Delta neutral strategy involves balancing a portfolio to offset directional market risk by combining positions in options and underlying assets, maintaining a net delta close to zero. Arbitrage exploits price discrepancies between related securities or markets to generate risk-free profits through simultaneous buying and selling. Explore the nuances of these strategies to enhance your trading expertise.
Why it is important
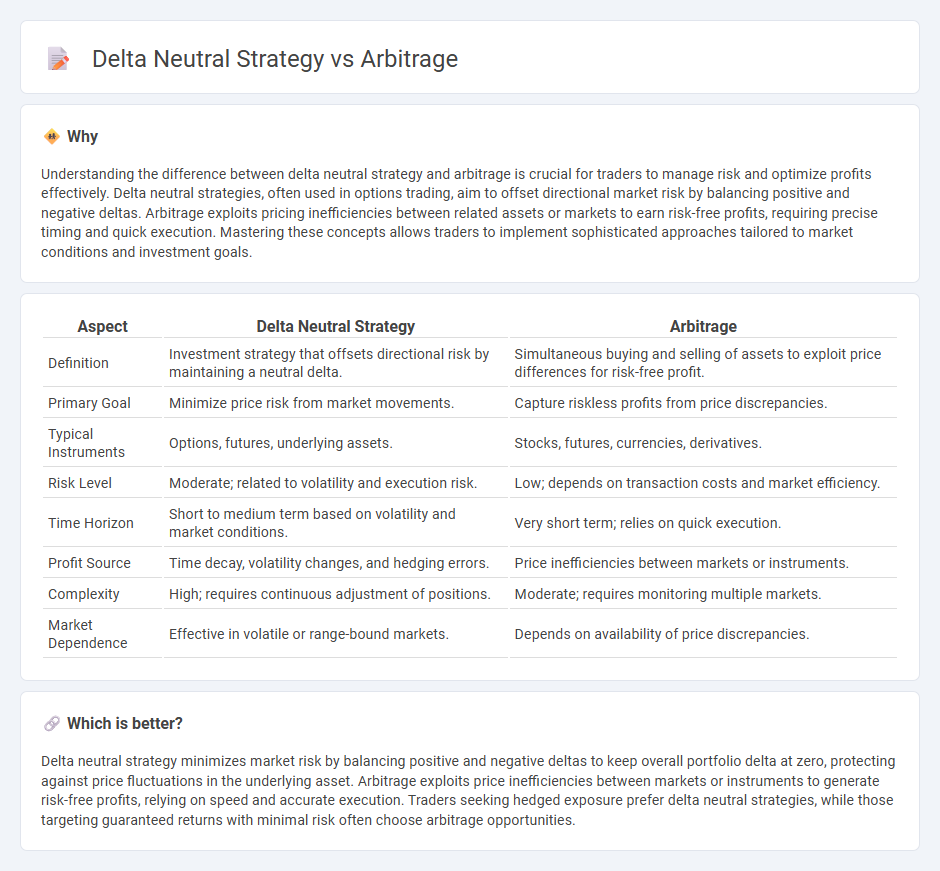
Understanding the difference between delta neutral strategy and arbitrage is crucial for traders to manage risk and optimize profits effectively. Delta neutral strategies, often used in options trading, aim to offset directional market risk by balancing positive and negative deltas. Arbitrage exploits pricing inefficiencies between related assets or markets to earn risk-free profits, requiring precise timing and quick execution. Mastering these concepts allows traders to implement sophisticated approaches tailored to market conditions and investment goals.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Delta Neutral Strategy | Arbitrage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Investment strategy that offsets directional risk by maintaining a neutral delta. | Simultaneous buying and selling of assets to exploit price differences for risk-free profit. |
| Primary Goal | Minimize price risk from market movements. | Capture riskless profits from price discrepancies. |
| Typical Instruments | Options, futures, underlying assets. | Stocks, futures, currencies, derivatives. |
| Risk Level | Moderate; related to volatility and execution risk. | Low; depends on transaction costs and market efficiency. |
| Time Horizon | Short to medium term based on volatility and market conditions. | Very short term; relies on quick execution. |
| Profit Source | Time decay, volatility changes, and hedging errors. | Price inefficiencies between markets or instruments. |
| Complexity | High; requires continuous adjustment of positions. | Moderate; requires monitoring multiple markets. |
| Market Dependence | Effective in volatile or range-bound markets. | Depends on availability of price discrepancies. |
Which is better?
Delta neutral strategy minimizes market risk by balancing positive and negative deltas to keep overall portfolio delta at zero, protecting against price fluctuations in the underlying asset. Arbitrage exploits price inefficiencies between markets or instruments to generate risk-free profits, relying on speed and accurate execution. Traders seeking hedged exposure prefer delta neutral strategies, while those targeting guaranteed returns with minimal risk often choose arbitrage opportunities.
Connection
A delta neutral strategy involves creating a portfolio where the overall delta--sensitivity to price movements of the underlying asset--is zero, minimizing directional risk. Arbitrage exploits price discrepancies between related markets or instruments, often employing delta neutral positions to lock in risk-free profits. Combining these approaches allows traders to hedge market exposure while capitalizing on temporary inefficiencies in asset pricing.
Key Terms
**Arbitrage:**
Arbitrage involves exploiting price discrepancies of the same asset across different markets to secure risk-free profits, often through simultaneous buying and selling. This strategy capitalizes on inefficiencies in market pricing, using techniques such as statistical arbitrage, spatial arbitrage, or merger arbitrage. Discover comprehensive insights into how arbitrage can maximize returns while minimizing exposure.
Price Discrepancy
Arbitrage strategies exploit price discrepancies between two or more markets by simultaneously buying low and selling high to lock in risk-free profits, capitalizing on market inefficiencies. Delta neutral strategies aim to hedge portfolio risks by balancing positive and negative delta positions, minimizing exposure to price movements in the underlying asset rather than focusing on price differences. To explore how these approaches uniquely manage risk and profit, discover detailed insights on price discrepancy arbitrage and delta neutral techniques.
Risk-Free Profit
Arbitrage strategies exploit price discrepancies between markets to secure risk-free profit, often through simultaneous buying and selling of identical or related assets. Delta neutral strategies focus on eliminating directional market risk by balancing positions in options and underlying assets to maintain a zero delta, aiming to profit from volatility rather than price movement. Explore these methods in depth to understand their applications in achieving risk-free returns.
Source and External Links
Arbitrage - Wikipedia - Arbitrage is the practice of simultaneously buying and selling an asset in different markets to profit from price differences, ideally achieving a risk-free profit; this causes prices to converge across markets.
What Is Arbitrage? 3 Strategies to Know - Arbitrage is an investment strategy where investors buy and sell assets simultaneously in different markets to exploit price differences, including types like pure arbitrage, merger arbitrage, and convertible arbitrage.
What is arbitrage and how does it work in financial markets | StoneX - Arbitrage involves trading the same asset in multiple markets to profit from price differences, including specific forms like pure arbitrage, merger arbitrage, and triangular arbitrage in forex markets.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com