Pair trading exploits price divergences between two correlated assets by simultaneously buying the undervalued asset and selling the overvalued one to profit from their convergence. Arbitrage involves exploiting price differences of the same asset across different markets or exchanges to achieve risk-free profits. Explore the nuances of pair trading and arbitrage strategies to enhance your trading approach.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between pair trading and arbitrage is crucial for optimizing trading strategies and managing risks effectively. Pair trading involves taking opposite positions in two correlated assets to capitalize on price divergences, while arbitrage exploits price inefficiencies between different markets or instruments for risk-free profit. Knowing these distinctions helps traders apply the right techniques for market conditions, enhancing profitability and minimizing exposure. Mastering both strategies enables informed decision-making in diverse market scenarios, increasing overall trading success.
Comparison Table
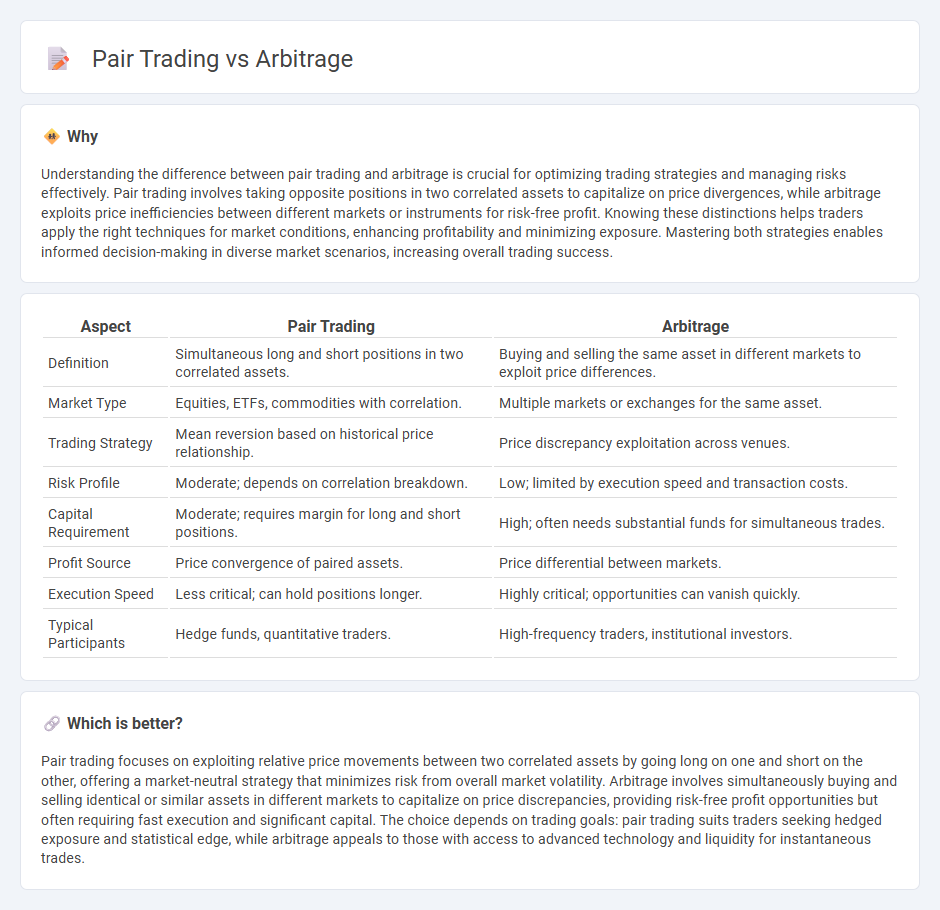
| Aspect | Pair Trading | Arbitrage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Simultaneous long and short positions in two correlated assets. | Buying and selling the same asset in different markets to exploit price differences. |
| Market Type | Equities, ETFs, commodities with correlation. | Multiple markets or exchanges for the same asset. |
| Trading Strategy | Mean reversion based on historical price relationship. | Price discrepancy exploitation across venues. |
| Risk Profile | Moderate; depends on correlation breakdown. | Low; limited by execution speed and transaction costs. |
| Capital Requirement | Moderate; requires margin for long and short positions. | High; often needs substantial funds for simultaneous trades. |
| Profit Source | Price convergence of paired assets. | Price differential between markets. |
| Execution Speed | Less critical; can hold positions longer. | Highly critical; opportunities can vanish quickly. |
| Typical Participants | Hedge funds, quantitative traders. | High-frequency traders, institutional investors. |
Which is better?
Pair trading focuses on exploiting relative price movements between two correlated assets by going long on one and short on the other, offering a market-neutral strategy that minimizes risk from overall market volatility. Arbitrage involves simultaneously buying and selling identical or similar assets in different markets to capitalize on price discrepancies, providing risk-free profit opportunities but often requiring fast execution and significant capital. The choice depends on trading goals: pair trading suits traders seeking hedged exposure and statistical edge, while arbitrage appeals to those with access to advanced technology and liquidity for instantaneous trades.
Connection
Pair trading and arbitrage are connected through their reliance on exploiting price inefficiencies between related financial instruments. Pair trading involves taking simultaneous long and short positions in correlated assets to profit from their relative price movements, while arbitrage seeks risk-free profits by exploiting price discrepancies across different markets or platforms. Both strategies require precise market timing and sophisticated analytical models to identify and capitalize on short-term mispricings.
Key Terms
Price Discrepancy
Arbitrage exploits price discrepancies of identical or similar assets across different markets, enabling risk-free profit through simultaneous buying and selling. Pair trading involves identifying two historically correlated securities and trading one long and the other short when their price relationship diverges, aiming to profit from reversion to the mean. Discover the key differences and strategies in price discrepancy exploitation by exploring deeper insights into arbitrage and pair trading techniques.
Correlation
Arbitrage exploits price discrepancies between identical or similar financial instruments across different markets, often with minimal correlation risk since the trades are designed to be risk-free. Pair trading relies heavily on the correlation between two co-moving stocks or assets, aiming to profit from the relative price movements when the correlation temporarily weakens or strengthens. Explore deeper insights into how correlation impacts these strategies and their risk management approaches.
Convergence
Arbitrage exploits price discrepancies of identical or similar assets across different markets to lock in risk-free profits, while pair trading relies on statistical convergence between correlated assets to identify entry and exit points. The convergence principle in pair trading assumes the price spread will revert to its historical mean, making it ideal for relative value strategies in equities and other correlated securities. Discover how mastering these convergence dynamics can enhance your trading strategies and risk management.
Source and External Links
Arbitrage - Wikipedia - Arbitrage is the practice of exploiting price differences of the same asset in different markets to make a risk-free profit.
What Is Arbitrage? 3 Strategies to Know - It is an investment strategy where an investor simultaneously buys and sells an asset in different markets to capitalize on price discrepancies and generate profit.
What is arbitrage and how does it work in financial markets | StoneX - Common forms include pure arbitrage (exploiting price gaps for the same asset), merger arbitrage (betting on acquisition outcomes), and triangular arbitrage (using currency exchange rate inconsistencies).
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com