Ledger tokenization transforms physical or digital assets into blockchain-based tokens, enhancing transparency and liquidity in accounting records. Asset securitization involves pooling financial assets and issuing securities backed by those assets, improving capital management and risk distribution. Explore the detailed differences and benefits of ledger tokenization and asset securitization in modern accounting.
Why it is important
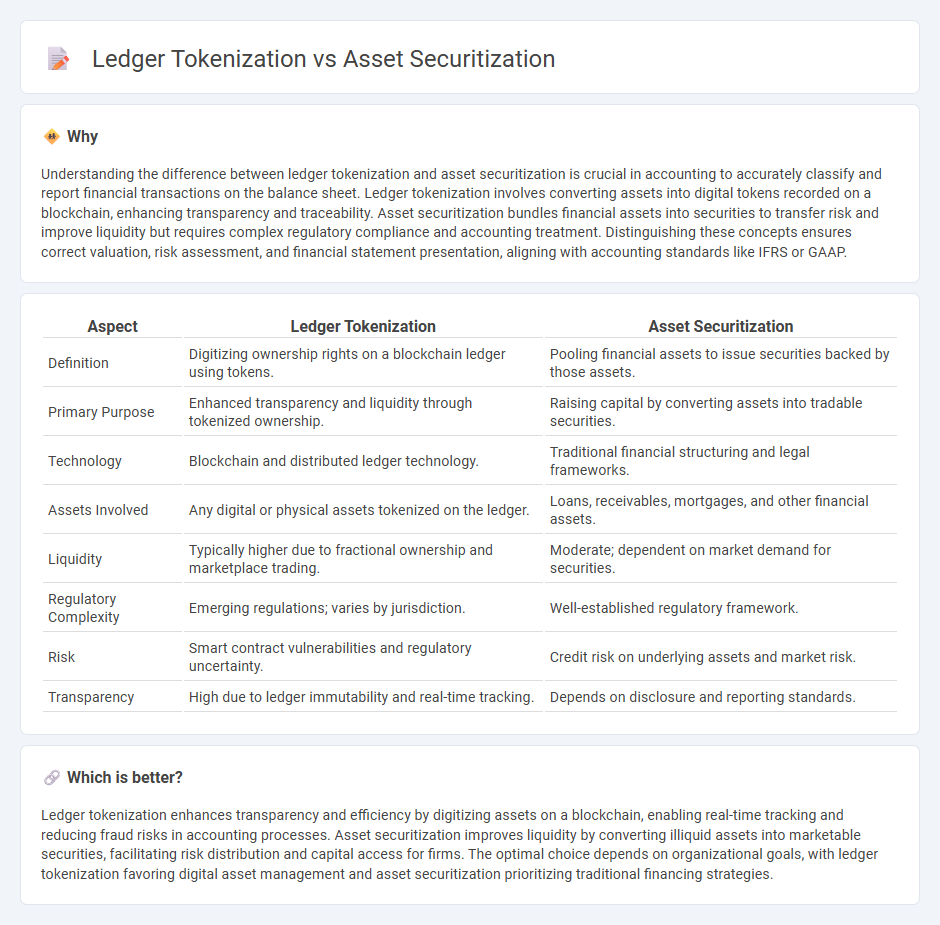
Understanding the difference between ledger tokenization and asset securitization is crucial in accounting to accurately classify and report financial transactions on the balance sheet. Ledger tokenization involves converting assets into digital tokens recorded on a blockchain, enhancing transparency and traceability. Asset securitization bundles financial assets into securities to transfer risk and improve liquidity but requires complex regulatory compliance and accounting treatment. Distinguishing these concepts ensures correct valuation, risk assessment, and financial statement presentation, aligning with accounting standards like IFRS or GAAP.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Ledger Tokenization | Asset Securitization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Digitizing ownership rights on a blockchain ledger using tokens. | Pooling financial assets to issue securities backed by those assets. |
| Primary Purpose | Enhanced transparency and liquidity through tokenized ownership. | Raising capital by converting assets into tradable securities. |
| Technology | Blockchain and distributed ledger technology. | Traditional financial structuring and legal frameworks. |
| Assets Involved | Any digital or physical assets tokenized on the ledger. | Loans, receivables, mortgages, and other financial assets. |
| Liquidity | Typically higher due to fractional ownership and marketplace trading. | Moderate; dependent on market demand for securities. |
| Regulatory Complexity | Emerging regulations; varies by jurisdiction. | Well-established regulatory framework. |
| Risk | Smart contract vulnerabilities and regulatory uncertainty. | Credit risk on underlying assets and market risk. |
| Transparency | High due to ledger immutability and real-time tracking. | Depends on disclosure and reporting standards. |
Which is better?
Ledger tokenization enhances transparency and efficiency by digitizing assets on a blockchain, enabling real-time tracking and reducing fraud risks in accounting processes. Asset securitization improves liquidity by converting illiquid assets into marketable securities, facilitating risk distribution and capital access for firms. The optimal choice depends on organizational goals, with ledger tokenization favoring digital asset management and asset securitization prioritizing traditional financing strategies.
Connection
Ledger tokenization transforms financial assets into digital tokens recorded on a blockchain ledger, enabling increased transparency and traceability. Asset securitization involves pooling these tokenized assets to create tradable securities, enhancing liquidity and market accessibility. This integration streamlines accounting processes by automating asset tracking and improving valuation accuracy.
Key Terms
Securitized Assets
Securitized assets involve pooling financial assets such as mortgages or loans and issuing securities backed by these assets, providing liquidity and risk distribution to investors. Ledger tokenization digitizes these assets on blockchain platforms, enhancing transparency, reducing transaction costs, and facilitating fractional ownership through secure digital tokens. Explore the evolving landscape of asset securitization and ledger tokenization for a deeper understanding of their impact on financial markets.
Digital Tokens
Asset securitization involves pooling financial assets to create tradable securities, enabling liquidity and risk distribution, while ledger tokenization converts physical or financial assets into blockchain-based digital tokens, enhancing transparency and efficiency. Digital tokens facilitate fractional ownership, real-time transfer, and reduce intermediaries, positioning them as innovative tools in digitized asset management. Explore how digital tokens are revolutionizing asset securitization and ledger tokenization to optimize investment strategies.
Ownership Rights
Asset securitization involves pooling financial assets into securities, transferring legal ownership rights to investors, which are enforceable through traditional regulatory frameworks. Ledger tokenization assigns digital tokens on blockchain platforms representing ownership rights, enabling fractional ownership, faster transfers, and transparent, immutable records. Explore the nuances of ownership rights in both models to understand their impact on investor control and asset liquidity.
Source and External Links
Securitization - Wikipedia - Asset securitization is the financial practice of pooling various types of contractual debt such as mortgages, auto loans, or credit card debt, and selling their related cash flows to third-party investors as securities, which may be bonds, pass-through securities, or collateralized debt obligations (CDOs), allowing credit risk to be spread and potentially reduced.
The ABCs of Asset-Backed Securities (ABS) - The securitization process begins with creating a special purpose vehicle (SPV) that purchases a pool of assets and issues the asset-backed securities (ABS) to fund the purchase, often structured with tranches and governed by specific contractual rules to manage cash flow and risk.
Back to basics: What Is Securitization? - Asset securitization involves an originator pooling income-producing assets and selling them to an issuer, typically an SPV, which finances the purchase by issuing securities to investors who receive payments funded by the cash flows from the underlying assets, often with the originator servicing the loans.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com