Triple entry bookkeeping enhances traditional double entry systems by incorporating a cryptographic receipt that verifies transactions on a blockchain, increasing transparency and reducing fraud. Cryptographic accounting leverages distributed ledger technology to ensure immutable, real-time records that improve auditability and trust among stakeholders. Explore how these innovative approaches transform financial record-keeping and strengthen data security.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between triple entry bookkeeping and cryptographic accounting is crucial for enhancing transparency and security in financial records. Triple entry bookkeeping introduces a third ledger that employs cryptographic proofs to ensure transaction authenticity and immutability. Cryptographic accounting leverages blockchain technology to create tamper-proof and verifiable transaction histories, reducing fraud and errors. Accurate knowledge of these systems improves audit reliability and regulatory compliance in modern finance.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Triple Entry Bookkeeping | Cryptographic Accounting |
|---|---|---|
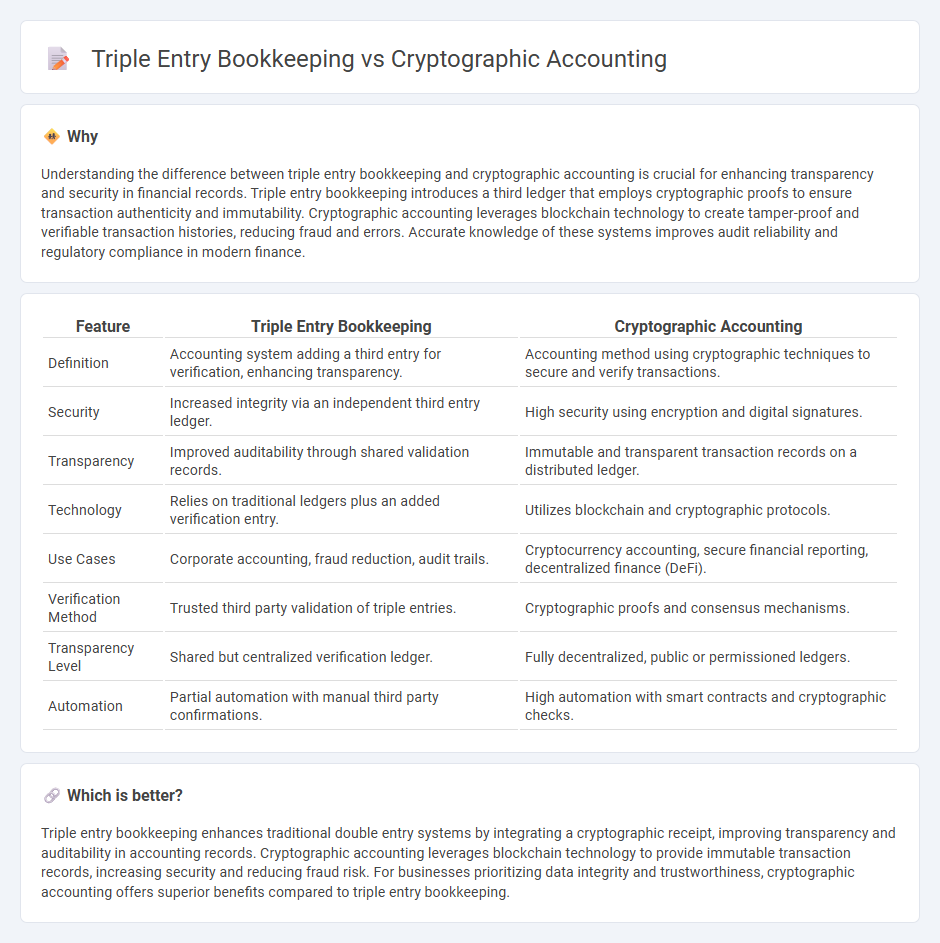
| Definition | Accounting system adding a third entry for verification, enhancing transparency. | Accounting method using cryptographic techniques to secure and verify transactions. |
| Security | Increased integrity via an independent third entry ledger. | High security using encryption and digital signatures. |
| Transparency | Improved auditability through shared validation records. | Immutable and transparent transaction records on a distributed ledger. |
| Technology | Relies on traditional ledgers plus an added verification entry. | Utilizes blockchain and cryptographic protocols. |
| Use Cases | Corporate accounting, fraud reduction, audit trails. | Cryptocurrency accounting, secure financial reporting, decentralized finance (DeFi). |
| Verification Method | Trusted third party validation of triple entries. | Cryptographic proofs and consensus mechanisms. |
| Transparency Level | Shared but centralized verification ledger. | Fully decentralized, public or permissioned ledgers. |
| Automation | Partial automation with manual third party confirmations. | High automation with smart contracts and cryptographic checks. |
Which is better?
Triple entry bookkeeping enhances traditional double entry systems by integrating a cryptographic receipt, improving transparency and auditability in accounting records. Cryptographic accounting leverages blockchain technology to provide immutable transaction records, increasing security and reducing fraud risk. For businesses prioritizing data integrity and trustworthiness, cryptographic accounting offers superior benefits compared to triple entry bookkeeping.
Connection
Triple entry bookkeeping integrates cryptographic accounting by embedding blockchain technology to secure transactions with immutable, time-stamped digital receipts. This method enhances transparency and fraud prevention by recording a third ledger entry verified through cryptographic protocols beyond traditional double-entry bookkeeping. The synergy between cryptographic proof and triple entry bookkeeping supports real-time auditability and strengthens financial data integrity.
Key Terms
Blockchain
Cryptographic accounting leverages blockchain technology to ensure transactional transparency, immutability, and security through cryptographic hashes, creating verifiable and tamper-proof records. Triple entry bookkeeping extends traditional double-entry systems by adding a cryptographically sealed third entry (a blockchain transaction), enabling enhanced auditability and trust without relying on centralized authorities. Explore how blockchain-driven cryptographic accounting transforms financial record-keeping and drives innovation in bookkeeping methods.
Immutable Ledger
Cryptographic accounting leverages advanced encryption and blockchain technology to create an immutable ledger, ensuring data integrity and preventing unauthorized alterations. Triple entry bookkeeping enhances traditional double entry systems by including a cryptographically secured third entry, which acts as a verifiable and tamper-proof record on the ledger. Explore the definitive impact of immutable ledgers on financial transparency and auditability to understand their transformative role in modern accounting.
Encrypted Transactions
Encrypted transactions enhance security by ensuring data confidentiality and integrity through cryptographic algorithms, unlike traditional triple entry bookkeeping which relies on a third ledger copy for verification. Cryptographic accounting integrates encryption directly into transaction records, enabling tamper-proof audit trails and decentralized validation. Explore how encrypted transactions revolutionize trust and transparency in financial systems.
Source and External Links
FASB Announces First-Ever Crypto Accounting Rules | Gordon Law - The Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) issued ASU 2023-08, establishing that cryptocurrency must be accounted for at fair market value with changes recognized in net income, replacing prior treatment as intangible assets and increasing transparency in financial reporting for crypto holdings.
Accounting for Cryptocurrencies in 2025 - BDO USA - ASU 2023-08 requires public and private entities to measure crypto assets at fair value each reporting period, recognize changes in net income, and provide enhanced disclosures, effective January 1, 2025 for calendar year entities.
FASB's New Guidance on Accounting for Crypto Assets - FASB's guidance classifies cryptocurrencies as assets measured at fair value with gains and losses reflected in net income, including specific accounting implications for cryptocurrency mining activities.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com