Dark pool activity involves private trading venues where large orders are executed away from public exchanges to minimize market impact and maintain anonymity, often attracting institutional investors seeking discretion. Liquidity provision refers to market participants, such as market makers, who supply buy and sell orders to ensure smoother trading and tighter bid-ask spreads, enhancing overall market efficiency. Discover how dark pool activity and liquidity provision shape trading strategies and market dynamics.
Why it is important
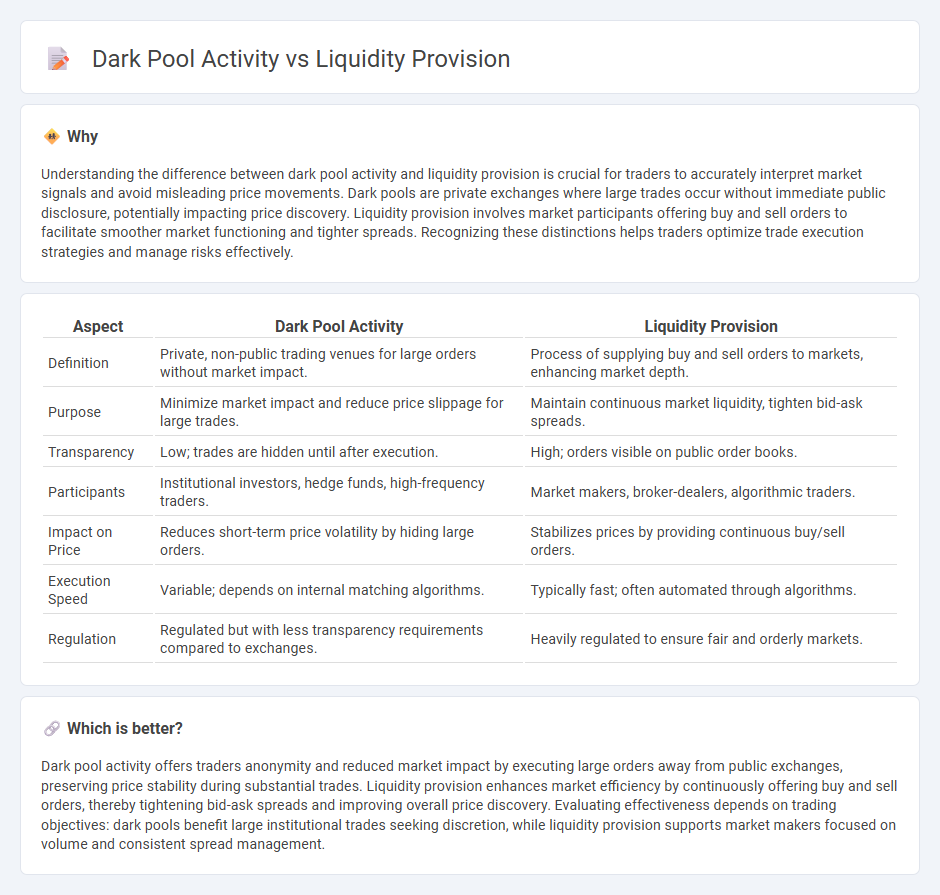
Understanding the difference between dark pool activity and liquidity provision is crucial for traders to accurately interpret market signals and avoid misleading price movements. Dark pools are private exchanges where large trades occur without immediate public disclosure, potentially impacting price discovery. Liquidity provision involves market participants offering buy and sell orders to facilitate smoother market functioning and tighter spreads. Recognizing these distinctions helps traders optimize trade execution strategies and manage risks effectively.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Dark Pool Activity | Liquidity Provision |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Private, non-public trading venues for large orders without market impact. | Process of supplying buy and sell orders to markets, enhancing market depth. |
| Purpose | Minimize market impact and reduce price slippage for large trades. | Maintain continuous market liquidity, tighten bid-ask spreads. |
| Transparency | Low; trades are hidden until after execution. | High; orders visible on public order books. |
| Participants | Institutional investors, hedge funds, high-frequency traders. | Market makers, broker-dealers, algorithmic traders. |
| Impact on Price | Reduces short-term price volatility by hiding large orders. | Stabilizes prices by providing continuous buy/sell orders. |
| Execution Speed | Variable; depends on internal matching algorithms. | Typically fast; often automated through algorithms. |
| Regulation | Regulated but with less transparency requirements compared to exchanges. | Heavily regulated to ensure fair and orderly markets. |
Which is better?
Dark pool activity offers traders anonymity and reduced market impact by executing large orders away from public exchanges, preserving price stability during substantial trades. Liquidity provision enhances market efficiency by continuously offering buy and sell orders, thereby tightening bid-ask spreads and improving overall price discovery. Evaluating effectiveness depends on trading objectives: dark pools benefit large institutional trades seeking discretion, while liquidity provision supports market makers focused on volume and consistent spread management.
Connection
Dark pool activity significantly influences liquidity provision by allowing large institutional traders to execute sizeable orders without impacting public market prices. These private trading venues enhance overall market liquidity by reducing information leakage and minimizing price slippage. Increased dark pool participation often leads to tighter bid-ask spreads and improved execution quality within public exchanges.
Key Terms
Bid-Ask Spread
Liquidity provision directly impacts the bid-ask spread by narrowing it through continuous market-making activities, enhancing market efficiency and price stability. Dark pool activity, while providing large block trades with reduced market impact, often leads to wider bid-ask spreads on public exchanges due to reduced displayed liquidity. Explore the interplay between liquidity provision and dark pools to better understand their effects on market dynamics and trading costs.
Order Book Transparency
Liquidity provision enhances order book transparency by displaying available buy and sell orders, promoting price discovery and market efficiency. Dark pool activity, characterized by private trading venues, obscures order flow and reduces visibility, potentially impacting market fairness. Explore the nuances of order book transparency in different trading environments to optimize your market strategy.
Execution Price
Liquidity provision plays a crucial role in enhancing market efficiency by narrowing bid-ask spreads and stabilizing execution prices in transparent exchanges. Dark pool activity often offers large institutional traders the ability to execute significant orders with minimal market impact, though it may lead to price uncertainty due to limited pre-trade transparency. Explore the nuances of how liquidity provision and dark pools influence execution price dynamics for informed trading decisions.
Source and External Links
Liquidity Provision - Commercial Bank Financial Services - A Liquidity Provider is a financial institution acting as an intermediary to improve liquidity in the securities market by increasing market depth and trading volume for listed stocks.
DeFi Basics: Liquidity Provision - EMURGO - Liquidity provision in DeFi involves users depositing cryptocurrency into liquidity pools of decentralized protocols, enabling token swaps on demand, with providers earning fees from the platform.
Liquidity Provision by the Federal Reserve - Central banks provide liquidity during financial crises through mechanisms like open market operations or lending facilities to ensure institutions can meet payment demands and stabilize markets.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com