Ambient computing integrates smart environments and IoT devices to create seamless, context-aware interactions without direct user input, enhancing daily life through automation and interconnected systems. Wearable computing centers on portable devices like smartwatches and fitness trackers that provide real-time data and personalized experiences close to the body. Explore the evolving impacts and innovations of ambient and wearable computing to understand their transformative role in technology.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between ambient computing and wearable computing is crucial for optimizing user interaction and enhancing technology integration in daily life. Ambient computing involves environments equipped with interconnected devices that operate seamlessly without direct user input, while wearable computing refers to devices worn on the body, providing personalized, on-the-go computing capabilities. This distinction helps developers and businesses design tailored solutions that improve user experience and address specific needs in smart homes, healthcare, and personal fitness. Knowing these differences drives innovation and ensures effective application of emerging technologies in diverse sectors.
Comparison Table
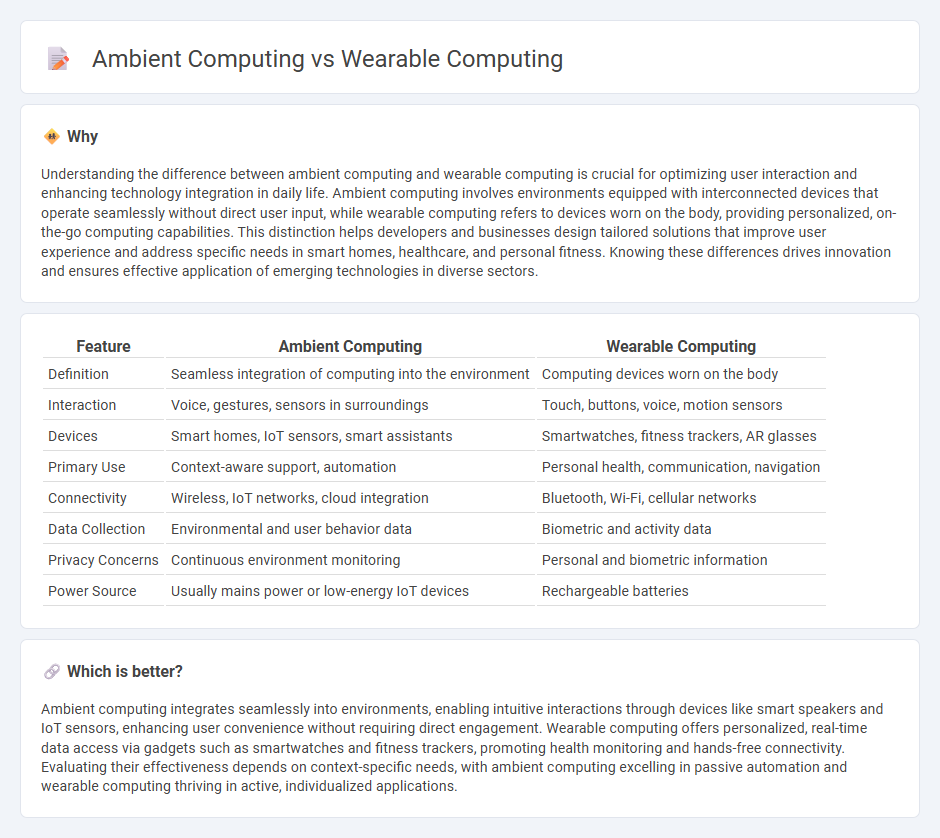
| Feature | Ambient Computing | Wearable Computing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Seamless integration of computing into the environment | Computing devices worn on the body |
| Interaction | Voice, gestures, sensors in surroundings | Touch, buttons, voice, motion sensors |
| Devices | Smart homes, IoT sensors, smart assistants | Smartwatches, fitness trackers, AR glasses |
| Primary Use | Context-aware support, automation | Personal health, communication, navigation |
| Connectivity | Wireless, IoT networks, cloud integration | Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, cellular networks |
| Data Collection | Environmental and user behavior data | Biometric and activity data |
| Privacy Concerns | Continuous environment monitoring | Personal and biometric information |
| Power Source | Usually mains power or low-energy IoT devices | Rechargeable batteries |
Which is better?
Ambient computing integrates seamlessly into environments, enabling intuitive interactions through devices like smart speakers and IoT sensors, enhancing user convenience without requiring direct engagement. Wearable computing offers personalized, real-time data access via gadgets such as smartwatches and fitness trackers, promoting health monitoring and hands-free connectivity. Evaluating their effectiveness depends on context-specific needs, with ambient computing excelling in passive automation and wearable computing thriving in active, individualized applications.
Connection
Ambient computing integrates seamlessly with wearable computing by enabling devices to interact contextually and intuitively within a user's environment, enhancing real-time data processing and personalized experiences. Wearable devices serve as key nodes in ambient systems, collecting biometric and environmental data to facilitate continuous, unobtrusive computing. This synergy advances smart ecosystems, improving health monitoring, situational awareness, and user engagement through interconnected sensor technologies.
Key Terms
Sensors
Wearable computing relies on sensors embedded in personal devices like smartwatches and fitness trackers to monitor physiological data such as heart rate, movement, and temperature in real-time, enabling personalized user experiences. Ambient computing integrates sensors into the environment, such as smart thermostats, lighting systems, and motion detectors, allowing seamless context-aware interactions without direct user input. Explore the latest advancements to understand how sensor technology drives the future of human-computer interaction.
Context-awareness
Wearable computing emphasizes personalized context-awareness by continuously sensing user-specific data such as physiological signals and location through devices like smartwatches and augmented reality glasses. Ambient computing integrates sensors and smart devices into the environment to create a seamless, context-aware experience by analyzing spatial data, environmental conditions, and user behavior patterns. Explore how these distinct approaches transform interaction paradigms in smart technology by learning more about context-aware systems.
User interaction
Wearable computing enables direct user interaction through devices like smartwatches and fitness trackers that provide personalized feedback and real-time data access, enhancing mobility and convenience. In contrast, ambient computing integrates sensors and smart environments that respond to user presence and context seamlessly without explicit commands, promoting a natural and intuitive experience. Explore more to understand how these technologies transform user engagement and interface design.
Source and External Links
Wearable computer - Wearable computing devices are body-worn computers including fitness trackers, smartwatches, and implantable devices used for health monitoring, augmented reality, and service management, running on operating systems like Wear OS and watchOS.
23. Wearable Computing - Wearable computing involves designing miniature computational and sensory devices worn on or in the body, extending to smart clothing and implantables, also called body-borne or bearable computing.
What is Wearable Computers? - Wearable computers are electronic devices worn on the body, such as smartwatches and smart glasses, enhancing health monitoring, communication, and augmented reality with sensors and connectivity.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com