Integrated reporting combines financial data with environmental, social, and governance (ESG) information to provide a comprehensive view of a company's overall value creation and sustainability. Financial reporting focuses primarily on historical financial performance, adhering to standardized accounting principles such as GAAP or IFRS to ensure accuracy and comparability. Explore how integrated reporting transforms transparency and decision-making beyond traditional financial statements.
Why it is important
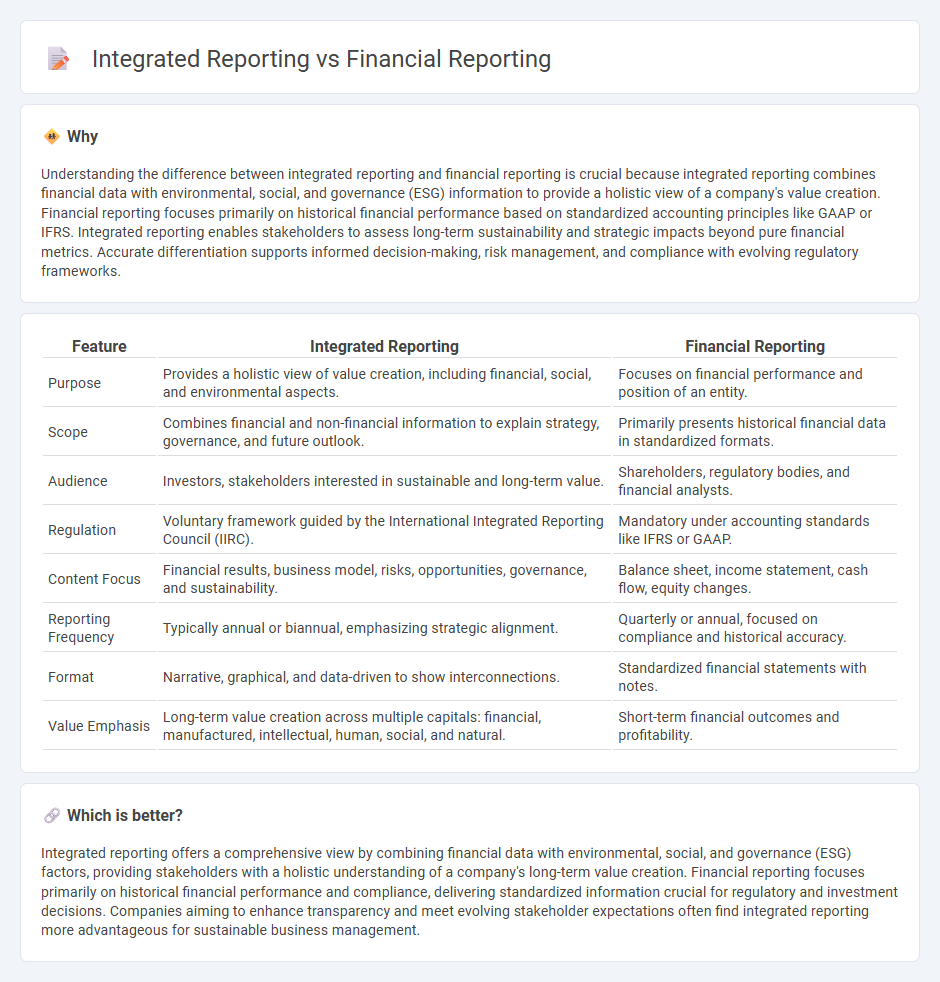
Understanding the difference between integrated reporting and financial reporting is crucial because integrated reporting combines financial data with environmental, social, and governance (ESG) information to provide a holistic view of a company's value creation. Financial reporting focuses primarily on historical financial performance based on standardized accounting principles like GAAP or IFRS. Integrated reporting enables stakeholders to assess long-term sustainability and strategic impacts beyond pure financial metrics. Accurate differentiation supports informed decision-making, risk management, and compliance with evolving regulatory frameworks.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Integrated Reporting | Financial Reporting |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Provides a holistic view of value creation, including financial, social, and environmental aspects. | Focuses on financial performance and position of an entity. |
| Scope | Combines financial and non-financial information to explain strategy, governance, and future outlook. | Primarily presents historical financial data in standardized formats. |
| Audience | Investors, stakeholders interested in sustainable and long-term value. | Shareholders, regulatory bodies, and financial analysts. |
| Regulation | Voluntary framework guided by the International Integrated Reporting Council (IIRC). | Mandatory under accounting standards like IFRS or GAAP. |
| Content Focus | Financial results, business model, risks, opportunities, governance, and sustainability. | Balance sheet, income statement, cash flow, equity changes. |
| Reporting Frequency | Typically annual or biannual, emphasizing strategic alignment. | Quarterly or annual, focused on compliance and historical accuracy. |
| Format | Narrative, graphical, and data-driven to show interconnections. | Standardized financial statements with notes. |
| Value Emphasis | Long-term value creation across multiple capitals: financial, manufactured, intellectual, human, social, and natural. | Short-term financial outcomes and profitability. |
Which is better?
Integrated reporting offers a comprehensive view by combining financial data with environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors, providing stakeholders with a holistic understanding of a company's long-term value creation. Financial reporting focuses primarily on historical financial performance and compliance, delivering standardized information crucial for regulatory and investment decisions. Companies aiming to enhance transparency and meet evolving stakeholder expectations often find integrated reporting more advantageous for sustainable business management.
Connection
Integrated reporting combines financial reporting with sustainability and non-financial information to provide a comprehensive view of an organization's value creation over time. It extends traditional financial reporting by incorporating environmental, social, and governance (ESG) metrics alongside financial data, enabling stakeholders to make more informed decisions. This connection enhances transparency and accountability, aligning corporate performance with long-term strategic goals.
Key Terms
**Financial Reporting:**
Financial reporting primarily involves the preparation and presentation of accurate financial statements, such as balance sheets, income statements, and cash flow statements, to stakeholders including investors, regulators, and management. It emphasizes historical financial performance, compliance with accounting standards like GAAP or IFRS, and transparent disclosure of financial data to facilitate decision-making. Discover how financial reporting contrasts with integrated reporting and its implications for business transparency and strategy.
Financial Statements
Financial reporting primarily emphasizes the preparation and presentation of financial statements, such as the balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement, to provide a clear snapshot of an organization's financial performance and position. Integrated reporting expands this scope by combining financial data with non-financial information, including environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors, to offer a comprehensive view of value creation over time. Explore the differences in depth to understand how each reporting approach supports stakeholder decision-making.
Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP)
Financial reporting primarily adheres to Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP), ensuring standardized, transparent, and comparable financial statements for investors and regulators. Integrated reporting expands beyond GAAP by combining financial data with environmental, social, and governance (ESG) metrics to provide a holistic view of an organization's value creation. Explore how integrating non-financial elements with GAAP-based financial data transforms corporate accountability and stakeholder communication.
Source and External Links
What Is Financial Reporting & Why Is It Important? - NetSuite - Financial reporting is the process of communicating financial information through statements like balance sheets, income statements, and cash flow statements used both internally by management and externally by investors, regulators, and other stakeholders, with external reports subject to strict standards.
What Is Financial Reporting? Definition, Importance, and Types - Financial reporting summarizes a company's financial performance and includes key statements such as the balance sheet, income statement, cash flows, and equity, aiming to provide complete, accurate, and timely information compliant with regulations like GAAP for external stakeholders.
What is Financial Reporting? I Planful - Financial reporting evaluates a company's financial data periodically to help executives, investors, and others make decisions by providing clear, accurate, and timely reports that reveal business health, trends, risks, and opportunities for growth.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com