RISC-V and MIPS represent two influential instruction set architectures (ISAs) shaping modern computing, with RISC-V gaining traction due to its open-source, modular design that fosters innovation and customization. MIPS, a veteran ISA, remains notable for its streamlined architecture and wide adoption in embedded systems, despite facing declining popularity in recent years. Explore the detailed comparison to understand how these ISAs impact processor performance, ecosystem support, and future technology trends.
Why it is important
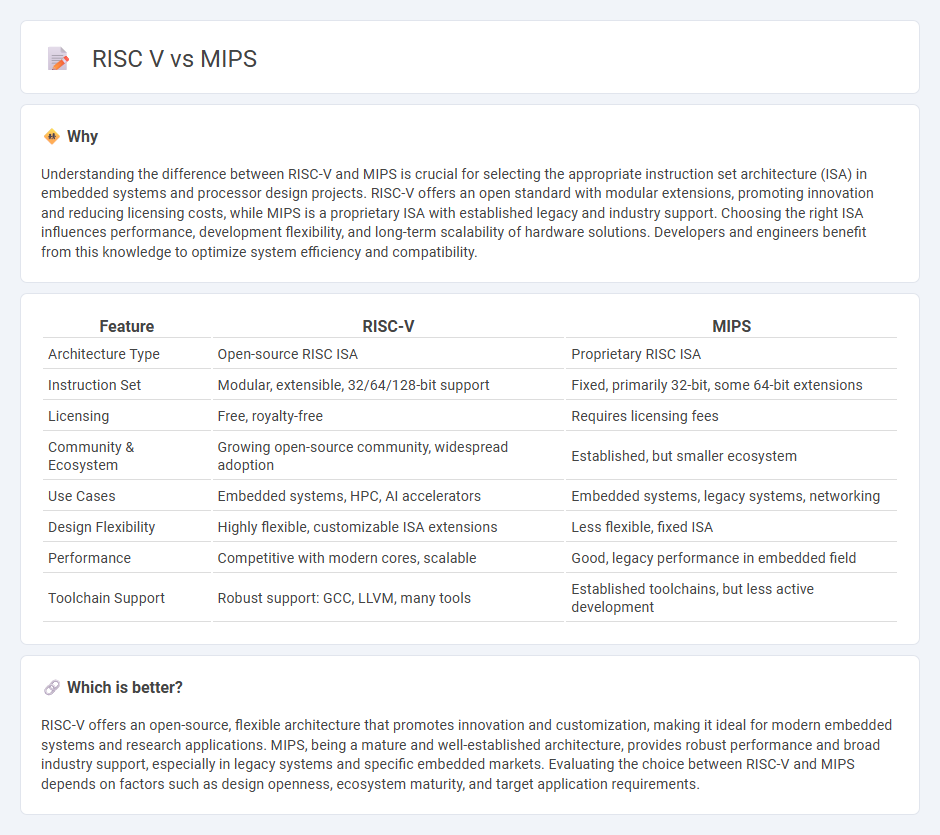
Understanding the difference between RISC-V and MIPS is crucial for selecting the appropriate instruction set architecture (ISA) in embedded systems and processor design projects. RISC-V offers an open standard with modular extensions, promoting innovation and reducing licensing costs, while MIPS is a proprietary ISA with established legacy and industry support. Choosing the right ISA influences performance, development flexibility, and long-term scalability of hardware solutions. Developers and engineers benefit from this knowledge to optimize system efficiency and compatibility.
Comparison Table
| Feature | RISC-V | MIPS |
|---|---|---|
| Architecture Type | Open-source RISC ISA | Proprietary RISC ISA |
| Instruction Set | Modular, extensible, 32/64/128-bit support | Fixed, primarily 32-bit, some 64-bit extensions |
| Licensing | Free, royalty-free | Requires licensing fees |
| Community & Ecosystem | Growing open-source community, widespread adoption | Established, but smaller ecosystem |
| Use Cases | Embedded systems, HPC, AI accelerators | Embedded systems, legacy systems, networking |
| Design Flexibility | Highly flexible, customizable ISA extensions | Less flexible, fixed ISA |
| Performance | Competitive with modern cores, scalable | Good, legacy performance in embedded field |
| Toolchain Support | Robust support: GCC, LLVM, many tools | Established toolchains, but less active development |
Which is better?
RISC-V offers an open-source, flexible architecture that promotes innovation and customization, making it ideal for modern embedded systems and research applications. MIPS, being a mature and well-established architecture, provides robust performance and broad industry support, especially in legacy systems and specific embedded markets. Evaluating the choice between RISC-V and MIPS depends on factors such as design openness, ecosystem maturity, and target application requirements.
Connection
RISC-V and MIPS are connected through their shared foundation in Reduced Instruction Set Computing (RISC) architecture, emphasizing simplicity and efficiency in instruction execution. Both architectures influence modern processor design, with RISC-V emerging as an open-source alternative that draws architectural principles initially established by MIPS. Their connection highlights the evolution and diversification of RISC processors in the semiconductor industry.
Key Terms
Instruction Set Architecture (ISA)
MIPS and RISC-V are prominent RISC architectures distinguished by their respective instruction set designs; MIPS features a fixed 32-bit instruction length optimizing pipeline efficiency, while RISC-V offers a modular ISA with base integer instructions and customizable extensions enhancing flexibility and scalability. RISC-V's open-source nature promotes widespread industry adoption and innovation compared to MIPS' proprietary framework. Explore the detailed ISA comparison to understand how these architectures influence processor performance and application domains.
Register-based Design
MIPS architecture features a fixed set of 32 general-purpose registers optimized for high-speed instruction execution, while RISC-V offers a more flexible register design with up to 32 integer registers and customizable extensions. The register-based design of RISC-V enhances scalability and adaptability for diverse applications, making it ideal for both embedded systems and high-performance computing. Explore the detailed differences in register utilization and architecture efficiency to understand which ISA best suits your development needs.
Source and External Links
MIPS architecture - Wikipedia - MIPS (Microprocessor without Interlocked Pipelined Stages) is a family of RISC instruction set architectures, originally 32-bit and later 64-bit, widely used in education and industry, which has multiple versions and extensions but development has transitioned to RISC-V as of 2021.
Merit based Incentive Payment System (MIPS) - What is MIPS? - MIPS in healthcare stands for the Merit-based Incentive Payment System, a program combining multiple quality reporting measures into one system that evaluates providers' performance in four categories affecting Medicare payment adjustments.
MIPS Processor, RISC-V, Innovate Compute - The modern MIPS technology leads in advanced compute solutions for AI in automotive, industrial, and edge markets, focusing on multithreading, efficiency, and integration with heterogeneous computing platforms.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com