Ambient computing integrates smart devices seamlessly into daily environments, enabling intuitive interactions without explicit user commands. Ubiquitous computing extends this concept by embedding computational capabilities everywhere, making technology omnipresent and context-aware. Explore the distinctions and applications of these transformative computing paradigms to understand their impact on modern technology.
Why it is important
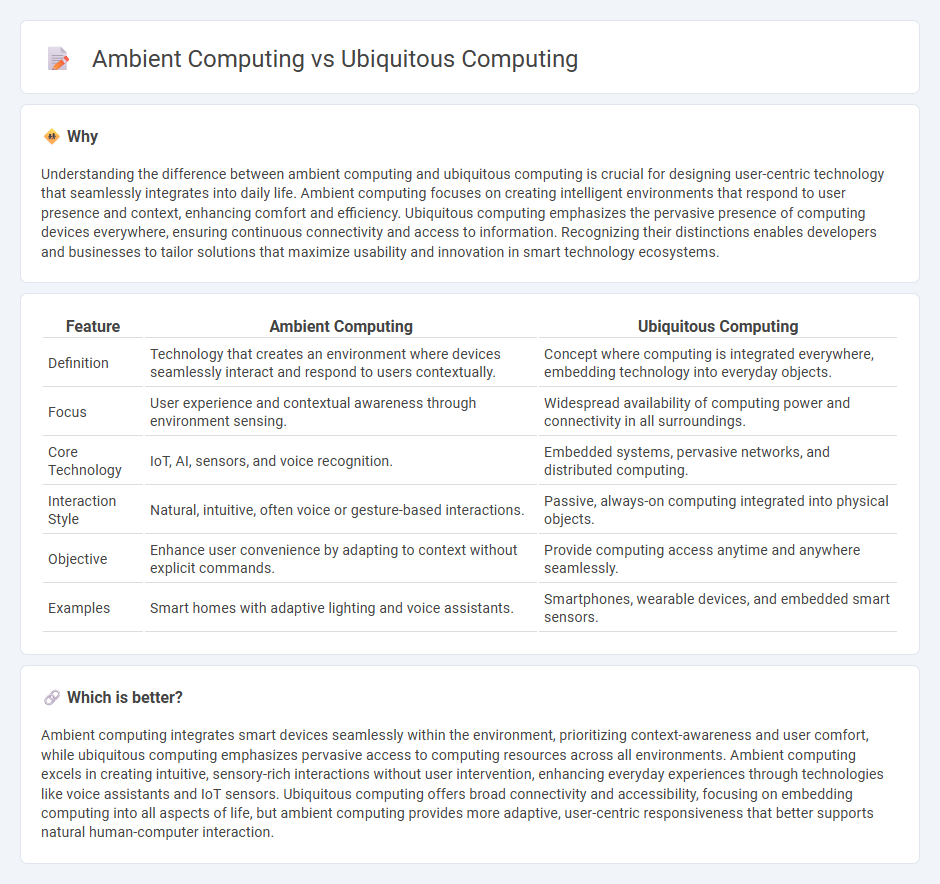
Understanding the difference between ambient computing and ubiquitous computing is crucial for designing user-centric technology that seamlessly integrates into daily life. Ambient computing focuses on creating intelligent environments that respond to user presence and context, enhancing comfort and efficiency. Ubiquitous computing emphasizes the pervasive presence of computing devices everywhere, ensuring continuous connectivity and access to information. Recognizing their distinctions enables developers and businesses to tailor solutions that maximize usability and innovation in smart technology ecosystems.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Ambient Computing | Ubiquitous Computing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Technology that creates an environment where devices seamlessly interact and respond to users contextually. | Concept where computing is integrated everywhere, embedding technology into everyday objects. |
| Focus | User experience and contextual awareness through environment sensing. | Widespread availability of computing power and connectivity in all surroundings. |
| Core Technology | IoT, AI, sensors, and voice recognition. | Embedded systems, pervasive networks, and distributed computing. |
| Interaction Style | Natural, intuitive, often voice or gesture-based interactions. | Passive, always-on computing integrated into physical objects. |
| Objective | Enhance user convenience by adapting to context without explicit commands. | Provide computing access anytime and anywhere seamlessly. |
| Examples | Smart homes with adaptive lighting and voice assistants. | Smartphones, wearable devices, and embedded smart sensors. |
Which is better?
Ambient computing integrates smart devices seamlessly within the environment, prioritizing context-awareness and user comfort, while ubiquitous computing emphasizes pervasive access to computing resources across all environments. Ambient computing excels in creating intuitive, sensory-rich interactions without user intervention, enhancing everyday experiences through technologies like voice assistants and IoT sensors. Ubiquitous computing offers broad connectivity and accessibility, focusing on embedding computing into all aspects of life, but ambient computing provides more adaptive, user-centric responsiveness that better supports natural human-computer interaction.
Connection
Ambient computing and ubiquitous computing are closely connected through their focus on integrating technology seamlessly into everyday environments to create smart, context-aware systems. Both paradigms utilize sensors, IoT devices, and AI to enable continuous interaction between users and digital environments without explicit input. This convergence drives innovations in smart homes, wearable devices, and pervasive data analytics, enhancing user experience and operational efficiency.
Key Terms
Context-awareness
Ubiquitous computing integrates technology seamlessly into everyday environments, emphasizing devices' constant connectivity and availability. Ambient computing builds on this by enhancing context-awareness, enabling systems to interpret and respond intelligently to contextual cues such as location, user activity, and environmental factors. Explore how these technologies revolutionize personalized interactions by delving deeper into their context-aware capabilities.
Pervasiveness
Ubiquitous computing integrates embedded devices seamlessly into everyday environments to ensure constant access and interaction, emphasizing omnipresence in users' lives. Ambient computing enhances this by creating intelligent, context-aware systems that respond adaptively to a user's presence and activities, promoting a more intuitive experience. Explore how these evolving technologies leverage pervasiveness to transform digital interaction and environment awareness.
Seamless integration
Ubiquitous computing emphasizes embedding computational capabilities into everyday objects, creating an environment where technology is seamlessly integrated into daily life without explicit user interaction. Ambient computing builds on this by enhancing context-awareness and adaptability, enabling devices to respond intelligently to user behaviors and environmental changes for a more intuitive experience. Explore the nuances and practical applications of these technologies to understand how seamless integration shapes the future of smart environments.
Source and External Links
What is Ubiquitous Computing? - Arm - Ubiquitous computing, also called pervasive computing, integrates AI-driven computing capabilities seamlessly into everyday objects and environments, enabling devices like sensors, wearables, and smart city infrastructures to interact intelligently and proactively without direct user interaction.
Ubiquitous computing - Wikipedia - Ubiquitous computing, or ubicomp, is the concept of making computing available anytime and everywhere on various devices embedded in everyday objects, supported by networks, sensors, and AI to create seamless, context-aware interactions across physical and digital spaces.
Comprehensive Guide to Ubiquitous Computing: Impact & Future - Ubiquitous computing embeds microprocessors into everyday objects to provide invisible, non-intrusive smart capabilities, leveraging sensors, connectivity, and AI for autonomous data collection, decision-making, and seamless user experiences integrated into daily life.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com