Triple entry accounting enhances traditional double entry bookkeeping by integrating a cryptographic receipt for each transaction, ensuring transparency and reducing fraud risks. Blockchain accounting leverages decentralized ledger technology to provide immutable, real-time transaction records accessible to all participants. Explore the advantages and operational differences between these innovative accounting methods to understand their impact on financial accuracy and security.
Why it is important
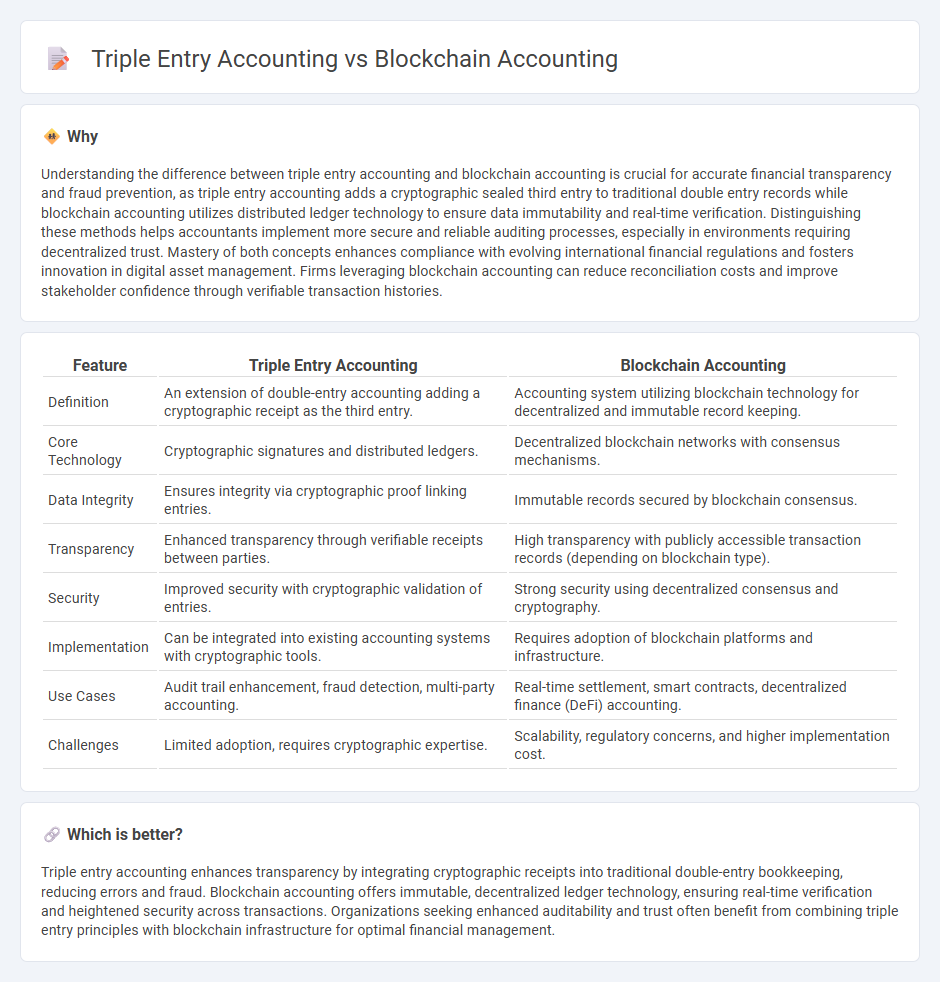
Understanding the difference between triple entry accounting and blockchain accounting is crucial for accurate financial transparency and fraud prevention, as triple entry accounting adds a cryptographic sealed third entry to traditional double entry records while blockchain accounting utilizes distributed ledger technology to ensure data immutability and real-time verification. Distinguishing these methods helps accountants implement more secure and reliable auditing processes, especially in environments requiring decentralized trust. Mastery of both concepts enhances compliance with evolving international financial regulations and fosters innovation in digital asset management. Firms leveraging blockchain accounting can reduce reconciliation costs and improve stakeholder confidence through verifiable transaction histories.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Triple Entry Accounting | Blockchain Accounting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | An extension of double-entry accounting adding a cryptographic receipt as the third entry. | Accounting system utilizing blockchain technology for decentralized and immutable record keeping. |
| Core Technology | Cryptographic signatures and distributed ledgers. | Decentralized blockchain networks with consensus mechanisms. |
| Data Integrity | Ensures integrity via cryptographic proof linking entries. | Immutable records secured by blockchain consensus. |
| Transparency | Enhanced transparency through verifiable receipts between parties. | High transparency with publicly accessible transaction records (depending on blockchain type). |
| Security | Improved security with cryptographic validation of entries. | Strong security using decentralized consensus and cryptography. |
| Implementation | Can be integrated into existing accounting systems with cryptographic tools. | Requires adoption of blockchain platforms and infrastructure. |
| Use Cases | Audit trail enhancement, fraud detection, multi-party accounting. | Real-time settlement, smart contracts, decentralized finance (DeFi) accounting. |
| Challenges | Limited adoption, requires cryptographic expertise. | Scalability, regulatory concerns, and higher implementation cost. |
Which is better?
Triple entry accounting enhances transparency by integrating cryptographic receipts into traditional double-entry bookkeeping, reducing errors and fraud. Blockchain accounting offers immutable, decentralized ledger technology, ensuring real-time verification and heightened security across transactions. Organizations seeking enhanced auditability and trust often benefit from combining triple entry principles with blockchain infrastructure for optimal financial management.
Connection
Triple entry accounting enhances traditional double entry bookkeeping by introducing a third, cryptographically secured ledger entry that ensures data integrity and transparency. Blockchain accounting leverages this concept by recording transactions on a decentralized, immutable ledger, enabling real-time verification and reducing the risk of fraud. The integration of triple entry accounting with blockchain technology creates a tamper-proof audit trail, improving trust and accountability in financial reporting.
Key Terms
Immutable Ledger
Blockchain accounting leverages an immutable ledger that records every transaction in a decentralized and tamper-proof manner, enhancing transparency and reducing fraud risks. Triple entry accounting introduces a third record, the blockchain receipt, which validates the traditional double-entry bookkeeping by providing cryptographic proof of each transaction. Discover how this innovative approach transforms financial auditing and accountability by exploring the core principles of immutable ledger technology.
Cryptographic Receipts
Blockchain accounting leverages cryptographic receipts to ensure tamper-proof transaction records by embedding digital signatures within a decentralized ledger, enhancing transparency and auditability. Triple entry accounting incorporates a third ledger entry--cryptographic receipts--that acts as an immutable proof of transaction, reducing fraud and reconciliation errors in financial reporting. Explore the detailed benefits and implementation of cryptographic receipts in modern accounting systems to optimize accuracy and trust.
Real-time Reconciliation
Blockchain accounting enables real-time reconciliation by recording immutable and time-stamped transactions across a decentralized ledger, reducing discrepancies and enhancing transparency. Triple entry accounting integrates a cryptographic receipt shared between transacting parties, creating a third entry that ensures data accuracy and instant verification of financial records. Explore the advantages and implementation strategies of these innovative accounting frameworks to optimize financial transparency and efficiency.
Source and External Links
Blockchain in Accounting: Transforming Financial Practices - Blockchain provides a secure, transparent, and immutable ledger that streamlines accounting processes such as transaction recording, audit trails, automated reconciliations, fraud detection, and financial reporting by enabling real-time verification and smart contract automation.
What is Blockchain Accounting? - Blockchain accounting enhances traditional accounting workflows by offering verifiable and tamper-proof record-keeping, greatly aiding audit accuracy and efficiency, though it does not replace the need for professional judgment on transaction context and categorization.
Blockchain Accounting - Guide & Use Cases - The use of blockchain in accounting facilitates a triple-entry bookkeeping system with immutable, consensus-secured data that improves fraud prevention, automates processes via smart contracts, and reduces costs related to reconciliation and auditing.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com