Ledger tokenization enhances data security by converting financial entries into unique cryptographic tokens, reducing exposure to fraud and unauthorized access. Auditable trails ensure transparency and compliance by maintaining detailed, tamper-evident records of all transaction activities. Explore how integrating these technologies can revolutionize accuracy and trust in accounting systems.
Why it is important
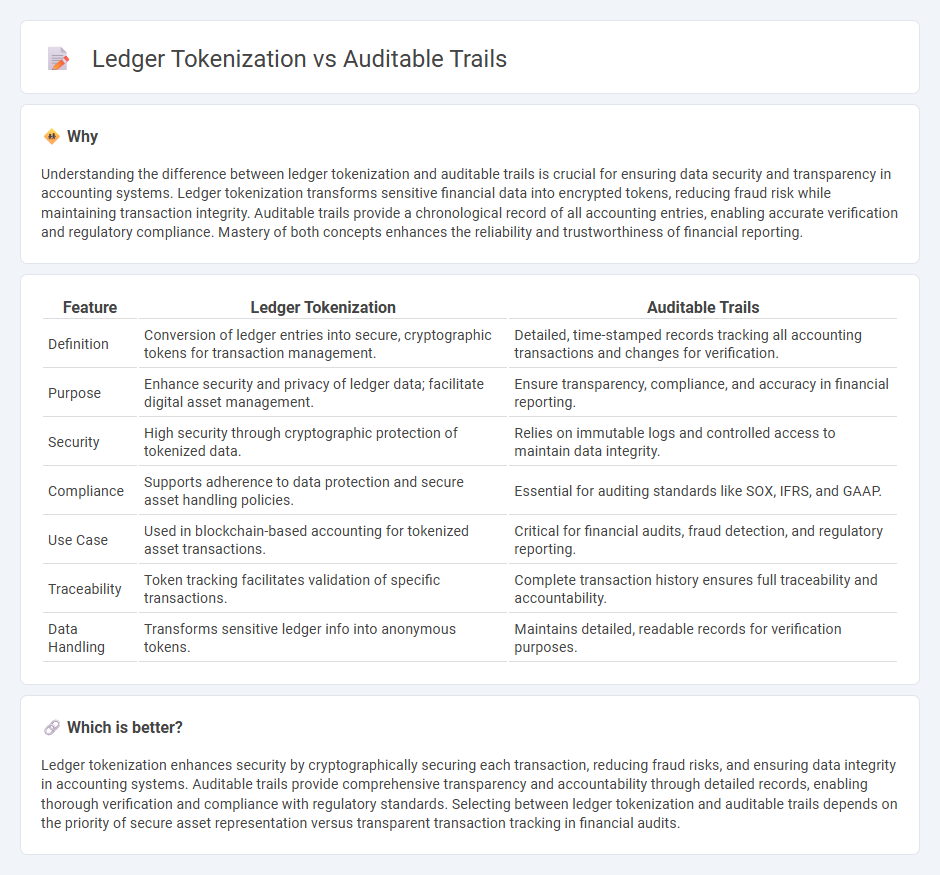
Understanding the difference between ledger tokenization and auditable trails is crucial for ensuring data security and transparency in accounting systems. Ledger tokenization transforms sensitive financial data into encrypted tokens, reducing fraud risk while maintaining transaction integrity. Auditable trails provide a chronological record of all accounting entries, enabling accurate verification and regulatory compliance. Mastery of both concepts enhances the reliability and trustworthiness of financial reporting.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Ledger Tokenization | Auditable Trails |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Conversion of ledger entries into secure, cryptographic tokens for transaction management. | Detailed, time-stamped records tracking all accounting transactions and changes for verification. |
| Purpose | Enhance security and privacy of ledger data; facilitate digital asset management. | Ensure transparency, compliance, and accuracy in financial reporting. |
| Security | High security through cryptographic protection of tokenized data. | Relies on immutable logs and controlled access to maintain data integrity. |
| Compliance | Supports adherence to data protection and secure asset handling policies. | Essential for auditing standards like SOX, IFRS, and GAAP. |
| Use Case | Used in blockchain-based accounting for tokenized asset transactions. | Critical for financial audits, fraud detection, and regulatory reporting. |
| Traceability | Token tracking facilitates validation of specific transactions. | Complete transaction history ensures full traceability and accountability. |
| Data Handling | Transforms sensitive ledger info into anonymous tokens. | Maintains detailed, readable records for verification purposes. |
Which is better?
Ledger tokenization enhances security by cryptographically securing each transaction, reducing fraud risks, and ensuring data integrity in accounting systems. Auditable trails provide comprehensive transparency and accountability through detailed records, enabling thorough verification and compliance with regulatory standards. Selecting between ledger tokenization and auditable trails depends on the priority of secure asset representation versus transparent transaction tracking in financial audits.
Connection
Ledger tokenization enhances accounting accuracy by converting financial transactions into secure, tamper-evident digital tokens that represent assets or liabilities on a blockchain. These tokens create auditable trails by providing a transparent and immutable record of every transaction, simplifying verification and compliance processes. The integration of tokenized ledgers ensures real-time tracking and accountability, reducing the risk of fraud and errors in financial reporting.
Key Terms
**Auditable Trails:**
Auditable trails provide a comprehensive, immutable record of every transaction or change within a system, ensuring transparency and accountability for regulatory compliance and forensic analysis. They capture detailed metadata, timestamps, and user actions that help detect fraud, operational errors, or unauthorized access, enhancing overall security posture. Explore how auditable trails can transform your organization's data integrity and governance strategy.
Traceability
Auditable trails provide a detailed, time-stamped record of every transaction, ensuring complete traceability and accountability in digital processes. Ledger tokenization enhances this by converting assets into digital tokens recorded on a blockchain, offering immutable and transparent ownership records. Explore how these technologies transform traceability in asset management.
Record Integrity
Auditable trails provide a transparent, chronological record of transactions that ensure data provenance and prevent unauthorized alterations, thereby maintaining robust record integrity. Ledger tokenization enhances security by representing assets as cryptographic tokens on a blockchain, immutable and tamper-evident, which guarantees that each transaction is unique and verifiable. Explore more about how these technologies reinforce trust through impeccable record integrity.
Source and External Links
What is an Audit Trail? | HR & Payroll Glossary - Paylocity - An audit trail is a chronological, detailed, tamper-proof record of all transactions and financial activities within an organization, used to ensure data accuracy, accountability, fraud prevention, and regulatory compliance.
What Is an Audit Trail? Everything You Need to Know - AuditBoard - An audit trail includes time-stamped event records detailing what happened, who initiated it, and the results, capturing all actions in chronological order to support audits and investigations, often built-in to IT systems and configurable by administrators.
Audit trail - Wikipedia - An audit trail or log is a security-relevant chronological record providing documentary evidence of the sequence of activities affecting an operation or event, designed to be protected from unauthorized modification and accessible only under strict role-based controls.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com