Quantum key distribution leverages principles of quantum mechanics to enable secure communication by generating encryption keys that are theoretically impervious to interception or cloning. Public key infrastructure relies on asymmetric cryptography and trusted certificate authorities to authenticate users and manage encryption keys, but it is vulnerable to advances in computing power and algorithmic attacks. Explore the differences, advantages, and future implications of these encryption methods for enhanced cybersecurity.
Why it is important
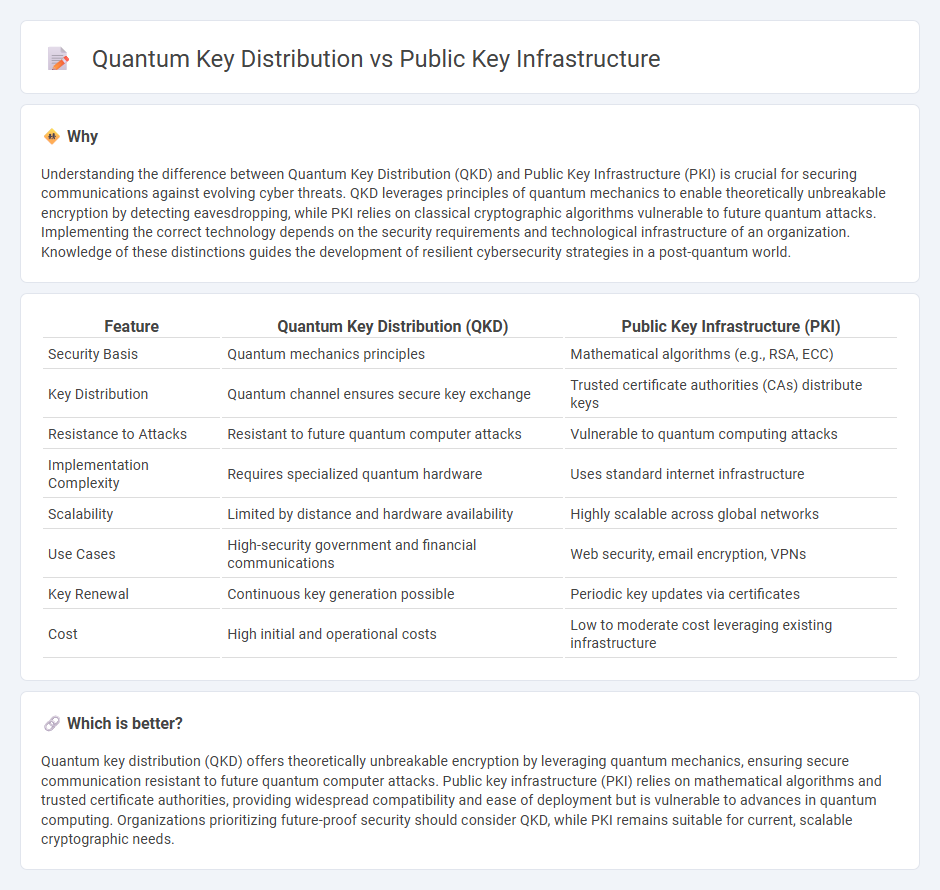
Understanding the difference between Quantum Key Distribution (QKD) and Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) is crucial for securing communications against evolving cyber threats. QKD leverages principles of quantum mechanics to enable theoretically unbreakable encryption by detecting eavesdropping, while PKI relies on classical cryptographic algorithms vulnerable to future quantum attacks. Implementing the correct technology depends on the security requirements and technological infrastructure of an organization. Knowledge of these distinctions guides the development of resilient cybersecurity strategies in a post-quantum world.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Quantum Key Distribution (QKD) | Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) |
|---|---|---|
| Security Basis | Quantum mechanics principles | Mathematical algorithms (e.g., RSA, ECC) |
| Key Distribution | Quantum channel ensures secure key exchange | Trusted certificate authorities (CAs) distribute keys |
| Resistance to Attacks | Resistant to future quantum computer attacks | Vulnerable to quantum computing attacks |
| Implementation Complexity | Requires specialized quantum hardware | Uses standard internet infrastructure |
| Scalability | Limited by distance and hardware availability | Highly scalable across global networks |
| Use Cases | High-security government and financial communications | Web security, email encryption, VPNs |
| Key Renewal | Continuous key generation possible | Periodic key updates via certificates |
| Cost | High initial and operational costs | Low to moderate cost leveraging existing infrastructure |
Which is better?
Quantum key distribution (QKD) offers theoretically unbreakable encryption by leveraging quantum mechanics, ensuring secure communication resistant to future quantum computer attacks. Public key infrastructure (PKI) relies on mathematical algorithms and trusted certificate authorities, providing widespread compatibility and ease of deployment but is vulnerable to advances in quantum computing. Organizations prioritizing future-proof security should consider QKD, while PKI remains suitable for current, scalable cryptographic needs.
Connection
Quantum key distribution (QKD) enhances Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) by providing theoretically unbreakable encryption keys through quantum mechanics principles, ensuring secure key exchange resistant to computational attacks. PKI relies on asymmetric cryptography for secure communication, while QKD addresses vulnerabilities in key distribution by leveraging quantum entanglement and no-cloning theorem. Integrating QKD with PKI frameworks strengthens overall cybersecurity by combining classical digital certificates with quantum-secure key management.
Key Terms
Digital Certificates
Digital Certificates are central to Public Key Infrastructure (PKI), providing authentication by linking public keys with user identities through trusted Certificate Authorities (CAs). Quantum Key Distribution (QKD), in contrast, uses quantum mechanics to securely exchange keys without relying on digital certificates or centralized authorities. Explore the fundamental differences between PKI and QKD to understand their impact on future cryptographic security.
Quantum Encryption
Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) relies on cryptographic algorithms that may be vulnerable to quantum computing attacks, while Quantum Key Distribution (QKD) leverages quantum mechanics principles to enable secure key exchange resistant to these threats. QKD protocols, such as BB84 and E91, provide theoretically unbreakable encryption by detecting eavesdropping through quantum state disturbances. Explore the advancements in quantum encryption to understand how QKD is transforming cybersecurity in the quantum era.
Key Exchange
Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) relies on asymmetric cryptography using mathematical algorithms like RSA or ECC to securely exchange keys over classical networks, providing widespread interoperability and established trust models. Quantum Key Distribution (QKD) uses principles of quantum mechanics, such as photon polarization and entanglement, to enable theoretically unbreakable key exchange by detecting eavesdropping through quantum channel disturbances. Explore the detailed mechanisms and applications of PKI and QKD to enhance your understanding of secure key exchange technologies.
Source and External Links
Public Key Infrastructure - Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) is a framework that issues digital certificates, ensuring secure data transmission and unique identities for users and systems.
What is Public Key Infrastructure (PKI)? - Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) is a comprehensive framework for assigning, identifying, and verifying user identities through digital certificates, facilitating secure communications.
What Is Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) & How Does It Work? - Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) uses digital certificates issued by a trusted source, such as a certificate authority, to protect and authenticate digital communications.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com