Microtransaction accounting records revenue from small, individual purchases as they occur, reflecting real-time customer spending behavior and immediate income recognition. Breakage revenue accounting, however, estimates and recognizes revenue from unused services or prepaid balances that customers are unlikely to redeem, such as unused gift cards or subscription credits. Explore the detailed differences and implications of these two accounting methods to optimize financial reporting accuracy.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between microtransaction accounting and breakage revenue accounting is crucial for accurate financial reporting and compliance with accounting standards. Microtransaction accounting focuses on recognizing revenue from small, frequent transactions, while breakage revenue accounting deals with unredeemed balances from prepaid services or gift cards. Knowing these distinctions helps businesses properly match revenues with the corresponding expenses, improving profitability analysis and cash flow management. Accurate application prevents revenue misstatement and supports better strategic decision-making.
Comparison Table
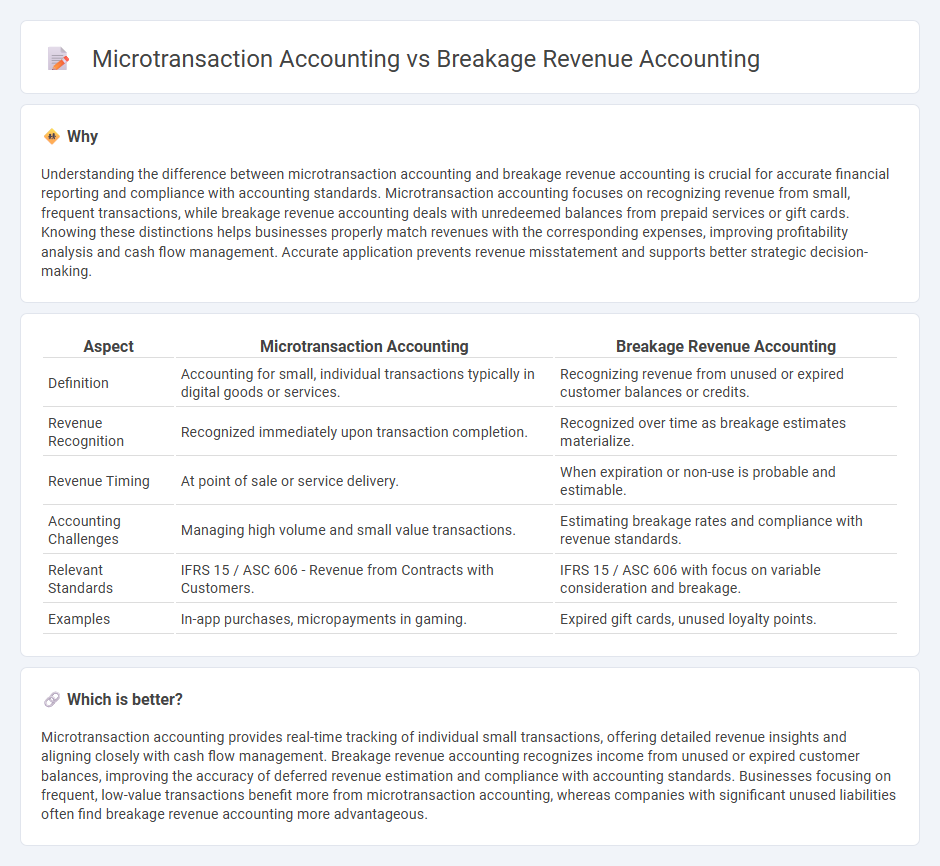
| Aspect | Microtransaction Accounting | Breakage Revenue Accounting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Accounting for small, individual transactions typically in digital goods or services. | Recognizing revenue from unused or expired customer balances or credits. |
| Revenue Recognition | Recognized immediately upon transaction completion. | Recognized over time as breakage estimates materialize. |
| Revenue Timing | At point of sale or service delivery. | When expiration or non-use is probable and estimable. |
| Accounting Challenges | Managing high volume and small value transactions. | Estimating breakage rates and compliance with revenue standards. |
| Relevant Standards | IFRS 15 / ASC 606 - Revenue from Contracts with Customers. | IFRS 15 / ASC 606 with focus on variable consideration and breakage. |
| Examples | In-app purchases, micropayments in gaming. | Expired gift cards, unused loyalty points. |
Which is better?
Microtransaction accounting provides real-time tracking of individual small transactions, offering detailed revenue insights and aligning closely with cash flow management. Breakage revenue accounting recognizes income from unused or expired customer balances, improving the accuracy of deferred revenue estimation and compliance with accounting standards. Businesses focusing on frequent, low-value transactions benefit more from microtransaction accounting, whereas companies with significant unused liabilities often find breakage revenue accounting more advantageous.
Connection
Microtransaction accounting meticulously tracks small, frequent financial exchanges, requiring precise recognition of revenue as transactions occur. Breakage revenue accounting accounts for unredeemed balances or unused service credits, often arising from these microtransactions. Together, they ensure accurate financial reporting by aligning revenue recognition with actual consumer behavior and transaction patterns.
Key Terms
**Unredeemed Liability**
Breakage revenue accounting recognizes income from unredeemed liabilities when it becomes probable that the customer will not exercise their rights, commonly applied in gift card or prepaid service contexts. Microtransaction accounting tracks revenue by matching small, frequent purchases to specific virtual goods or services delivered, minimizing unredeemed liabilities through immediate recognition. Explore detailed distinctions and practical impacts on financial reporting and compliance by learning more about unredeemed liability treatments.
**Revenue Recognition**
Breakage revenue accounting recognizes revenue from unused prepaid balances or gift cards when it's probable the customer will not redeem them, relying on historical data to estimate breakage amounts. Microtransaction accounting records revenue immediately upon purchase or delivery of virtual goods and services, ensuring compliance with ASC 606 by identifying performance obligations and satisfaction points. Explore detailed guidelines and best practices to optimize your revenue recognition strategy.
**Deferred Revenue**
Breakage revenue accounting recognizes unredeemed balances from prepaid products or gift cards as revenue after a specific period, impacting the Deferred Revenue account by reducing liabilities. Microtransaction accounting records revenue as earned from small, discrete purchases, immediately decreasing Deferred Revenue with each completed transaction. Explore deeper insights into managing Deferred Revenue for optimized financial reporting and compliance.
Source and External Links
Recognition of Breakage Revenue Under the New Revenue Recognition Standard - Breakage revenue is recognized when a company estimates a portion of prepaid services (like gift cards) that will not be redeemed by customers and recognizes that estimated amount as revenue, reducing the liability on the balance sheet proportionate to redemption rates under ASC 606 guidelines.
Breakage Revenue: The Complete Guide to Accounting - HubiFi - Breakage revenue accounting involves estimating unredeemed gift card values using methods such as the proportionate method, recognizing breakage revenue as customers redeem partial amounts, with considerations for state escheatment laws and compliance.
8.8 Customers' Unexercised Rights -- Breakage | DART - Under ASC 606, breakage is recognized in proportion to customer redemptions even before legal release of obligations, with breakage not treated as variable consideration but affecting the timing of revenue recognition.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com