Circular electronics focus on designing devices with sustainable lifecycles, emphasizing reuse, recycling, and reduction of electronic waste. Upgradeable hardware prioritizes modular components that allow users to easily replace or enhance parts, extending device longevity and performance. Explore how these approaches reshape the future of technology sustainability and consumer electronics.
Why it is important
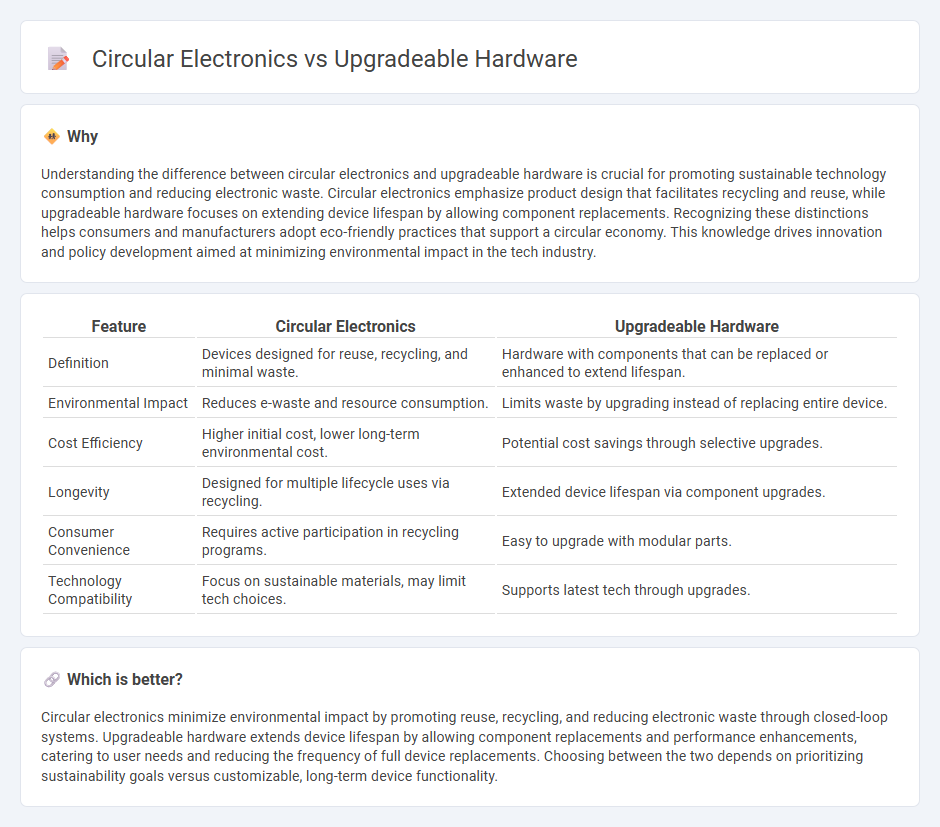
Understanding the difference between circular electronics and upgradeable hardware is crucial for promoting sustainable technology consumption and reducing electronic waste. Circular electronics emphasize product design that facilitates recycling and reuse, while upgradeable hardware focuses on extending device lifespan by allowing component replacements. Recognizing these distinctions helps consumers and manufacturers adopt eco-friendly practices that support a circular economy. This knowledge drives innovation and policy development aimed at minimizing environmental impact in the tech industry.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Circular Electronics | Upgradeable Hardware |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Devices designed for reuse, recycling, and minimal waste. | Hardware with components that can be replaced or enhanced to extend lifespan. |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces e-waste and resource consumption. | Limits waste by upgrading instead of replacing entire device. |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher initial cost, lower long-term environmental cost. | Potential cost savings through selective upgrades. |
| Longevity | Designed for multiple lifecycle uses via recycling. | Extended device lifespan via component upgrades. |
| Consumer Convenience | Requires active participation in recycling programs. | Easy to upgrade with modular parts. |
| Technology Compatibility | Focus on sustainable materials, may limit tech choices. | Supports latest tech through upgrades. |
Which is better?
Circular electronics minimize environmental impact by promoting reuse, recycling, and reducing electronic waste through closed-loop systems. Upgradeable hardware extends device lifespan by allowing component replacements and performance enhancements, catering to user needs and reducing the frequency of full device replacements. Choosing between the two depends on prioritizing sustainability goals versus customizable, long-term device functionality.
Connection
Circular electronics prioritize reducing electronic waste by designing devices with upgradeable hardware components, enabling extended product lifespans and easier repairs. Upgradeable hardware supports modular design principles, allowing consumers to replace or enhance individual parts instead of discarding entire devices. This synergy promotes sustainability by minimizing resource extraction and electronic landfill contributions.
Key Terms
Modular Design
Modular design in upgradeable hardware allows users to replace or enhance individual components such as memory, storage, or graphics cards, extending device lifespan and reducing electronic waste. Circular electronics emphasize closed-loop systems where products are designed for easy disassembly, repair, and recycling, minimizing environmental impact and resource consumption. Explore how modular design drives sustainability and innovation in electronic devices by learning more about circular electronics principles.
Lifecycle Extension
Upgradeable hardware significantly enhances device lifecycle extension by allowing users to replace or add components like RAM, storage, or processors, reducing electronic waste and delaying obsolescence. Circular electronics emphasize reuse, refurbishment, and recycling to maximize the value of materials and components throughout multiple product lifecycles, aligning with sustainable consumption goals. Explore how these strategies complement each other to create more sustainable and long-lasting electronic ecosystems.
Resource Efficiency
Upgradeable hardware extends the lifespan of electronic devices by allowing components like RAM, storage, and graphics cards to be replaced or enhanced, reducing electronic waste and conserving raw materials. Circular electronics embrace a cradle-to-cradle design principle, prioritizing recycling, refurbishing, and reusing materials to minimize environmental impact and maximize resource efficiency throughout a product's lifecycle. Explore the latest advancements in sustainable electronic design to understand how these approaches contribute to a greener tech future.
Source and External Links
Best upgradeable laptops in 2025 - XDA Developers - The most upgradeable laptops today include models like the Framework Laptop 13, which allows upgrading almost all components including CPU, RAM, storage, ports, display, and webcam, making it a modular option for users seeking long-term hardware flexibility.
What Is a Hardware Upgrade? | Key Considerations - A hardware upgrade involves replacing or adding physical components such as CPU, RAM, storage, or GPU to improve performance, capacity, or efficiency, and plays a crucial role in IT environments to maintain operational effectiveness and compatibility with evolving software and technologies.
How to Upgrade Your PC Step by Step (2024) - Upgrading a PC requires evaluating current system specs like CPU, motherboard, RAM, storage, GPU, and power supply to ensure compatibility and to identify bottlenecks, enabling users to improve performance cost-effectively instead of buying new systems.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com