Transfer pricing analytics focuses on analyzing and optimizing the prices charged between related business units for goods and services to ensure compliance with tax regulations and maximize profitability. Cost allocation assigns shared costs across departments or products to accurately reflect resource usage and support financial decision-making. Explore more to understand how these accounting techniques improve financial accuracy and regulatory adherence.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between transfer pricing analytics and cost allocation is crucial for accurate financial reporting and tax compliance. Transfer pricing analytics focus on setting prices for transactions between related business entities to comply with international tax regulations and avoid penalties. Cost allocation involves distributing indirect costs across departments or products to determine true profitability and support internal decision-making. Accurate differentiation helps businesses optimize tax strategies and improve internal cost management effectively.
Comparison Table
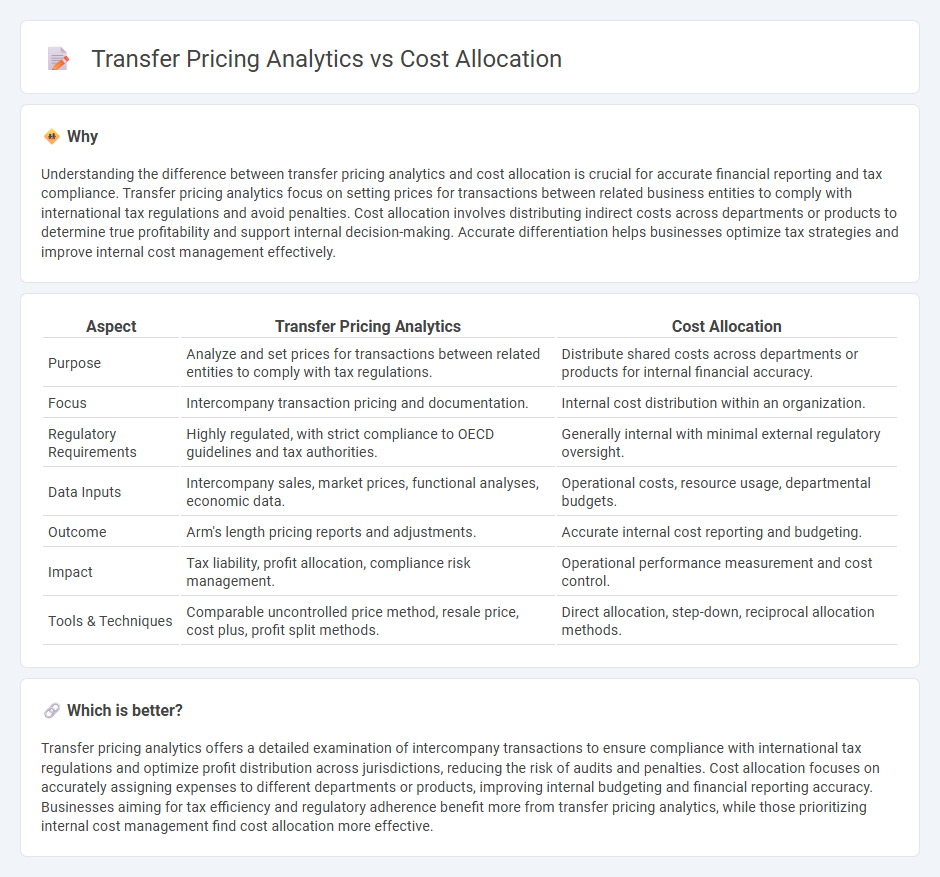
| Aspect | Transfer Pricing Analytics | Cost Allocation |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Analyze and set prices for transactions between related entities to comply with tax regulations. | Distribute shared costs across departments or products for internal financial accuracy. |
| Focus | Intercompany transaction pricing and documentation. | Internal cost distribution within an organization. |
| Regulatory Requirements | Highly regulated, with strict compliance to OECD guidelines and tax authorities. | Generally internal with minimal external regulatory oversight. |
| Data Inputs | Intercompany sales, market prices, functional analyses, economic data. | Operational costs, resource usage, departmental budgets. |
| Outcome | Arm's length pricing reports and adjustments. | Accurate internal cost reporting and budgeting. |
| Impact | Tax liability, profit allocation, compliance risk management. | Operational performance measurement and cost control. |
| Tools & Techniques | Comparable uncontrolled price method, resale price, cost plus, profit split methods. | Direct allocation, step-down, reciprocal allocation methods. |
Which is better?
Transfer pricing analytics offers a detailed examination of intercompany transactions to ensure compliance with international tax regulations and optimize profit distribution across jurisdictions, reducing the risk of audits and penalties. Cost allocation focuses on accurately assigning expenses to different departments or products, improving internal budgeting and financial reporting accuracy. Businesses aiming for tax efficiency and regulatory adherence benefit more from transfer pricing analytics, while those prioritizing internal cost management find cost allocation more effective.
Connection
Transfer pricing analytics involves evaluating intercompany transaction prices to ensure compliance with tax regulations, directly impacting cost allocation strategies within multinational corporations. Accurate transfer pricing analysis enables businesses to allocate costs efficiently across different divisions and jurisdictions, optimizing tax liabilities and financial reporting. Integrating these processes enhances transparency, reduces audit risks, and supports strategic decision-making in global financial management.
Key Terms
**Cost Allocation:**
Cost allocation analytics focuses on identifying and distributing indirect costs such as overhead, utilities, and administrative expenses to various departments or products based on predefined cost drivers, enhancing financial transparency and resource management. It supports budgeting and performance evaluation by accurately assigning shared costs, which helps in identifying cost-saving opportunities and improving profitability. Explore detailed methodologies and tools to optimize cost allocation in your organization.
Cost Pools
Cost allocation involves distributing shared costs among departments or products using cost pools that group similar expenses, ensuring accurate expense tracking and budgeting. Transfer pricing sets prices for transactions between related business units to allocate income and expenses, demanding precise cost pool data for compliance and profitability analysis. Explore detailed strategies on optimizing cost pools for both cost allocation and transfer pricing analytics.
Cost Drivers
Cost allocation analytics centers on identifying cost drivers that directly influence overhead distribution across departments or products, ensuring accurate internal cost reporting and budgeting. Transfer pricing analytics examines cost drivers related to intercompany transactions to establish compliant and optimized pricing strategies under tax regulations. Explore more to understand how cost drivers impact financial decision-making and regulatory compliance in these financial processes.
Source and External Links
Cost Allocation - Meaning, Types, Methods & Examples - This webpage provides an overview of cost allocation, including steps like identifying costs, determining cost objects, and selecting allocation bases.
Cost Allocation - This article describes cost allocation as a process that assigns costs to internal clients based on their consumption of shared services within an organization.
What is Cost Allocation? - This webpage explains cost allocation as a business process to understand the true costs of products, services, or departments and outlines key steps to implement it effectively.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com