Data lake reconciliation involves harmonizing large volumes of raw, unstructured data from diverse sources into a unified repository, optimizing data integrity and accessibility for advanced analytics. Account reconciliation focuses on the systematic comparison and validation of financial records to ensure accuracy, compliance, and detection of discrepancies in accounting statements. Explore further to understand how these reconciliation methods enhance financial data management and decision-making.
Why it is important
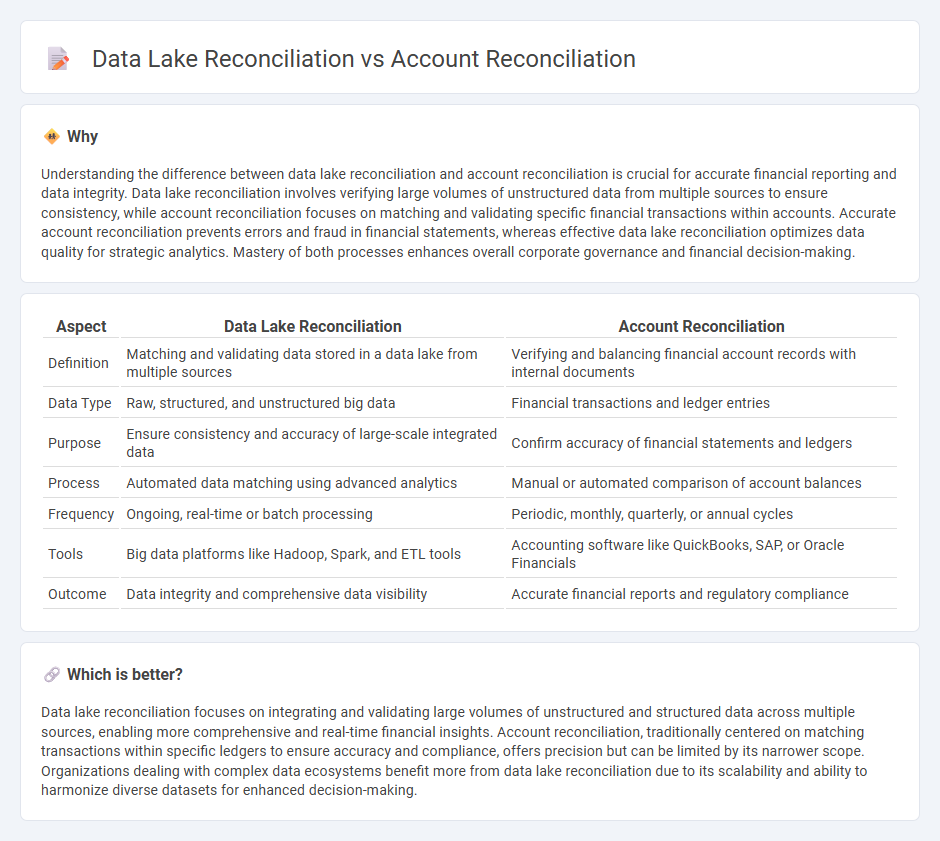
Understanding the difference between data lake reconciliation and account reconciliation is crucial for accurate financial reporting and data integrity. Data lake reconciliation involves verifying large volumes of unstructured data from multiple sources to ensure consistency, while account reconciliation focuses on matching and validating specific financial transactions within accounts. Accurate account reconciliation prevents errors and fraud in financial statements, whereas effective data lake reconciliation optimizes data quality for strategic analytics. Mastery of both processes enhances overall corporate governance and financial decision-making.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Data Lake Reconciliation | Account Reconciliation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Matching and validating data stored in a data lake from multiple sources | Verifying and balancing financial account records with internal documents |
| Data Type | Raw, structured, and unstructured big data | Financial transactions and ledger entries |
| Purpose | Ensure consistency and accuracy of large-scale integrated data | Confirm accuracy of financial statements and ledgers |
| Process | Automated data matching using advanced analytics | Manual or automated comparison of account balances |
| Frequency | Ongoing, real-time or batch processing | Periodic, monthly, quarterly, or annual cycles |
| Tools | Big data platforms like Hadoop, Spark, and ETL tools | Accounting software like QuickBooks, SAP, or Oracle Financials |
| Outcome | Data integrity and comprehensive data visibility | Accurate financial reports and regulatory compliance |
Which is better?
Data lake reconciliation focuses on integrating and validating large volumes of unstructured and structured data across multiple sources, enabling more comprehensive and real-time financial insights. Account reconciliation, traditionally centered on matching transactions within specific ledgers to ensure accuracy and compliance, offers precision but can be limited by its narrower scope. Organizations dealing with complex data ecosystems benefit more from data lake reconciliation due to its scalability and ability to harmonize diverse datasets for enhanced decision-making.
Connection
Data lake reconciliation enhances account reconciliation by providing a centralized repository for diverse financial data, ensuring data consistency and integrity across multiple sources. This integration allows accountants to efficiently compare transactional records against ledger entries, identifying discrepancies with greater accuracy. Leveraging data lakes accelerates the reconciliation process and improves financial reporting reliability.
Key Terms
**Account reconciliation:**
Account reconciliation involves verifying and matching financial records to ensure accuracy and consistency between internal accounts and external statements, enhancing the reliability of financial reporting. It is critical for detecting discrepancies, preventing fraud, and maintaining compliance with regulatory standards such as GAAP or IFRS. Explore more about the processes and benefits of account reconciliation to improve your organization's financial integrity.
Ledger balances
Account reconciliation ensures ledger balances accurately reflect financial transactions by comparing internal records with external statements, identifying discrepancies for correction. Data lake reconciliation involves validating and harmonizing large volumes of transactional data from diverse sources to maintain consistency and integrity across enterprise systems. Explore how leveraging advanced reconciliation techniques can optimize ledger accuracy and improve financial reporting.
Supporting documents
Account reconciliation relies heavily on supporting documents such as invoices, receipts, and bank statements to verify transaction accuracy and resolve discrepancies. Data lake reconciliation involves validating large volumes of raw data from diverse sources, often requiring metadata and data lineage documentation to ensure data integrity. Explore our detailed comparison to understand the nuances of supporting documentation in both reconciliation processes.
Source and External Links
What is Account Reconciliation? | F&A Glossary - BlackLine - Account reconciliation is the process of comparing an account balance with specified source data, such as invoices and bank statements, to ensure the balance is complete and accurate, frequently performed at the end of accounting periods for verification.
What Is Account Reconciliation? The Clear Guide to All You Need - Account reconciliation involves comparing two sets of financial records, such as bank statements or vendor records, to ensure figures match and discrepancies are identified and corrected, which maintains accuracy and prevents fraud.
What is Account Reconciliation? Meaning and Steps | Versapay - Account reconciliation can be done by either documentation review, comparing each transaction to supporting documents, or analytics review, using statistical methods to detect errors or discrepancies in account activity.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com