Volatility harvesting capitalizes on market fluctuations by systematically trading assets to exploit price changes, while options straddles involve purchasing both call and put options at the same strike price to profit from expected volatility regardless of direction. This strategic contrast reveals volatility harvesting as a dynamic approach focused on ongoing rebalancing, whereas straddles offer a defined-risk opportunity tied to significant price movements. Discover more about these trading strategies to enhance your market positioning and risk management.
Why it is important
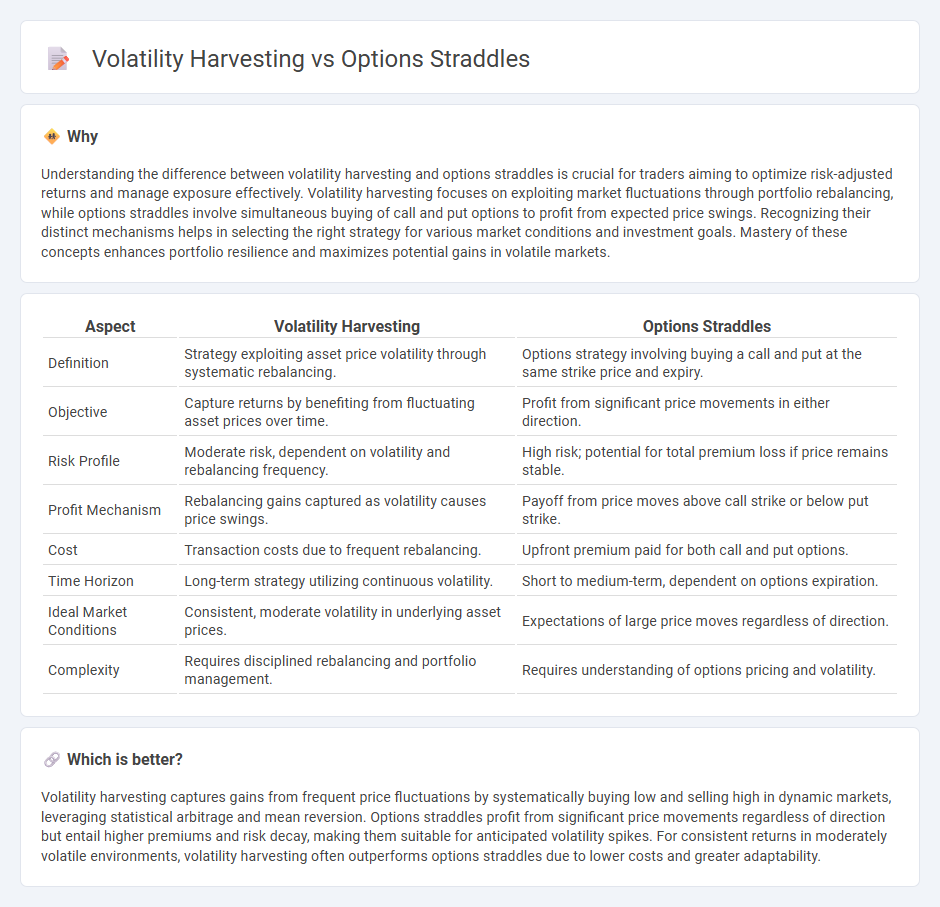
Understanding the difference between volatility harvesting and options straddles is crucial for traders aiming to optimize risk-adjusted returns and manage exposure effectively. Volatility harvesting focuses on exploiting market fluctuations through portfolio rebalancing, while options straddles involve simultaneous buying of call and put options to profit from expected price swings. Recognizing their distinct mechanisms helps in selecting the right strategy for various market conditions and investment goals. Mastery of these concepts enhances portfolio resilience and maximizes potential gains in volatile markets.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Volatility Harvesting | Options Straddles |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Strategy exploiting asset price volatility through systematic rebalancing. | Options strategy involving buying a call and put at the same strike price and expiry. |
| Objective | Capture returns by benefiting from fluctuating asset prices over time. | Profit from significant price movements in either direction. |
| Risk Profile | Moderate risk, dependent on volatility and rebalancing frequency. | High risk; potential for total premium loss if price remains stable. |
| Profit Mechanism | Rebalancing gains captured as volatility causes price swings. | Payoff from price moves above call strike or below put strike. |
| Cost | Transaction costs due to frequent rebalancing. | Upfront premium paid for both call and put options. |
| Time Horizon | Long-term strategy utilizing continuous volatility. | Short to medium-term, dependent on options expiration. |
| Ideal Market Conditions | Consistent, moderate volatility in underlying asset prices. | Expectations of large price moves regardless of direction. |
| Complexity | Requires disciplined rebalancing and portfolio management. | Requires understanding of options pricing and volatility. |
Which is better?
Volatility harvesting captures gains from frequent price fluctuations by systematically buying low and selling high in dynamic markets, leveraging statistical arbitrage and mean reversion. Options straddles profit from significant price movements regardless of direction but entail higher premiums and risk decay, making them suitable for anticipated volatility spikes. For consistent returns in moderately volatile environments, volatility harvesting often outperforms options straddles due to lower costs and greater adaptability.
Connection
Volatility harvesting exploits market fluctuations to generate returns by systematically rebalancing portfolios during periods of changing volatility. Options straddles, which involve simultaneous buying of call and put options at the same strike price, directly benefit from increased volatility as they profit from significant price movements in either direction. Combining volatility harvesting strategies with options straddles enhances the ability to capture gains from unpredictable market swings by leveraging the intrinsic link between volatility and option pricing.
Key Terms
Implied Volatility
Options straddles capitalize on anticipated increases in implied volatility by purchasing both call and put options at the same strike price and expiration date, benefiting from significant price movements regardless of direction. Volatility harvesting involves systematically exploiting discrepancies between implied and realized volatility, often through dynamic option strategies to generate consistent returns. Dive deeper to understand how implied volatility influences these strategies and their practical applications in trading.
Delta Neutral
Options straddles involve buying both a call and put option at the same strike price and expiration, capitalizing on significant price movements regardless of direction, while volatility harvesting focuses on capturing returns from fluctuations in volatility through strategic option trades without market exposure. Delta neutral strategies aim to maintain a portfolio with near-zero sensitivity to underlying asset price changes, often implemented by combining options with offsetting delta values to balance directional risk. Explore how delta neutral approaches optimize gains in volatile markets by managing risk precisely and enhancing volatility capture efficiency.
Theta Decay
Options straddles involve simultaneously buying a call and put option at the same strike price, profiting from significant volatility but suffering from Theta decay as time erodes option values. Volatility harvesting strategies exploit moments of realized volatility divergence without being as negatively impacted by Theta decay, as they often involve more dynamic adjustments and short-term trading horizons. Explore the nuances of Theta decay in options strategies and how it impacts profitability in volatility harvesting versus straddles.
Source and External Links
What is a Straddle Options Strategy & How to Use it? - tastylive - A straddle involves simultaneously buying or selling a call and a put option with the same strike price and expiration date; a long straddle profits from big price moves in either direction, while a short straddle profits if the price remains stable.
Straddle - Wikipedia - A straddle strategy consists of purchasing or selling a call and put option with the same strike and expiry, designed to profit from significant price movement regardless of direction, with long straddles benefiting from volatility and short straddles profiting from stability.
Straddle - Definition, How to Create It, Examples - The straddle strategy involves buying or selling both call and put options for the same underlying with the same expiry and strike, used when an investor expects substantial price fluctuations but is unsure of direction.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com