Delta-neutral strategies focus on minimizing exposure to price movements in the underlying asset by balancing long and short positions to achieve near-zero delta, reducing market risk and enhancing portfolio stability. Directional strategies involve taking clear positions based on anticipated price direction, aiming for profit through asset appreciation or depreciation, and often carry higher risk due to market volatility. Explore more to understand how these trading approaches can align with your investment goals and risk tolerance.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between delta-neutral strategies and directional strategies is crucial for effective risk management and tailored trade execution in financial markets. Delta-neutral strategies minimize exposure to price movements in the underlying asset, optimizing for income or volatility, while directional strategies capitalize on anticipated market trends for potential profit. Traders leverage delta-neutral approaches to hedge positions against market fluctuations, whereas directional strategies focus on forecasting price direction to maximize returns. Mastery of both strategy types enables informed decision-making aligned with specific investment goals and market conditions.
Comparison Table
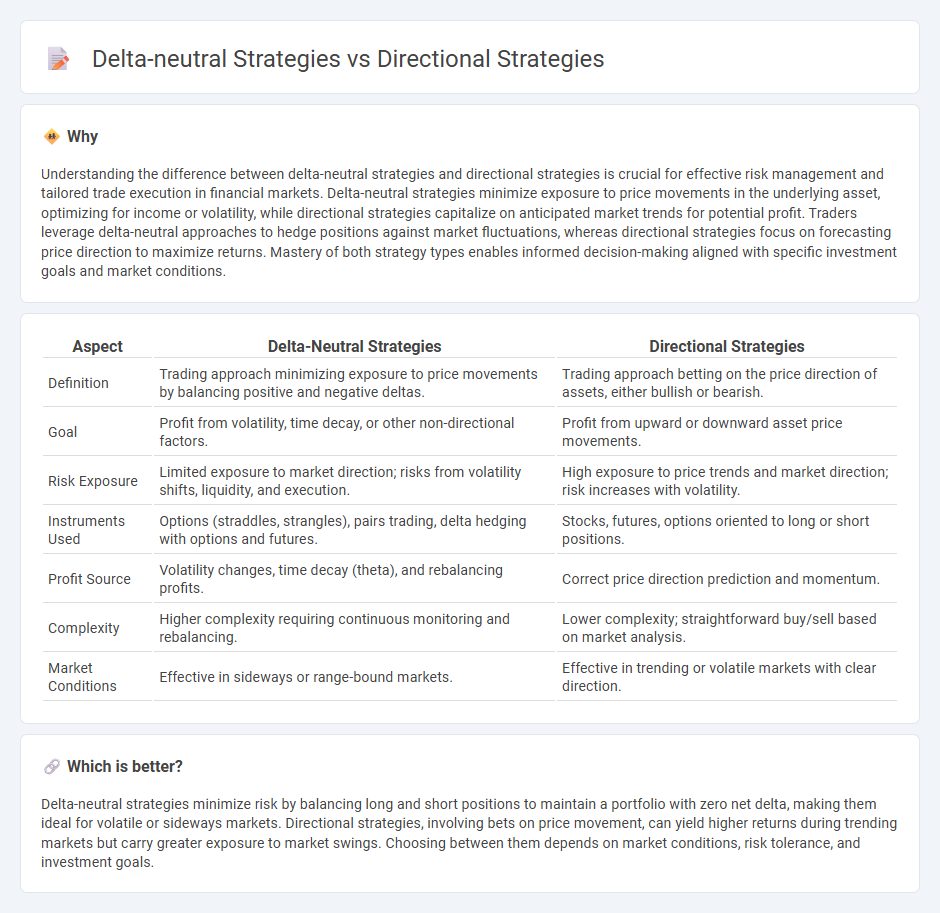
| Aspect | Delta-Neutral Strategies | Directional Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Trading approach minimizing exposure to price movements by balancing positive and negative deltas. | Trading approach betting on the price direction of assets, either bullish or bearish. |
| Goal | Profit from volatility, time decay, or other non-directional factors. | Profit from upward or downward asset price movements. |
| Risk Exposure | Limited exposure to market direction; risks from volatility shifts, liquidity, and execution. | High exposure to price trends and market direction; risk increases with volatility. |
| Instruments Used | Options (straddles, strangles), pairs trading, delta hedging with options and futures. | Stocks, futures, options oriented to long or short positions. |
| Profit Source | Volatility changes, time decay (theta), and rebalancing profits. | Correct price direction prediction and momentum. |
| Complexity | Higher complexity requiring continuous monitoring and rebalancing. | Lower complexity; straightforward buy/sell based on market analysis. |
| Market Conditions | Effective in sideways or range-bound markets. | Effective in trending or volatile markets with clear direction. |
Which is better?
Delta-neutral strategies minimize risk by balancing long and short positions to maintain a portfolio with zero net delta, making them ideal for volatile or sideways markets. Directional strategies, involving bets on price movement, can yield higher returns during trending markets but carry greater exposure to market swings. Choosing between them depends on market conditions, risk tolerance, and investment goals.
Connection
Delta-neutral strategies and directional strategies intersect through their approach to market exposure and risk management, with delta-neutral strategies aiming to hedge against price movements while directional strategies capitalize on anticipated market trends. Traders often integrate delta-neutral techniques within directional frameworks to fine-tune risk-reward profiles and enhance portfolio stability. This connection facilitates dynamic adjustments, enabling traders to optimize returns regardless of short-term market volatility.
Key Terms
Market Bias
Directional strategies involve taking positions based on a market bias, aiming to profit from expected price movements in a specific direction, such as bullish or bearish trends. Delta-neutral strategies, in contrast, seek to minimize exposure to market direction by balancing positive and negative delta positions, generating returns through volatility, time decay, or other factors independent of price direction. Explore more insights on aligning your trading approach with market bias to optimize risk and reward profiles.
Hedging
Directional strategies involve taking positions based on the anticipated price movement of an asset, exposing investors to market risk, while delta-neutral strategies aim to hedge this risk by maintaining a net zero delta, balancing long and short positions in options and underlying assets. Hedging using delta-neutral strategies minimizes exposure to price fluctuations by offsetting gains and losses in the portfolio, making it ideal for risk-averse investors seeking consistent returns. Explore more about optimizing hedging techniques with directional and delta-neutral strategies to enhance portfolio performance.
Delta
Directional strategies aim to profit from significant price movements in an asset, leveraging the Delta by taking long or short positions to capture bullish or bearish trends. Delta-neutral strategies minimize exposure to price fluctuations by balancing positive and negative Delta positions, maintaining a net Delta close to zero to reduce risk from price changes. Discover how mastering Delta can optimize your trading approach and risk management.
Source and External Links
7 Types of Strategic Direction | Indeed.com - Directional strategies guide organizations toward a future vision by setting measurable short-, medium-, and long-term goals based on the company's mission and vision, involving stakeholders in the planning process.
Directional Trading Strategies - Corporate Finance Institute - Directional trading strategies involve betting on market movements, such as going long on rising prices or short on falling prices, using options strategies like bull calls to capitalize on predicted market direction.
What Is Directional Strategy? - Small Business - Chron.com - Directional strategies focus on achieving stability, growth, or retrenchment by targeting either vertical growth (deepening current market/customer base) or horizontal growth (expanding into new markets or products) to align with business goals.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com