Decentralized ledger accounting leverages blockchain technology to provide a transparent, tamper-resistant record of transactions across multiple nodes, enhancing security and trust compared to traditional methods. Single-entry bookkeeping, by contrast, records each financial transaction only once, often leading to limited error detection and reduced financial insight. Discover how these accounting approaches can transform financial management and accuracy.
Why it is important
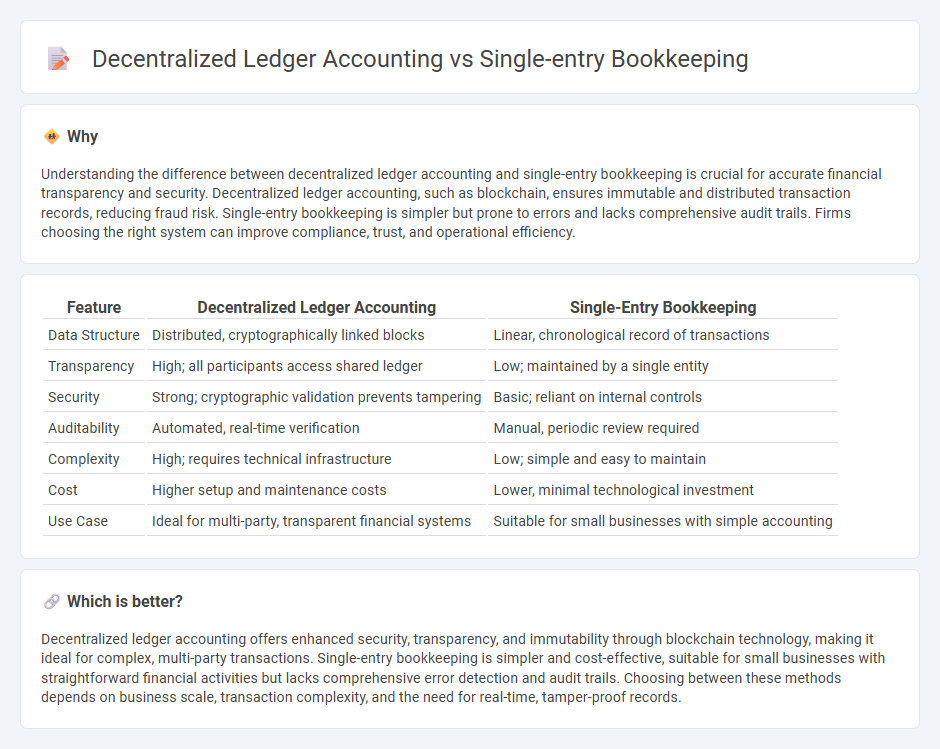
Understanding the difference between decentralized ledger accounting and single-entry bookkeeping is crucial for accurate financial transparency and security. Decentralized ledger accounting, such as blockchain, ensures immutable and distributed transaction records, reducing fraud risk. Single-entry bookkeeping is simpler but prone to errors and lacks comprehensive audit trails. Firms choosing the right system can improve compliance, trust, and operational efficiency.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Decentralized Ledger Accounting | Single-Entry Bookkeeping |
|---|---|---|
| Data Structure | Distributed, cryptographically linked blocks | Linear, chronological record of transactions |
| Transparency | High; all participants access shared ledger | Low; maintained by a single entity |
| Security | Strong; cryptographic validation prevents tampering | Basic; reliant on internal controls |
| Auditability | Automated, real-time verification | Manual, periodic review required |
| Complexity | High; requires technical infrastructure | Low; simple and easy to maintain |
| Cost | Higher setup and maintenance costs | Lower, minimal technological investment |
| Use Case | Ideal for multi-party, transparent financial systems | Suitable for small businesses with simple accounting |
Which is better?
Decentralized ledger accounting offers enhanced security, transparency, and immutability through blockchain technology, making it ideal for complex, multi-party transactions. Single-entry bookkeeping is simpler and cost-effective, suitable for small businesses with straightforward financial activities but lacks comprehensive error detection and audit trails. Choosing between these methods depends on business scale, transaction complexity, and the need for real-time, tamper-proof records.
Connection
Decentralized ledger accounting enhances transparency and security by distributing financial records across multiple nodes, contrasting with traditional single-entry bookkeeping that records transactions only once. Single-entry bookkeeping's simplicity makes it susceptible to errors and fraud, whereas decentralized ledgers provide immutable audit trails essential for verifying transaction integrity. Integrating single-entry records into decentralized ledgers can improve reliability and reduce the risk of discrepancies in accounting systems.
Key Terms
Transaction Record
Single-entry bookkeeping records transactions in a simple ledger where each entry affects only one account, making it easy for small businesses but limited in detail. Decentralized ledger accounting, often powered by blockchain technology, ensures every transaction is recorded across multiple nodes, providing enhanced transparency, immutability, and security. Explore the core differences and advantages between these methods to optimize your accounting system.
Double-Entry System
The Double-Entry System records each transaction with equal debits and credits, ensuring accurate financial tracking and error reduction, contrasting sharply with the simpler single-entry bookkeeping that logs transactions only once. Decentralized ledger accounting, often utilizing blockchain technology, enhances transparency and security by distributing transaction records across multiple nodes rather than centralizing them. Explore the distinct advantages and practical applications of these accounting methods in modern finance to deepen your understanding.
Ledger Synchronization
Single-entry bookkeeping records financial transactions in a single ledger, making synchronization straightforward but prone to errors and inconsistencies. Decentralized ledger accounting employs distributed ledgers, such as blockchain technology, to ensure real-time synchronization across multiple nodes, enhancing transparency and security. Explore the key differences in ledger synchronization to choose the right accounting system for your business needs.
Source and External Links
Double-Entry vs. Single-Entry Bookkeeping | Pros, Cons, & Examples - Single-entry bookkeeping records each transaction once in a spreadsheet with columns like Date, Description, and Amount, suitable for simple tracking but errors may go unnoticed until bank statements are reconciled.
Single Entry Bookkeeping: Everything You Need to Know - Single-entry bookkeeping uses one line per transaction, logging date, description, income or expense, and running balance, making it easy for small businesses to track cash flow without complex accounts.
A Complete Guide to Single-Entry Bookkeeping (With Example) - Single-entry bookkeeping involves recording the previous balance, then sequentially adding income and subtracting expenses in a cashbook to maintain an ongoing total balance for simple financial record-keeping.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com