Edge intelligence processes data locally on IoT devices or edge servers, reducing latency and improving real-time decision-making, while serverless computing relies on cloud-based infrastructure to execute code with dynamic resource allocation and scalability. Both technologies aim to enhance efficiency in distributed computing but differ in deployment, speed, and resource management. Explore the unique advantages of edge intelligence and serverless computing to discover which suits your tech strategy best.
Why it is important
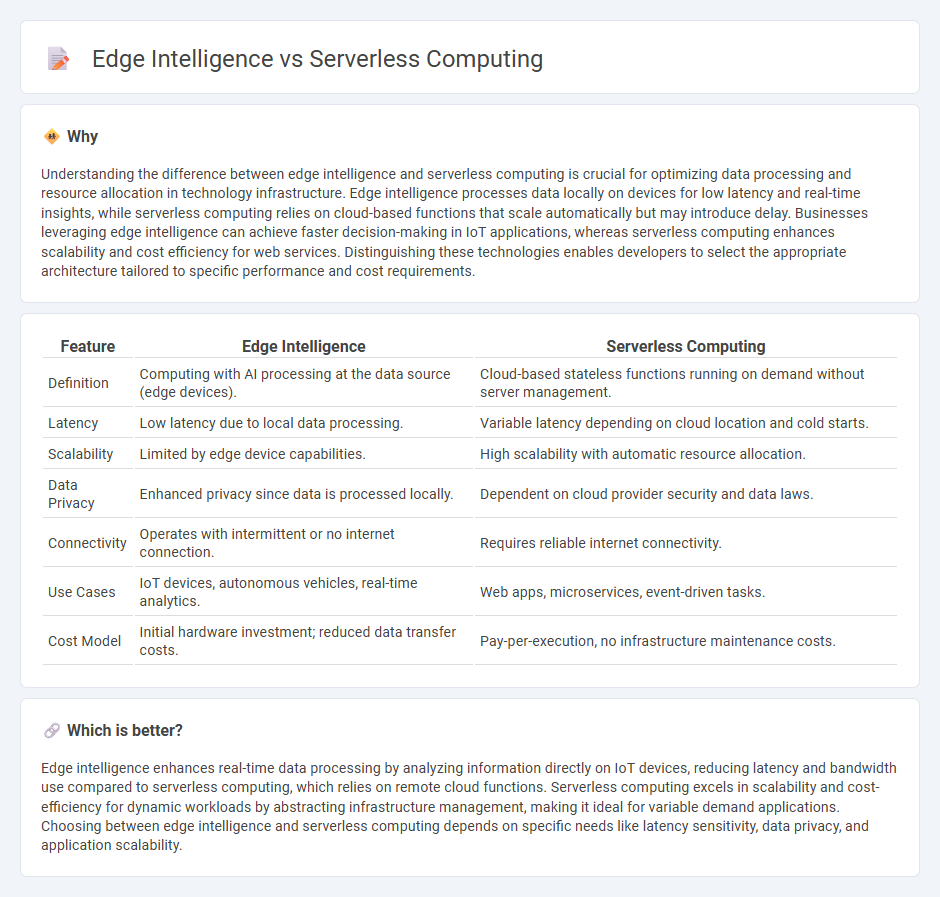
Understanding the difference between edge intelligence and serverless computing is crucial for optimizing data processing and resource allocation in technology infrastructure. Edge intelligence processes data locally on devices for low latency and real-time insights, while serverless computing relies on cloud-based functions that scale automatically but may introduce delay. Businesses leveraging edge intelligence can achieve faster decision-making in IoT applications, whereas serverless computing enhances scalability and cost efficiency for web services. Distinguishing these technologies enables developers to select the appropriate architecture tailored to specific performance and cost requirements.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Edge Intelligence | Serverless Computing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Computing with AI processing at the data source (edge devices). | Cloud-based stateless functions running on demand without server management. |
| Latency | Low latency due to local data processing. | Variable latency depending on cloud location and cold starts. |
| Scalability | Limited by edge device capabilities. | High scalability with automatic resource allocation. |
| Data Privacy | Enhanced privacy since data is processed locally. | Dependent on cloud provider security and data laws. |
| Connectivity | Operates with intermittent or no internet connection. | Requires reliable internet connectivity. |
| Use Cases | IoT devices, autonomous vehicles, real-time analytics. | Web apps, microservices, event-driven tasks. |
| Cost Model | Initial hardware investment; reduced data transfer costs. | Pay-per-execution, no infrastructure maintenance costs. |
Which is better?
Edge intelligence enhances real-time data processing by analyzing information directly on IoT devices, reducing latency and bandwidth use compared to serverless computing, which relies on remote cloud functions. Serverless computing excels in scalability and cost-efficiency for dynamic workloads by abstracting infrastructure management, making it ideal for variable demand applications. Choosing between edge intelligence and serverless computing depends on specific needs like latency sensitivity, data privacy, and application scalability.
Connection
Edge intelligence leverages real-time data processing at the network's edge, reducing latency and bandwidth usage by executing AI algorithms closer to IoT devices. Serverless computing complements this by providing scalable, event-driven cloud functions that dynamically manage backend processes without dedicated servers. Together, they enable efficient, responsive, and cost-effective deployment of smart applications across distributed environments.
Key Terms
Function-as-a-Service (FaaS)
Function-as-a-Service (FaaS) in serverless computing enables developers to run code in response to events without managing infrastructure, optimizing scalability and cost efficiency in cloud environments. Edge intelligence leverages FaaS by processing data closer to the source, reducing latency and enhancing real-time analytics for IoT and AI applications. Explore how the integration of FaaS with edge computing drives innovation and performance in distributed systems.
Latency
Serverless computing offers scalable cloud services but may incur higher latency due to centralized data processing, making it less ideal for time-sensitive applications. Edge intelligence processes data closer to the source at the network edge, drastically reducing latency and enabling real-time responsiveness in IoT and critical systems. Explore how edge intelligence optimizes latency compared to serverless models for enhanced application performance.
Distributed Processing
Serverless computing enables distributed processing by abstracting server management and automatically scaling functions across cloud resources to execute tasks efficiently. Edge intelligence distributes processing closer to data sources using local devices or edge nodes, reducing latency and bandwidth usage while supporting real-time decision-making. Explore how integrating serverless computing with edge intelligence enhances distributed processing for optimal performance and scalability.
Source and External Links
What is serverless computing | Google Cloud - Serverless computing is a cloud execution model where developers run code on demand without managing servers, and pay only for resources used, while the cloud provider handles provisioning, scaling, and infrastructure management invisibly.
What Is Serverless Computing? - IBM - Serverless computing enables developers to deploy application code without provisioning or managing servers, with the cloud provider handling infrastructure management and billing based on execution time and resources used.
Serverless computing and applications | Microsoft Azure - Serverless computing allows developers to build applications faster by eliminating infrastructure management tasks, with automatic provisioning, scaling, and management handled by the cloud provider, resulting in improved developer productivity and dynamic scalability.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com