Quantum dot displays offer superior color accuracy, higher brightness, and energy efficiency compared to traditional CRT screens, which rely on cathode ray tubes and phosphor coatings. These advancements provide sharper images, deeper contrast, and a thinner, lighter design ideal for modern devices. Discover more about how quantum dot technology is revolutionizing the future of display screens.
Why it is important
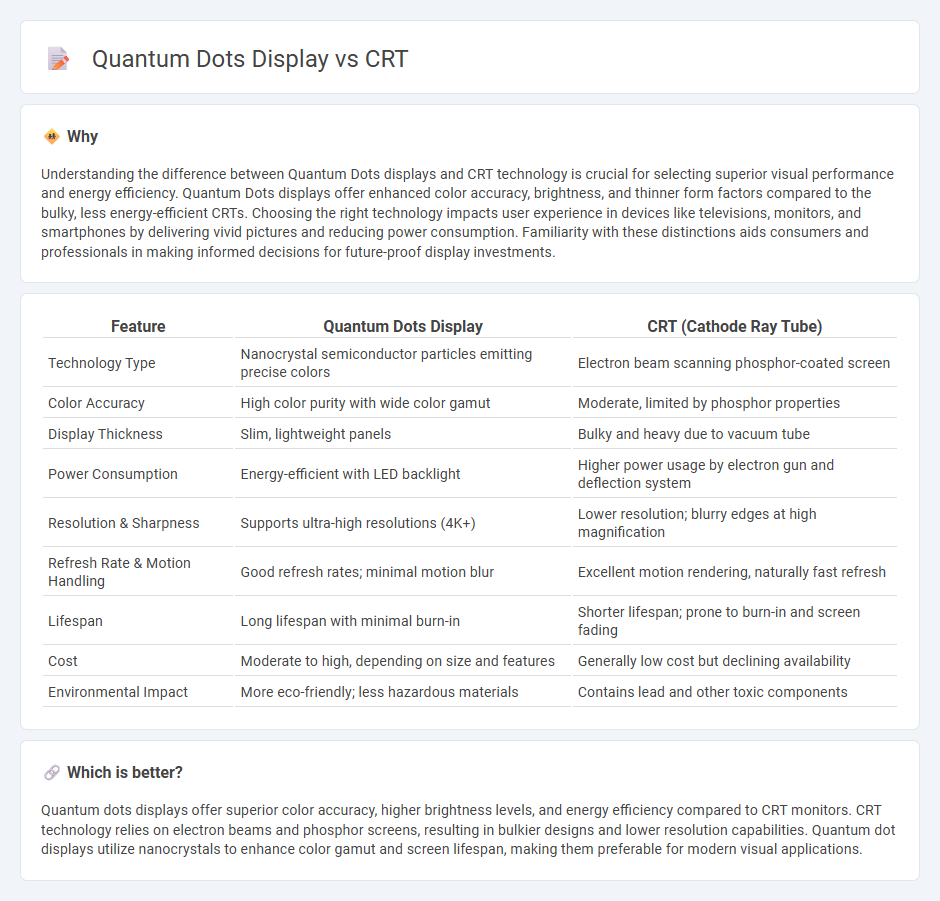
Understanding the difference between Quantum Dots displays and CRT technology is crucial for selecting superior visual performance and energy efficiency. Quantum Dots displays offer enhanced color accuracy, brightness, and thinner form factors compared to the bulky, less energy-efficient CRTs. Choosing the right technology impacts user experience in devices like televisions, monitors, and smartphones by delivering vivid pictures and reducing power consumption. Familiarity with these distinctions aids consumers and professionals in making informed decisions for future-proof display investments.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Quantum Dots Display | CRT (Cathode Ray Tube) |
|---|---|---|
| Technology Type | Nanocrystal semiconductor particles emitting precise colors | Electron beam scanning phosphor-coated screen |
| Color Accuracy | High color purity with wide color gamut | Moderate, limited by phosphor properties |
| Display Thickness | Slim, lightweight panels | Bulky and heavy due to vacuum tube |
| Power Consumption | Energy-efficient with LED backlight | Higher power usage by electron gun and deflection system |
| Resolution & Sharpness | Supports ultra-high resolutions (4K+) | Lower resolution; blurry edges at high magnification |
| Refresh Rate & Motion Handling | Good refresh rates; minimal motion blur | Excellent motion rendering, naturally fast refresh |
| Lifespan | Long lifespan with minimal burn-in | Shorter lifespan; prone to burn-in and screen fading |
| Cost | Moderate to high, depending on size and features | Generally low cost but declining availability |
| Environmental Impact | More eco-friendly; less hazardous materials | Contains lead and other toxic components |
Which is better?
Quantum dots displays offer superior color accuracy, higher brightness levels, and energy efficiency compared to CRT monitors. CRT technology relies on electron beams and phosphor screens, resulting in bulkier designs and lower resolution capabilities. Quantum dot displays utilize nanocrystals to enhance color gamut and screen lifespan, making them preferable for modern visual applications.
Connection
Quantum dots displays and CRT technology both manipulate light to produce images, but quantum dots use nanoscale semiconductor particles to emit precise colors when excited by blue LEDs, whereas CRTs rely on electron beams striking phosphorescent screens to generate images. Quantum dots offer enhanced color accuracy, higher energy efficiency, and thinner form factors compared to the bulky and power-consuming cathode ray tube displays. Despite different mechanisms, both technologies share the common principle of converting energy into visible light through controlled emission processes.
Key Terms
Electron Gun
CRT displays utilize an electron gun to emit electrons that scan phosphor-coated screens, producing images through precise beam control. Quantum dot displays rely on semiconductor nanocrystals emitting specific light wavelengths when energized but do not use electron guns, instead leveraging LED or OLED backlighting for color accuracy. Explore the technological differences further to understand how electron gun mechanisms contrast with quantum dot innovations in modern display technology.
Quantum Dots
Quantum dot displays utilize semiconductor nanocrystals that emit precise colors when illuminated, resulting in superior color accuracy and brightness compared to CRT technology. These displays offer enhanced energy efficiency and thinner form factors, making them ideal for modern high-definition screens. Explore more about how quantum dot technology is transforming the future of visual displays.
Color Gamut
Quantum dots displays offer a significantly wider color gamut compared to CRT screens, enabling more vivid and accurate color reproduction across the visible spectrum. CRT technology, while capable of deep blacks and high contrast, typically covers a smaller portion of color spaces like AdobeRGB or DCI-P3. Explore the advancements in quantum dot technology to enhance your color viewing experience.
Source and External Links
Cathode-ray tube - Wikipedia - A cathode-ray tube (CRT) is a vacuum tube with electron guns that emit electron beams to display images on a phosphorescent screen, used in older TVs and computer monitors.
Critical race theory - Wikipedia - Critical race theory (CRT) is an academic framework analyzing systemic racism embedded in laws and social systems, emphasizing race as a social construct and highlighting intersectionality.
What Is Critical Race Theory, and Why Is It Under Attack? - Critical race theory is a more than 40-year-old academic concept that views race as a social construct and racism as embedded in legal systems and policies, not just individual prejudice.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com