Spatial computing revolutionizes interaction by integrating digital information within physical environments, while artificial intelligence enhances decision-making through data analysis and pattern recognition. These technologies synergize to create immersive, intelligent systems that transform industries from healthcare to gaming. Discover how spatial computing and AI converge to shape the future of innovation.
Why it is important
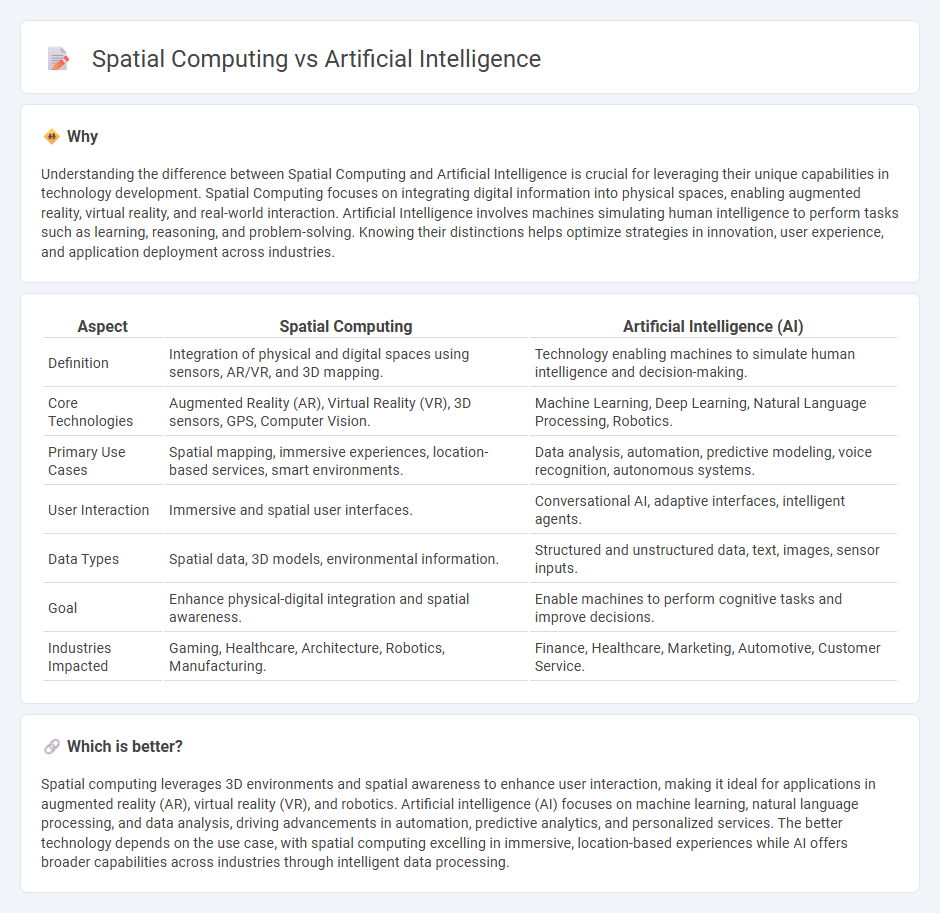
Understanding the difference between Spatial Computing and Artificial Intelligence is crucial for leveraging their unique capabilities in technology development. Spatial Computing focuses on integrating digital information into physical spaces, enabling augmented reality, virtual reality, and real-world interaction. Artificial Intelligence involves machines simulating human intelligence to perform tasks such as learning, reasoning, and problem-solving. Knowing their distinctions helps optimize strategies in innovation, user experience, and application deployment across industries.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Spatial Computing | Artificial Intelligence (AI) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Integration of physical and digital spaces using sensors, AR/VR, and 3D mapping. | Technology enabling machines to simulate human intelligence and decision-making. |
| Core Technologies | Augmented Reality (AR), Virtual Reality (VR), 3D sensors, GPS, Computer Vision. | Machine Learning, Deep Learning, Natural Language Processing, Robotics. |
| Primary Use Cases | Spatial mapping, immersive experiences, location-based services, smart environments. | Data analysis, automation, predictive modeling, voice recognition, autonomous systems. |
| User Interaction | Immersive and spatial user interfaces. | Conversational AI, adaptive interfaces, intelligent agents. |
| Data Types | Spatial data, 3D models, environmental information. | Structured and unstructured data, text, images, sensor inputs. |
| Goal | Enhance physical-digital integration and spatial awareness. | Enable machines to perform cognitive tasks and improve decisions. |
| Industries Impacted | Gaming, Healthcare, Architecture, Robotics, Manufacturing. | Finance, Healthcare, Marketing, Automotive, Customer Service. |
Which is better?
Spatial computing leverages 3D environments and spatial awareness to enhance user interaction, making it ideal for applications in augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and robotics. Artificial intelligence (AI) focuses on machine learning, natural language processing, and data analysis, driving advancements in automation, predictive analytics, and personalized services. The better technology depends on the use case, with spatial computing excelling in immersive, location-based experiences while AI offers broader capabilities across industries through intelligent data processing.
Connection
Spatial computing leverages artificial intelligence to interpret and interact with 3D environments, enabling devices to understand and respond to physical spaces in real-time. AI algorithms process spatial data, enhancing applications in augmented reality, virtual reality, and robotics through advanced object recognition and spatial mapping. The integration of AI and spatial computing drives innovations in immersive experiences, autonomous navigation, and smart environment interactions.
Key Terms
Machine Learning
Machine learning drives advancements in artificial intelligence by enabling systems to learn from data patterns and improve autonomously, crucial for tasks like image recognition and natural language processing. Spatial computing integrates machine learning with 3D environments and sensors to enhance augmented reality, virtual reality, and real-time spatial data analysis. Explore how the synergy between artificial intelligence and spatial computing transforms industries by visiting our detailed insights.
Computer Vision
Computer vision serves as a crucial intersection between artificial intelligence and spatial computing, enabling machines to interpret and understand visual data from the environment. Advances in AI-driven image recognition and spatial mapping have revolutionized applications in augmented reality, robotics, and autonomous navigation. Explore how cutting-edge developments are shaping the future of computer vision across these dynamic fields.
Augmented Reality
Artificial intelligence enhances augmented reality (AR) by enabling real-time object recognition, natural language processing, and adaptive user interfaces, creating immersive and interactive experiences. Spatial computing integrates AR with 3D mapping, environmental sensing, and gesture recognition to merge digital content seamlessly with physical surroundings. Explore how the synergy of AI and spatial computing is transforming augmented reality applications across industries like gaming, healthcare, and education.
Source and External Links
What Is Artificial Intelligence (AI)? - Artificial intelligence (AI) is a set of technologies that enable computers to perform intelligent tasks such as image analysis, speech recognition, data analytics, and natural language processing by learning and improving through vast amounts of data.
Artificial intelligence - AI is the capability of computational systems to perform tasks like learning, reasoning, and problem-solving that humans typically do, with applications in search engines, virtual assistants, autonomous vehicles, and more, drawing from multiple scientific disciplines.
Artificial Intelligence (AI): What it is and why it matters - AI enables machines to learn from experience and perform human-like tasks using methods such as machine learning, neural networks, deep learning, computer vision, and natural language processing.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com