Ambient computing integrates smart devices seamlessly into everyday environments, enabling intuitive and context-aware interactions without explicit user input. Mobile computing focuses on portable devices like smartphones and tablets, offering anytime-anywhere access to data and applications through wireless technology. Explore further to discover how these computing paradigms transform digital experiences.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between ambient computing and mobile computing is crucial because ambient computing provides seamless, context-aware interactions through embedded devices in the environment, while mobile computing emphasizes user-driven, portable device usage. Ambient computing integrates IoT, AI, and sensors for proactive automation, contrasting with mobile computing's reliance on smartphones, tablets, and laptops for on-the-go connectivity. This knowledge guides businesses and developers in designing optimized user experiences and infrastructure tailored to distinct interaction models. Recognizing these differences improves strategic decisions in technology deployment, enhancing efficiency and user satisfaction.
Comparison Table
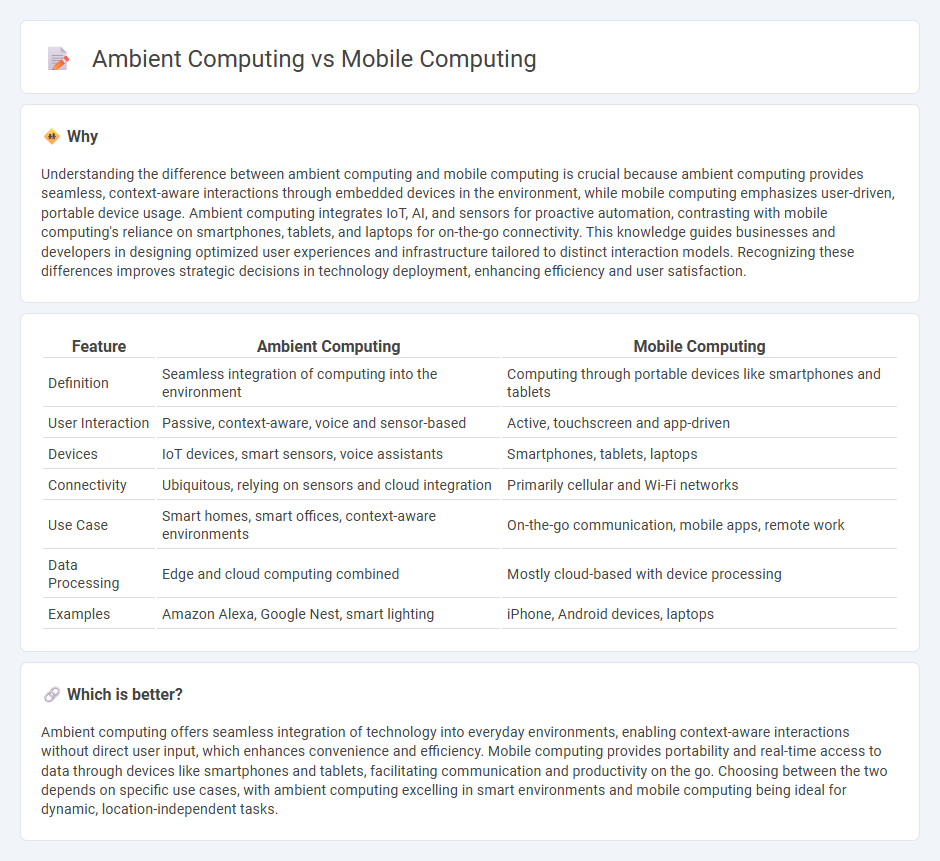
| Feature | Ambient Computing | Mobile Computing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Seamless integration of computing into the environment | Computing through portable devices like smartphones and tablets |
| User Interaction | Passive, context-aware, voice and sensor-based | Active, touchscreen and app-driven |
| Devices | IoT devices, smart sensors, voice assistants | Smartphones, tablets, laptops |
| Connectivity | Ubiquitous, relying on sensors and cloud integration | Primarily cellular and Wi-Fi networks |
| Use Case | Smart homes, smart offices, context-aware environments | On-the-go communication, mobile apps, remote work |
| Data Processing | Edge and cloud computing combined | Mostly cloud-based with device processing |
| Examples | Amazon Alexa, Google Nest, smart lighting | iPhone, Android devices, laptops |
Which is better?
Ambient computing offers seamless integration of technology into everyday environments, enabling context-aware interactions without direct user input, which enhances convenience and efficiency. Mobile computing provides portability and real-time access to data through devices like smartphones and tablets, facilitating communication and productivity on the go. Choosing between the two depends on specific use cases, with ambient computing excelling in smart environments and mobile computing being ideal for dynamic, location-independent tasks.
Connection
Ambient computing and mobile computing are interconnected through their shared goal of providing seamless, context-aware user experiences by leveraging sensors, AI, and cloud connectivity. Ambient computing integrates smart environments that anticipate user needs, while mobile computing delivers on-the-go access to data and applications via portable devices. Together, they enable continuous interaction and real-time responsiveness across diverse settings, enhancing convenience and productivity.
Key Terms
Ubiquity
Mobile computing offers users the ability to access information and perform tasks anytime and anywhere through devices such as smartphones, tablets, and laptops, emphasizing portability and connectivity. Ambient computing extends this concept by embedding technology seamlessly into the environment, enabling continuous and context-aware interactions without explicit user input, thus achieving true ubiquity in digital interactions. Explore the evolving landscape of computing paradigms to understand how ubiquity redefines user experience and technological integration.
Context-awareness
Mobile computing relies on portable devices like smartphones and tablets to provide context-aware services through GPS, accelerometers, and user behavior analysis, enabling personalized experiences based on location, movement, and preferences. Ambient computing integrates sensors and AI into the environment, creating seamless context-aware interactions without explicit user input by continuously monitoring surroundings, temperature, lighting, and presence. Discover how these evolving technologies enhance user environments by exploring their unique approaches to context-awareness.
Device integration
Mobile computing relies on smartphones, tablets, and laptops to provide on-the-go access to data and applications, emphasizing portability and user control over device interactions. Ambient computing integrates diverse smart devices and sensors seamlessly within environments, enabling autonomous, context-aware processes that minimize direct user input. Discover how these technologies transform connectivity by exploring their device integration strategies in detail.
Source and External Links
How does mobile computing work? - Tencent Cloud - Mobile computing enables the use of devices like smartphones, tablets, and laptops to access information and communication services while moving, relying on mobile devices, wireless communication (Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, cellular networks), mobile OS, and mobile apps.
What is Mobile Computing? | Definition from TechTarget - Mobile computing encompasses the IT technologies and procedures allowing users to access computing resources anywhere and anytime, typically involving mobile devices with wireless connections like 5G or Wi-Fi, and supporting collaborative cloud services.
Mobile computing - Wikipedia - Mobile computing is defined as human-computer interaction where devices are portable and support data transmission, emphasizing principles like portability, connectivity, interactivity, and individualization for continuous data communication while in motion.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com