standardizing data according to regulatory frameworks like XBRL, enabling seamless comparability across different accounting systems. Currency translation focuses on converting financial statements from foreign subsidiaries into a parent company's reporting currency, essential for multinational corporations managing exchange rate fluctuations. Prioritizing taxonomy alignment is generally better for consistent data interoperability and compliance in complex accounting environments.
Connection
Taxonomy alignment ensures consistent classification of financial data across different accounting standards, facilitating accurate currency translation by standardizing financial statement elements. Currency translation converts financial statements from a foreign currency to the reporting currency, relying on taxonomy alignment to correctly map and interpret monetary values. This connection enhances financial comparability and compliance with international accounting regulations such as IFRS and GAAP.
Key Terms
Currency Translation:
Currency translation involves converting financial statements from one currency to another, enabling multinational companies to consolidate global financial data accurately. It ensures consistency in reporting by applying exchange rates according to accounting standards such as IFRS or GAAP, impacting financial analysis and decision-making. Discover how mastering currency translation enhances global financial transparency and compliance.
Exchange Rate
Exchange rate management is crucial when comparing currency translation to taxonomy alignment, as currency translation involves converting financial data between currencies based on fluctuating exchange rates, while taxonomy alignment standardizes classification systems for consistent data interpretation. Exchange rates directly impact the accuracy of financial reporting and cross-border transactions, making their precise incorporation vital in currency translation but less central in taxonomy alignment processes. Explore how exchange rate considerations shape these frameworks to enhance global financial accuracy and data consistency.
Functional Currency
Functional currency defines the primary currency used by a company for its financial reporting, directly impacting currency translation processes in accounting. Currency translation converts financial statements from the functional currency to the reporting currency based on exchange rates, while taxonomy alignment ensures consistency by mapping financial data to standardized accounting frameworks. Explore how mastering functional currency intricacies enhances accuracy in both currency translation and taxonomy alignment for global financial reporting.
Source and External Links
Deloitte Accounting Research Tool (DART) - Provides guidance on foreign currency translation, including the process of expressing amounts in the reporting currency.
Xe Currency Converter - Offers live foreign exchange rates for converting between major global currencies.
Oanda Currency Converter - Allows users to check the latest foreign exchange average bid/ask rates and convert major world currencies.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com