Sustainability assurance focuses on verifying environmental, social, and governance (ESG) disclosures to enhance corporate transparency and stakeholder trust. Forensic audit involves detailed examination of financial records to detect fraud, embezzlement, or compliance violations, ensuring regulatory adherence and risk mitigation. Explore the key differences and applications of sustainability assurance and forensic audit to strengthen your accounting practices.
Why it is important
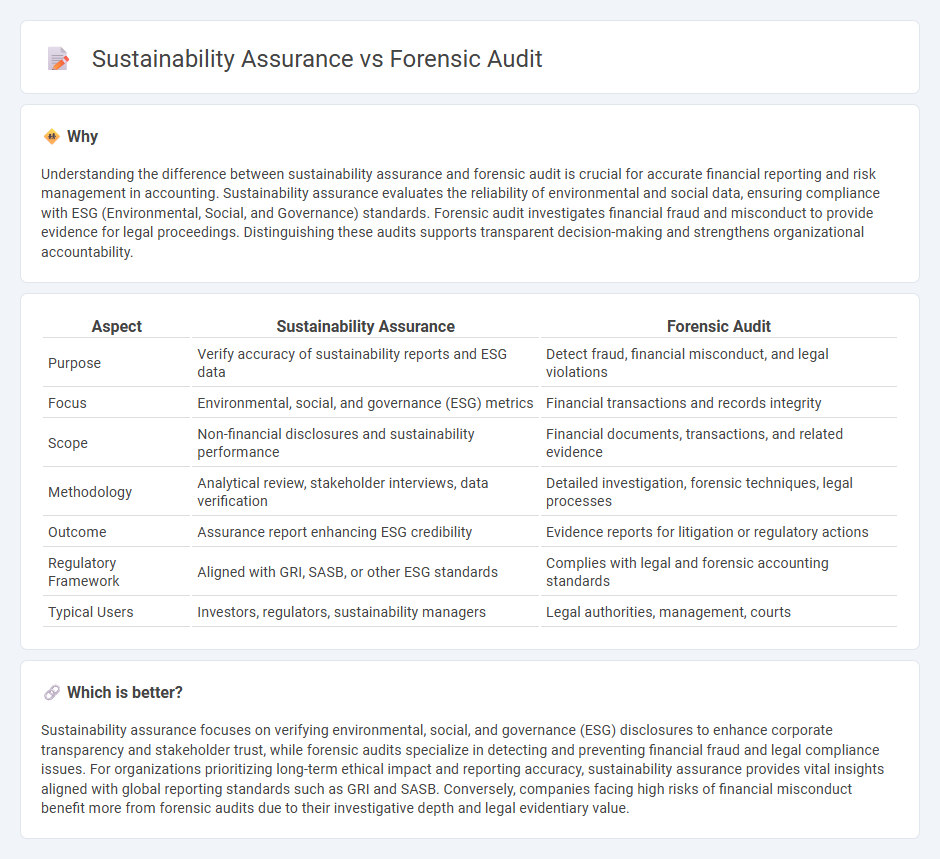
Understanding the difference between sustainability assurance and forensic audit is crucial for accurate financial reporting and risk management in accounting. Sustainability assurance evaluates the reliability of environmental and social data, ensuring compliance with ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) standards. Forensic audit investigates financial fraud and misconduct to provide evidence for legal proceedings. Distinguishing these audits supports transparent decision-making and strengthens organizational accountability.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Sustainability Assurance | Forensic Audit |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Verify accuracy of sustainability reports and ESG data | Detect fraud, financial misconduct, and legal violations |
| Focus | Environmental, social, and governance (ESG) metrics | Financial transactions and records integrity |
| Scope | Non-financial disclosures and sustainability performance | Financial documents, transactions, and related evidence |
| Methodology | Analytical review, stakeholder interviews, data verification | Detailed investigation, forensic techniques, legal processes |
| Outcome | Assurance report enhancing ESG credibility | Evidence reports for litigation or regulatory actions |
| Regulatory Framework | Aligned with GRI, SASB, or other ESG standards | Complies with legal and forensic accounting standards |
| Typical Users | Investors, regulators, sustainability managers | Legal authorities, management, courts |
Which is better?
Sustainability assurance focuses on verifying environmental, social, and governance (ESG) disclosures to enhance corporate transparency and stakeholder trust, while forensic audits specialize in detecting and preventing financial fraud and legal compliance issues. For organizations prioritizing long-term ethical impact and reporting accuracy, sustainability assurance provides vital insights aligned with global reporting standards such as GRI and SASB. Conversely, companies facing high risks of financial misconduct benefit more from forensic audits due to their investigative depth and legal evidentiary value.
Connection
Sustainability assurance and forensic audit are connected through their focus on verifying the accuracy and integrity of financial and non-financial information. Both processes involve detailed examination of records to detect misstatements, fraud, or non-compliance with regulatory standards. Integrating forensic audit techniques enhances the reliability of sustainability reports by uncovering potential risks and ensuring transparent corporate accountability.
Key Terms
**Forensic Audit:**
Forensic audit concentrates on identifying and investigating financial fraud, misappropriations, and legal compliance by examining detailed financial records and transactions. It employs specialized techniques to gather evidence for legal proceedings, ensuring accountability and transparency in financial reporting. Explore more to understand how forensic audits protect organizational integrity and deter financial misconduct.
Fraud Detection
Forensic audit specializes in fraud detection by systematically examining financial records to uncover misconduct, embezzlement, or financial discrepancies. Sustainability assurance emphasizes verifying the accuracy and reliability of environmental, social, and governance (ESG) disclosures, indirectly helping identify fraudulent claims related to corporate sustainability. Explore further to understand how these distinct approaches safeguard organizational integrity in different contexts.
Evidence Collection
Forensic audits emphasize rigorous evidence collection to detect fraud, financial discrepancies, and compliance violations, utilizing methods such as data analysis, document examination, and interviews. Sustainability assurance focuses on gathering evidence related to environmental, social, and governance (ESG) performance, verifying the accuracy of sustainability reports and claims through site visits, stakeholder consultations, and data validation. Explore deeper insights into the differences in evidence collection techniques between forensic audits and sustainability assurance.
Source and External Links
What is a Forensic Audit and Do I Need One - This webpage explains what a forensic audit is and outlines its process, including planning, collecting evidence, and often involves using computer-assisted research to uncover financial issues.
Forensic Audit Guide - This guide provides a definition of forensic audits, their steps, and reasons for their use, often involving cases of fraud that need evidence for legal proceedings.
Forensic Accounting - Forensic accounting involveskarth the use of specialized skills to investigate financial misconduct, often requiring experts to translate complex financial data into understandable terms for legal purposes.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com