Zero trust security challenges traditional perimeter security by eliminating implicit trust and continuously verifying every access request, regardless of location. Perimeter security relies on defined network boundaries to prevent unauthorized access but struggles with modern cloud environments and remote work setups. Explore how zero trust and perimeter security strategies differ to enhance your cybersecurity framework.
Why it is important
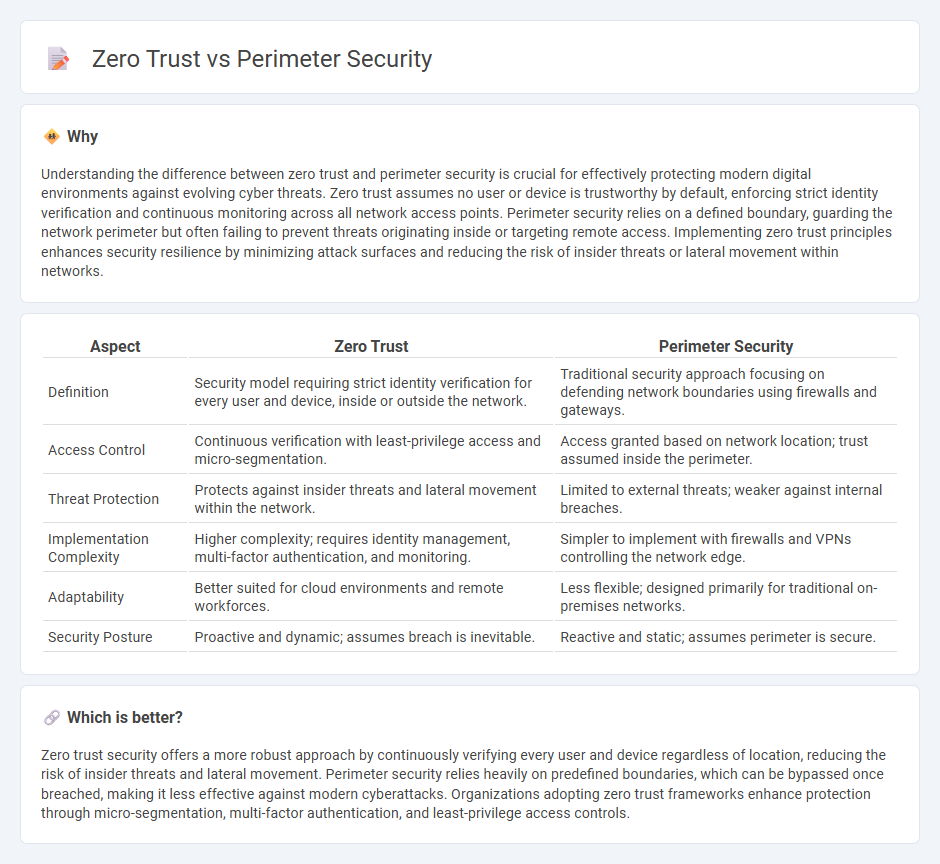
Understanding the difference between zero trust and perimeter security is crucial for effectively protecting modern digital environments against evolving cyber threats. Zero trust assumes no user or device is trustworthy by default, enforcing strict identity verification and continuous monitoring across all network access points. Perimeter security relies on a defined boundary, guarding the network perimeter but often failing to prevent threats originating inside or targeting remote access. Implementing zero trust principles enhances security resilience by minimizing attack surfaces and reducing the risk of insider threats or lateral movement within networks.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Zero Trust | Perimeter Security |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Security model requiring strict identity verification for every user and device, inside or outside the network. | Traditional security approach focusing on defending network boundaries using firewalls and gateways. |
| Access Control | Continuous verification with least-privilege access and micro-segmentation. | Access granted based on network location; trust assumed inside the perimeter. |
| Threat Protection | Protects against insider threats and lateral movement within the network. | Limited to external threats; weaker against internal breaches. |
| Implementation Complexity | Higher complexity; requires identity management, multi-factor authentication, and monitoring. | Simpler to implement with firewalls and VPNs controlling the network edge. |
| Adaptability | Better suited for cloud environments and remote workforces. | Less flexible; designed primarily for traditional on-premises networks. |
| Security Posture | Proactive and dynamic; assumes breach is inevitable. | Reactive and static; assumes perimeter is secure. |
Which is better?
Zero trust security offers a more robust approach by continuously verifying every user and device regardless of location, reducing the risk of insider threats and lateral movement. Perimeter security relies heavily on predefined boundaries, which can be bypassed once breached, making it less effective against modern cyberattacks. Organizations adopting zero trust frameworks enhance protection through micro-segmentation, multi-factor authentication, and least-privilege access controls.
Connection
Zero trust and perimeter security both focus on protecting digital environments but differ in approach; zero trust operates on the principle of "never trust, always verify," continuously authenticating users and devices regardless of location. Perimeter security traditionally establishes a boundary to prevent unauthorized access, relying on firewalls and gateways to control entry points. Integrating zero trust with perimeter security enhances overall defense by combining strict access control with robust boundary enforcement.
Key Terms
Network Boundary
Perimeter security relies on defending the network boundary using firewalls and intrusion detection systems to block unauthorized access, assuming threats exist outside the boundary. Zero trust eliminates the concept of a trusted network perimeter by continuously verifying every user and device, regardless of location, minimizing internal threats. Explore more to understand how zero trust transforms network security beyond traditional perimeter defenses.
Least Privilege
Perimeter security relies on safeguarding network boundaries to control access, whereas zero trust enforces the principle of Least Privilege by limiting user permissions to the minimum necessary for their role, reducing insider and external threats. By continuously verifying and authenticating every access attempt, zero trust prevents lateral movement within the network even if the perimeter is breached. Explore more about how implementing Least Privilege under zero trust models enhances overall cybersecurity resilience.
Micro-Segmentation
Micro-segmentation is a critical component distinguishing zero trust from traditional perimeter security by creating granular security zones within a network, limiting lateral movement of threats. While perimeter security relies on a strong external boundary, micro-segmentation enforces strict access controls at the workload level, enhancing protection against internal breaches. Explore how micro-segmentation fortifies zero trust architectures to secure modern enterprise networks effectively.
Source and External Links
What is Perimeter Security? - Perimeter security is the first line of defense protecting property boundaries using physical barriers like fences and walls, gates, surveillance cameras, motion sensors, and access control systems to prevent unauthorized access and detect potential breaches early.
Perimeter Security Systems: Different Types & How to Choose - Effective perimeter security combines physical barriers with technology such as video surveillance, motion sensors, alarms, and access control systems to deter intruders and enable real-time monitoring and response to security threats.
Perimeter protection and outdoor security - Axis Communications - Advanced perimeter security uses integrated networked solutions--including thermal and AI-analytics cameras, access control, and audio alerts--to strengthen perimeter monitoring and provide early intrusion detection with automated response capabilities.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com