eBPF (extended Berkeley Packet Filter) and LTTng (Linux Trace Toolkit Next Generation) are powerful tools for Linux system observability and performance analysis. eBPF enables dynamic tracing and enhanced security by running sandboxed programs directly within the kernel, while LTTng provides comprehensive kernel and user-space tracing with minimal overhead. Explore more to uncover which technology suits your system monitoring and debugging needs best.
Why it is important
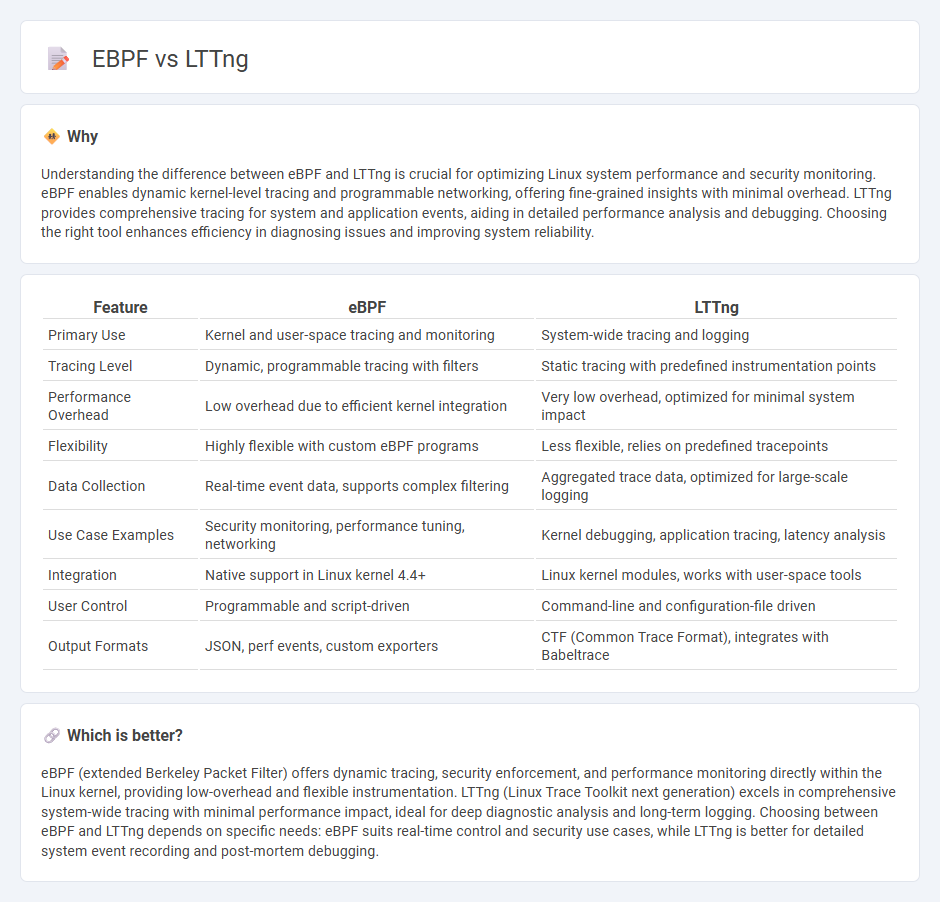
Understanding the difference between eBPF and LTTng is crucial for optimizing Linux system performance and security monitoring. eBPF enables dynamic kernel-level tracing and programmable networking, offering fine-grained insights with minimal overhead. LTTng provides comprehensive tracing for system and application events, aiding in detailed performance analysis and debugging. Choosing the right tool enhances efficiency in diagnosing issues and improving system reliability.
Comparison Table
| Feature | eBPF | LTTng |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Kernel and user-space tracing and monitoring | System-wide tracing and logging |
| Tracing Level | Dynamic, programmable tracing with filters | Static tracing with predefined instrumentation points |
| Performance Overhead | Low overhead due to efficient kernel integration | Very low overhead, optimized for minimal system impact |
| Flexibility | Highly flexible with custom eBPF programs | Less flexible, relies on predefined tracepoints |
| Data Collection | Real-time event data, supports complex filtering | Aggregated trace data, optimized for large-scale logging |
| Use Case Examples | Security monitoring, performance tuning, networking | Kernel debugging, application tracing, latency analysis |
| Integration | Native support in Linux kernel 4.4+ | Linux kernel modules, works with user-space tools |
| User Control | Programmable and script-driven | Command-line and configuration-file driven |
| Output Formats | JSON, perf events, custom exporters | CTF (Common Trace Format), integrates with Babeltrace |
Which is better?
eBPF (extended Berkeley Packet Filter) offers dynamic tracing, security enforcement, and performance monitoring directly within the Linux kernel, providing low-overhead and flexible instrumentation. LTTng (Linux Trace Toolkit next generation) excels in comprehensive system-wide tracing with minimal performance impact, ideal for deep diagnostic analysis and long-term logging. Choosing between eBPF and LTTng depends on specific needs: eBPF suits real-time control and security use cases, while LTTng is better for detailed system event recording and post-mortem debugging.
Connection
eBPF (extended Berkeley Packet Filter) and LTTng (Linux Trace Toolkit next generation) are connected through their roles in Linux kernel tracing and monitoring. eBPF provides a programmable interface for running custom tracing code inside the kernel, enhancing LTTng's capability to collect detailed system performance data. Together, they enable advanced observability by combining eBPF's dynamic tracing with LTTng's lightweight, high-performance tracing infrastructure.
Key Terms
Tracing
LTTng offers comprehensive kernel and userspace tracing with low overhead, ideal for detailed performance analysis and debugging in Linux environments. eBPF provides dynamic, programmable tracing capabilities with flexibility to insert custom code at various kernel hooks, enabling real-time observability and security monitoring. Explore the nuances of LTTng and eBPF to tailor your tracing strategy for optimal system insight.
Kernel-space
LTTng (Linux Trace Toolkit Next Generation) delivers high-performance kernel-space tracing by capturing system calls, interrupts, and scheduling events with minimal overhead, supporting detailed analysis of kernel behavior. eBPF (extended Berkeley Packet Filter) enhances kernel observability by enabling programmable instrumentation directly in the kernel, allowing dynamic tracing and customized event generation without recompiling or rebooting. Explore the trade-offs and use cases of LTTng and eBPF to optimize kernel-space monitoring and diagnostics.
Performance
LTTng (Linux Trace Toolkit Next Generation) provides high-performance tracing with minimal overhead, designed specifically for kernel and application-level diagnostics. eBPF (extended Berkeley Packet Filter) offers versatile, in-kernel instrumentation with dynamic programmability, enabling fine-grained performance monitoring and reduced latency impacts. Explore detailed performance comparisons to understand which tracing tool best suits your Linux observability needs.
Source and External Links
LTTng: an open source tracing framework for Linux - LTTng is an open source tracing framework providing low-overhead tracing on Linux for both kernel and user applications, suitable for systems from embedded devices to large clouds and offering tools for analysis via GUI, CLI, or scripts.
lttng(1) - Linux manual page - LTTng consists of kernel modules and user-space libraries to trace the Linux kernel and applications, controlled via a session daemon and CLI tools, supporting multiple tracing domains such as kernel and Java logging.
Howto tracing with LTTng - LTTng supports tracing of the Linux kernel and user-space applications using the Common Trace Format (CTF) for efficient, detailed event logging, and it can be installed from source or Linux distribution packages.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com