Liquidity sweep strategies target capturing large volumes by rapidly executing trades within available liquidity pools, minimizing market impact and price slippage. Time-weighted average price (TWAP) algorithms focus on evenly distributing trade execution over a specific time interval to achieve a price close to the average market price. Explore deeper insights into liquidity sweep and TWAP to optimize your trading approach.
Why it is important
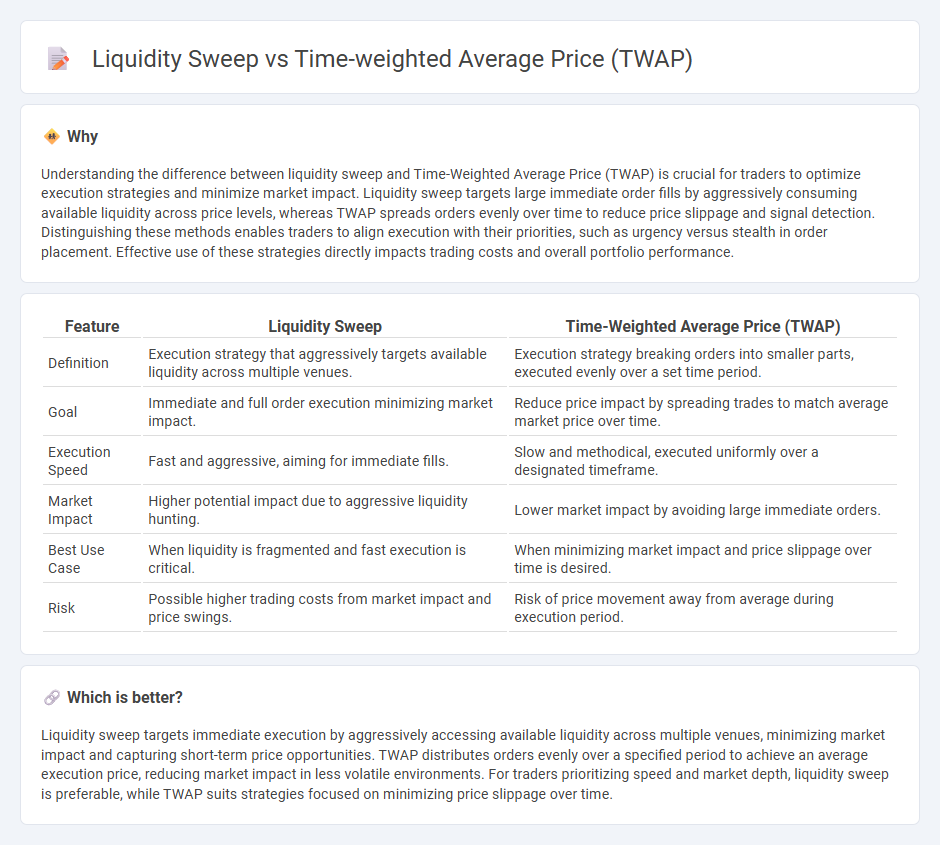
Understanding the difference between liquidity sweep and Time-Weighted Average Price (TWAP) is crucial for traders to optimize execution strategies and minimize market impact. Liquidity sweep targets large immediate order fills by aggressively consuming available liquidity across price levels, whereas TWAP spreads orders evenly over time to reduce price slippage and signal detection. Distinguishing these methods enables traders to align execution with their priorities, such as urgency versus stealth in order placement. Effective use of these strategies directly impacts trading costs and overall portfolio performance.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Liquidity Sweep | Time-Weighted Average Price (TWAP) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Execution strategy that aggressively targets available liquidity across multiple venues. | Execution strategy breaking orders into smaller parts, executed evenly over a set time period. |
| Goal | Immediate and full order execution minimizing market impact. | Reduce price impact by spreading trades to match average market price over time. |
| Execution Speed | Fast and aggressive, aiming for immediate fills. | Slow and methodical, executed uniformly over a designated timeframe. |
| Market Impact | Higher potential impact due to aggressive liquidity hunting. | Lower market impact by avoiding large immediate orders. |
| Best Use Case | When liquidity is fragmented and fast execution is critical. | When minimizing market impact and price slippage over time is desired. |
| Risk | Possible higher trading costs from market impact and price swings. | Risk of price movement away from average during execution period. |
Which is better?
Liquidity sweep targets immediate execution by aggressively accessing available liquidity across multiple venues, minimizing market impact and capturing short-term price opportunities. TWAP distributes orders evenly over a specified period to achieve an average execution price, reducing market impact in less volatile environments. For traders prioritizing speed and market depth, liquidity sweep is preferable, while TWAP suits strategies focused on minimizing price slippage over time.
Connection
Liquidity sweep strategies utilize rapid order execution to capture available market liquidity, while time-weighted average price (TWAP) algorithms spread trades evenly over a specified time to minimize market impact. TWAP can trigger liquidity sweeps during volatility spikes to execute large orders without significantly affecting price. The integration of liquidity sweep techniques within TWAP algorithms enhances execution efficiency by balancing price impact and timing in high-frequency trading environments.
Key Terms
Execution Algorithm
Time-weighted average price (TWAP) execution algorithms break large orders into smaller trades distributed evenly over a set period, minimizing market impact and tracking an average price over time. Liquidity sweep algorithms aggressively target available liquidity across multiple price levels and venues to execute quickly, prioritizing immediacy over price stability. Explore detailed comparisons and implementation strategies to optimize trading outcomes with these execution algorithms.
Order Book
Time-weighted average price (TWAP) executes trades evenly over a set period to minimize market impact, relying on time intervals and volume distribution without aggressively consuming the order book. Liquidity sweep strategies rapidly consume available liquidity at multiple price levels within the order book, aiming to fill large orders swiftly but potentially causing price slippage and market disturbance. Explore further how these order execution tactics influence trading efficiency and market dynamics.
Market Impact
Time-weighted average price (TWAP) minimizes market impact by slicing large orders into smaller, evenly spaced trades over a set period, reducing price distortion in highly liquid markets. Liquidity sweep targets immediate liquidity by quickly consuming available orders across price levels, often causing notable price shifts due to aggressive execution. Explore detailed comparisons and strategic insights to optimize execution and mitigate market impact effectively.
Source and External Links
TWAP vs. VWAP Price Algorithms - Chainlink - TWAP (Time-Weighted Average Price) is a pricing algorithm that calculates the average price of an asset over a set period by summing prices at multiple points and dividing by the number of points, commonly used both as a pricing mechanism and a trading strategy to minimize market impact when executing large orders.
Time-Weighted Average Price Trading Strategies - TrendSpider - TWAP is a trading indicator averaging an asset's price over time by dividing the total trade value by total volume during a period, often employed in algorithmic trading to minimize market disruption and potential adverse price changes during large trades.
Comparing Global VWAP and TWAP for Better Trade Execution - TWAP calculates an average price over a time interval by weighting each time slice equally regardless of volume, making it useful for executing large orders evenly over time to reduce slippage and avoid chasing volume spikes.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com