Forensic analytics involves analyzing financial data to detect fraud, errors, and irregularities, using advanced tools and techniques like data mining and predictive modeling. Internal controls comprise the policies and procedures implemented within an organization to safeguard assets, ensure financial accuracy, and promote operational efficiency. Explore the key distinctions and applications of forensic analytics and internal controls to enhance your accounting practices.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between forensic analytics and internal controls is crucial for accurately detecting and preventing financial fraud within an organization. Forensic analytics involves analyzing financial data to investigate and uncover suspicious activities, while internal controls are systematic procedures designed to safeguard assets and ensure accurate financial reporting. Knowledge of both disciplines enhances an organization's ability to identify risks, maintain compliance with regulatory standards, and protect shareholder value. Effective implementation reduces the likelihood of financial misstatements and promotes operational transparency.
Comparison Table
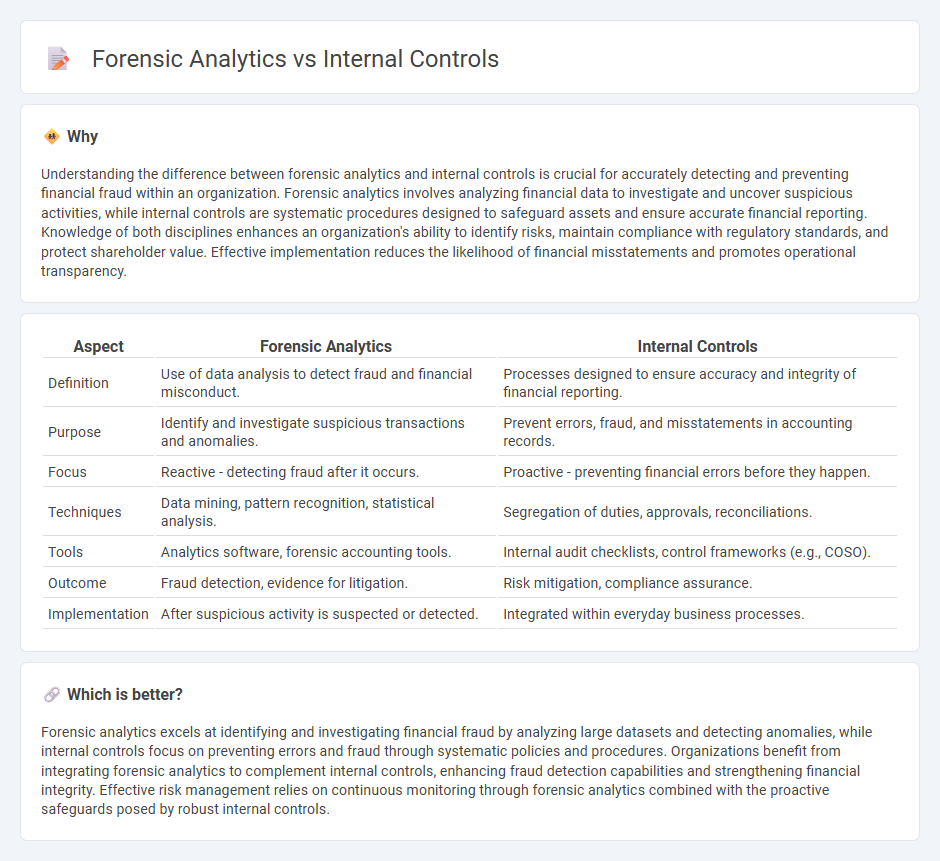
| Aspect | Forensic Analytics | Internal Controls |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Use of data analysis to detect fraud and financial misconduct. | Processes designed to ensure accuracy and integrity of financial reporting. |
| Purpose | Identify and investigate suspicious transactions and anomalies. | Prevent errors, fraud, and misstatements in accounting records. |
| Focus | Reactive - detecting fraud after it occurs. | Proactive - preventing financial errors before they happen. |
| Techniques | Data mining, pattern recognition, statistical analysis. | Segregation of duties, approvals, reconciliations. |
| Tools | Analytics software, forensic accounting tools. | Internal audit checklists, control frameworks (e.g., COSO). |
| Outcome | Fraud detection, evidence for litigation. | Risk mitigation, compliance assurance. |
| Implementation | After suspicious activity is suspected or detected. | Integrated within everyday business processes. |
Which is better?
Forensic analytics excels at identifying and investigating financial fraud by analyzing large datasets and detecting anomalies, while internal controls focus on preventing errors and fraud through systematic policies and procedures. Organizations benefit from integrating forensic analytics to complement internal controls, enhancing fraud detection capabilities and strengthening financial integrity. Effective risk management relies on continuous monitoring through forensic analytics combined with the proactive safeguards posed by robust internal controls.
Connection
Forensic analytics enhances internal controls by systematically identifying anomalies and fraud through data analysis, thereby strengthening an organization's risk management framework. Effective internal controls provide the foundational processes and checkpoints that forensic analytics tools leverage to detect irregular patterns and potential misconduct. Integrating forensic analytics with internal controls leads to proactive fraud detection and improved financial accuracy.
Key Terms
Internal controls:
Internal controls involve systematic processes and procedures designed to safeguard assets, ensure accuracy in financial reporting, and promote operational efficiency within an organization. These controls include preventive and detective measures such as segregation of duties, authorization protocols, and regular reconciliations to reduce risks of fraud and errors. Explore further to understand how robust internal controls enhance organizational governance and compliance.
Segregation of duties
Internal controls emphasize segregation of duties by assigning distinct responsibilities to different employees to minimize risks of errors and fraud. Forensic analytics complements this by analyzing transaction data to detect violations of duty segregation, uncovering patterns that suggest collusion or unauthorized access. Explore how integrating these approaches enhances organizational integrity and fraud prevention.
Authorization
Internal controls ensure authorization processes are standardized and consistently applied, minimizing risks of unauthorized access or transactions. Forensic analytics investigates anomalies or patterns within authorization data to detect potential fraud or policy violations. Explore in-depth how each approach strengthens organizational security and compliance frameworks.
Source and External Links
The Essential Guide to Internal Audit and Controls - AuditBoard - Internal controls are systems of policies and procedures designed to mitigate risks and achieve business objectives, including elements like control environment, risk assessment, control activities, information and communication, and monitoring for ongoing effectiveness.
Internal control - Wikipedia - Internal control encompasses all measures by which an organization directs and monitors its resources to manage risk, with responsibilities shared across management, employees, and the board of directors to ensure integrity and compliance.
Top Ten Things to Strengthen Internal Controls in the Office - Key practices include segregating duties to prevent fraud and errors, maintaining written procedures for consistency, and performing regular reconciliations and reviews to detect and resolve discrepancies promptly.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com