Generative video utilizes AI models to create original video content from scratch by interpreting data inputs, enabling innovative storytelling and visual effects. Video synthesis, on the other hand, focuses on transforming or enhancing existing video footage using deep learning techniques to modify scenes or generate realistic animations. Explore the latest advancements in generative video and video synthesis to understand their distinct applications and potential impact on media production.
Why it is important
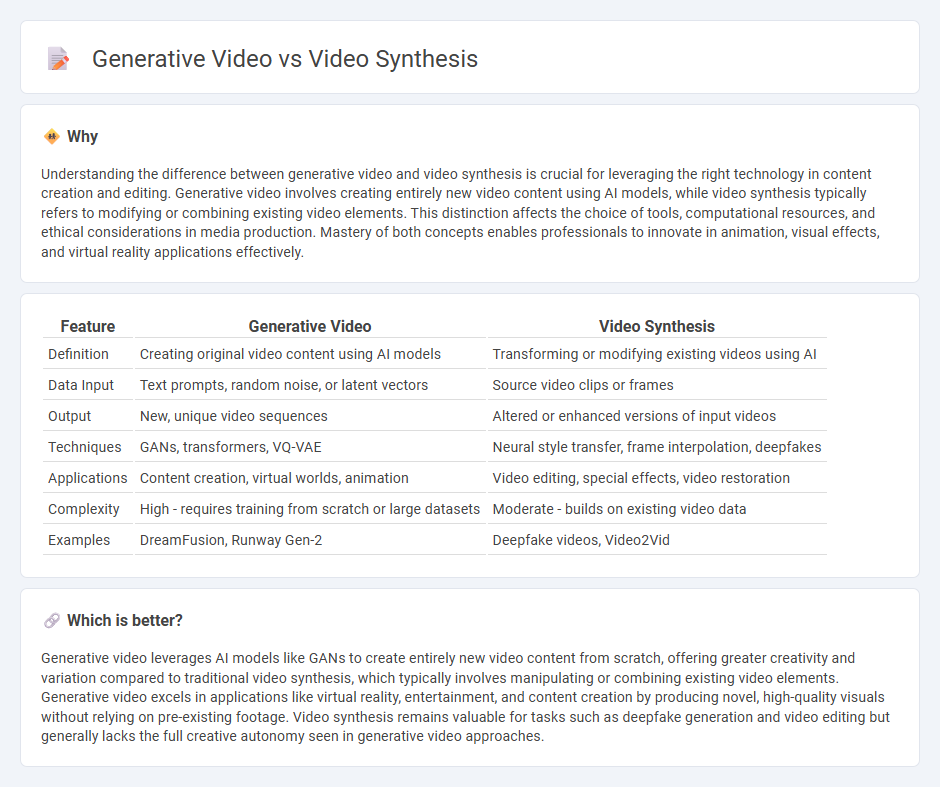
Understanding the difference between generative video and video synthesis is crucial for leveraging the right technology in content creation and editing. Generative video involves creating entirely new video content using AI models, while video synthesis typically refers to modifying or combining existing video elements. This distinction affects the choice of tools, computational resources, and ethical considerations in media production. Mastery of both concepts enables professionals to innovate in animation, visual effects, and virtual reality applications effectively.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Generative Video | Video Synthesis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Creating original video content using AI models | Transforming or modifying existing videos using AI |
| Data Input | Text prompts, random noise, or latent vectors | Source video clips or frames |
| Output | New, unique video sequences | Altered or enhanced versions of input videos |
| Techniques | GANs, transformers, VQ-VAE | Neural style transfer, frame interpolation, deepfakes |
| Applications | Content creation, virtual worlds, animation | Video editing, special effects, video restoration |
| Complexity | High - requires training from scratch or large datasets | Moderate - builds on existing video data |
| Examples | DreamFusion, Runway Gen-2 | Deepfake videos, Video2Vid |
Which is better?
Generative video leverages AI models like GANs to create entirely new video content from scratch, offering greater creativity and variation compared to traditional video synthesis, which typically involves manipulating or combining existing video elements. Generative video excels in applications like virtual reality, entertainment, and content creation by producing novel, high-quality visuals without relying on pre-existing footage. Video synthesis remains valuable for tasks such as deepfake generation and video editing but generally lacks the full creative autonomy seen in generative video approaches.
Connection
Generative video leverages deep learning algorithms to create new video content by synthesizing frames based on learned patterns from existing datasets, embodying the principles of video synthesis. Video synthesis involves generating or transforming video sequences through AI models such as generative adversarial networks (GANs) or variational autoencoders (VAEs), enabling realistic and coherent video creation. Both technologies rely on neural networks that understand spatial and temporal dynamics to produce seamless, high-quality video outputs from limited input data.
Key Terms
Deep Learning
Video synthesis leverages deep learning algorithms to create realistic video frames by reconstructing scenes from existing data, often using convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and generative adversarial networks (GANs). Generative video models extend this approach by producing entirely new video sequences from noise or sparse inputs, utilizing recurrent neural networks (RNNs) or transformers for temporal consistency. Explore the latest research and applications to understand the potential and challenges in deep learning-driven video generation.
GANs (Generative Adversarial Networks)
Generative video leverages GANs to create realistic video content by training two neural networks--a generator and a discriminator--that iteratively improve video quality through adversarial training. Video synthesis, in contrast, emphasizes reconstructing or manipulating existing videos using techniques like frame interpolation and style transfer, often relying on GANs for enhancing visual coherence. Explore the latest advancements in GAN-based generative video models to understand their transformative impact on digital content creation.
Motion Transfer
Video synthesis creates new video content by combining or manipulating existing footage, often leveraging deep learning models to generate realistic visuals. Generative video, specifically in motion transfer, involves transferring movements from a source to a target subject, enabling the creation of novel sequences that mimic original motion patterns. Explore the latest advancements in motion transfer techniques to understand their impact on video generation technology.
Source and External Links
Video Synthesizer - A device that electronically generates video signals, capable of creating a variety of visual material without camera input through internal pattern generators.
AI for Video Synthesis - Introduces AI tools for video synthesis, enabling the creation of new videos from simplified inputs, including video interpolation and prediction techniques.
Lumen - A Mac app that allows users to create engaging visuals in real-time using a semi-modular design similar to a hardware video synthesizer.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com